在標頭檔案"execinfo.h"中宣告瞭三個函式用於獲取當前執行緒的函式呼叫堆疊。
#include <execinfo.h>
int backtrace(void **buffer, int size);
char **backtrace_symbols(void *const *buffer, int size);
void backtrace_symbols_fd(void *const *buffer, int size, int fd);
man 幫助:
DESCRIPTION
backtrace() returns a backtrace for the calling program, in the array
pointed to by buffer. A backtrace is the series of currently active
function calls for the program. Each item in the array pointed to by
buffer is of type void *, and is the return address from the
corresponding stack frame. The size argument specifies the maximum
number of addresses that can be stored in buffer. If the backtrace
is larger than size, then the addresses corresponding to the size
most recent function calls are returned; to obtain the complete
backtrace, make sure that buffer and size are large enough.
Given the set of addresses returned by backtrace() in buffer,
backtrace_symbols() translates the addresses into an array of strings
that describe the addresses symbolically. The size argument
specifies the number of addresses in buffer. The symbolic
representation of each address consists of the function name (if this
can be determined), a hexadecimal offset into the function, and the
actual return address (in hexadecimal). The address of the array of
string pointers is returned as the function result of
backtrace_symbols(). This array is malloc(3)ed by
backtrace_symbols(), and must be freed by the caller. (The strings
pointed to by the array of pointers need not and should not be
freed.)
backtrace_symbols_fd() takes the same buffer and size arguments as
backtrace_symbols(), but instead of returning an array of strings to
the caller, it writes the strings, one per line, to the file
descriptor fd. backtrace_symbols_fd() does not call malloc(3), and
so can be employed in situations where the latter function might
fail.
int backtrace(void **buffer,int size)
該函式用與獲取當前執行緒的呼叫堆疊,獲取的資訊將會被存放在buffer中,它是一個指標陣列。引數 size 用來指定buffer中可以儲存多少個void* 元素。函式返回值是實際獲取的指標個數,最大不超過size大小在buffer中的指標實際是從堆疊中獲取的返回地址,每一個堆疊框架有一個返回地址。
注意某些編譯器的優化選項對獲取正確的呼叫堆疊有干擾,另外行內函數沒有堆疊框架;刪除框架指標也會使無法正確解析堆疊內容
char ** backtrace_symbols (void *const *buffer, int size)
backtrace_symbols將從backtrace函式獲取的資訊轉化為一個字串陣列. 引數buffer應該是從backtrace函式獲取的陣列指標,size是該陣列中的元素個數(backtrace的返回值),函式返回值是一個指向字串陣列的指標,它的大小同buffer相同.每個字串包含了一個相對於buffer中對應元素的可列印資訊.它包括函式名,函式的偏移地址,和實際的返回地址
現在,只有使用ELF二進位制格式的程式和苦衷才能獲取函式名稱和偏移地址.在其他系統,只有16進位制的返回地址能被獲取.另外,你可能需要傳遞相應的標誌給連結器,以能支援函式名功能(比如,在使用GNU ld的系統中,你需要傳遞(-rdynamic))
backtrace_symbols生成的字串都是malloc出來的,但是不要最後一個一個的free,因為backtrace_symbols是根據backtrace給出的call stack層數,一次性的malloc出來一塊記憶體來存放結果字串的,所以,像上面程式碼一樣,只需要在最後,free backtrace_symbols的返回指標就OK了。這一點backtrace的manual中也是特別提到的。
注意:如果不能為字串獲取足夠的空間函式的返回值將會為NULL
void backtrace_symbols_fd (void *const *buffer, int size, int fd)
backtrace_symbols_fd與backtrace_symbols 函式具有相同的功能,不同的是它不會給呼叫者返回字串陣列,而是將結果寫入檔案描述符為fd的檔案中,每個函式對應一行.它不需要呼叫malloc函式,因此適用於有可能呼叫該函式會失敗的情況。
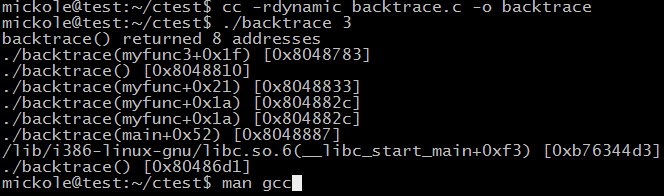
man手冊中示例:
#include <execinfo.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> void myfunc3(void) { int j, nptrs; #define SIZE 100 void *buffer[100]; char **strings; nptrs = backtrace(buffer, SIZE); printf("backtrace() returned %d addresses\n", nptrs); /* The call backtrace_symbols_fd(buffer, nptrs, STDOUT_FILENO) would produce similar output to the following: */ strings = backtrace_symbols(buffer, nptrs); if (strings == NULL) { perror("backtrace_symbols"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } for (j = 0; j < nptrs; j++) printf("%s\n", strings[j]); free(strings); } static void /* "static" means don't export the symbol... */ myfunc2(void) { myfunc3(); } void myfunc(int ncalls) { if (ncalls > 1) myfunc(ncalls - 1); else myfunc2(); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { fprintf(stderr, "%s num-calls\n", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } myfunc(atoi(argv[1])); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
結果:
總結:使用以下幾個函式既可完成堆疊資訊的列印
int backtrace (void **buffer, int size)
char ** backtrace_symbols (void *const *buffer, int size)
char* abi::__cxa_demangle
(
const char * mangled_name,
char * output_buffer,
size_t * length,
int * status
)
1. backtrace可以在程式執行的任何地方被呼叫,返回各個呼叫函式的返回地址,可以限制最大呼叫棧返回層數。
2. 在backtrace拿到函式返回地址之後,backtrace_symbols可以將其轉換為編譯符號,這些符號是編譯期間就確定的
3. 根據backtrace_symbols返回的編譯符號,abi::__cxa_demangle可以找到具體地函式方法