基礎概念
DBC API是一個Java API,可以訪問任何型別表列資料,特別是儲存在關聯式資料庫中的資料。JDBC代表Java資料庫連線。
簡單使用
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 1. 載入驅動程式
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 建立資料庫連線
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_db";
String username = "root";
String password = "password";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 3. 執行 SQL 語句
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// 4. 處理結果集
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name);
}
// 5. 關閉資源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
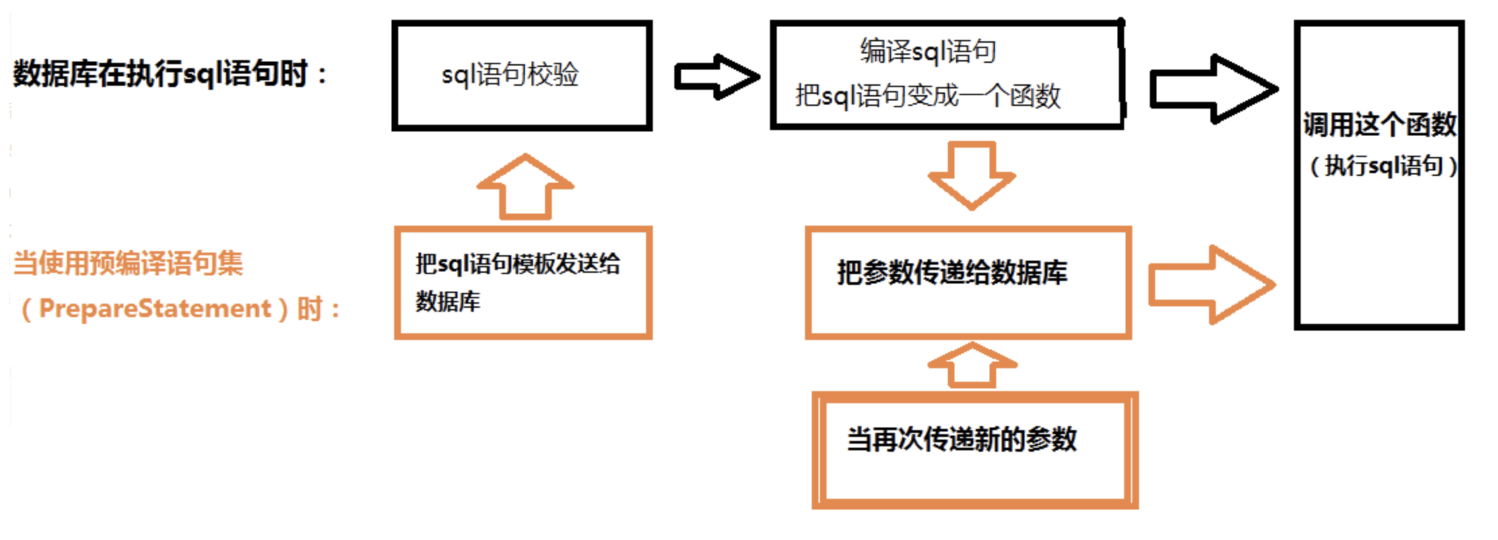
預編譯的原理
在java中JDBC中,我們寫 SQL 語句的時候,有個預處理功能,這個功能一大優勢就是能提高執行速度,尤其是多次運算元據庫的情況,再一個優勢就是預防SQL隱碼攻擊,嚴格的說,應該是預防絕大多數的SQL隱碼攻擊。
簡單使用
如下面的程式碼
import java.sql.*;
public class PreparedStatementExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 1. 載入驅動程式
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 建立資料庫連線
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_db";
String username = "root";
String password = "password";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 3. 建立預編譯語句
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = ?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4. 設定引數
pstmt.setString(1, "John Doe");
// 5. 執行查詢
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
// 6. 處理結果集
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name);
}
// 7. 關閉資源
rs.close();
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
底層原理
當執行時,JDBC動態地把引數傳給PreparedStatement時,即使引數裡有敏感字元,如: ' or ' 1' = '1 、updatexml(2,concat(0x7e,(version())),0)等,preparedStatement 會對入參中的關鍵字進行轉義,比如單引號轉義成',其流程大致如下: