IO流
https://drun1baby.top/2022/05/30/Java-IO%E6%B5%81/
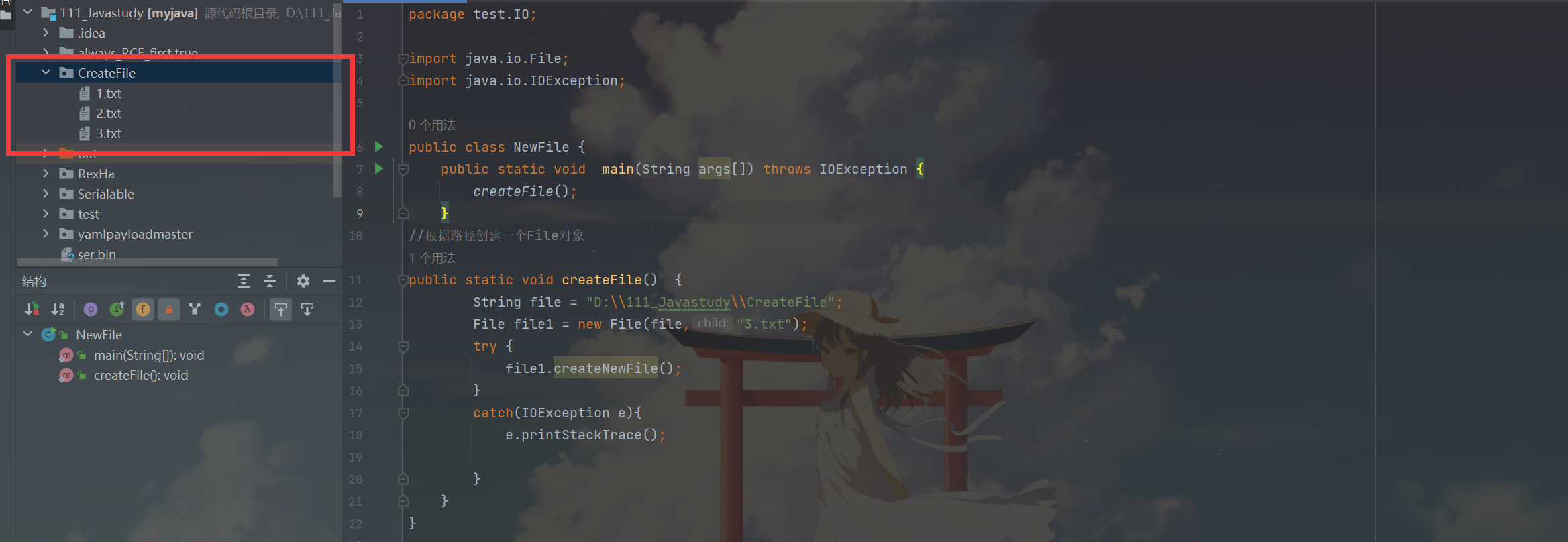
三種建立檔案的方式
第一種:new File(String pathname)
File file = new File("D:\111_Javastudy\CreateFile\1.txt");
file.createNewFile();
第二種:new File(File parent, String child)
File parentFile = new File("D:\111_Javastudy\CreateFile");
File file = new File(parentFile, "2.txt");
file.createNewFile();
第三種:new File(String parent, String child)
String parentFile = "D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile";
File file = new File(file,"3.txt");
file.createNewFile();
獲取檔案資訊的方式
package test.IO;
import java.io.File;
public class GetFileInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getFileContents();
}
public static void getFileContents(){
File file = new File("Serialable/src/IOStream/CreateForFile/new1.txt");
System.out.println("檔名稱為:" + file.getName());
System.out.println("檔案的絕對路徑為:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("檔案的父級目錄為:" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("檔案的大小(位元組)為:" + file.length());
System.out.println("這是不是一個檔案:" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("這是不是一個目錄:" + file.isDirectory());
}
}
目錄與檔案操作
1.檔案刪除file.delete(檔案)
File file = new File("D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile\\3.txt");
System.out.println(file.delete()?"deleted":"failed");
2.目錄刪除file.delete(目錄),這裡有個小坑,只有空的目錄才可以刪除,不然會顯示刪除失敗。
File file = new File("D:\\111_Javastudy\\testdelete");
System.out.println(file.delete()?"deleted":"failed");
3. 建立單級目錄file.mkdir()
File file = new File("D:\\111_Javastudy\\testdelete");
System.out.println(file.mkdir()?"made":"failed");
4. 建立多級目錄file.mkdirs()
File file = new File("D:\\111_Javastudy\\testdelete\aa\bb");
System.out.println(file.mkdirs()?"made":"failed");
檔案流操作
1. Runtime 命令執行操作的 Payload
package test.IO;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
// 使用 Runtime 類進行命令執行
public class RuntimeExec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream inputStream = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("whoami").getInputStream();
byte[] cache = new byte[1024]; // 緩衝區,大小為1024位元組,它充當了一個臨時緩衝區,用來儲存從 inputStream 中讀取到的資料。在每次呼叫 inputStream.read(cache) 時,cache 中會填充最多 1024 位元組的資料(除非資料不足 1024 位元組)。如果流中的資料多於 1024 位元組,那麼讀取將被分成多次。
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int readLen = 0; // 記錄每次讀取的位元組數
while ((readLen = inputStream.read(cache))!=-1){ //inputStream.read(cache) 會嘗試從 inputStream 中讀取資料,並將資料寫入到 cache 緩衝區中。每次讀取時,inputStream.read() 會返回讀取的位元組數,將其儲存在 readLen 變數中。
byteArrayOutputStream.write(cache, 0, readLen); //將 cache 緩衝區中從索引 0 開始的 readLen 位元組資料寫入到 ByteArrayOutputStream 中。注意,並不是每次都會寫入 1024 位元組,readLen 決定了實際讀取並寫入的資料長度。
}
System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream);
}
}
其中,byte[] cache = new byte[1024] 用來快取資料,我們結合這一串 Payload 來學習 Java IO 流甚好。
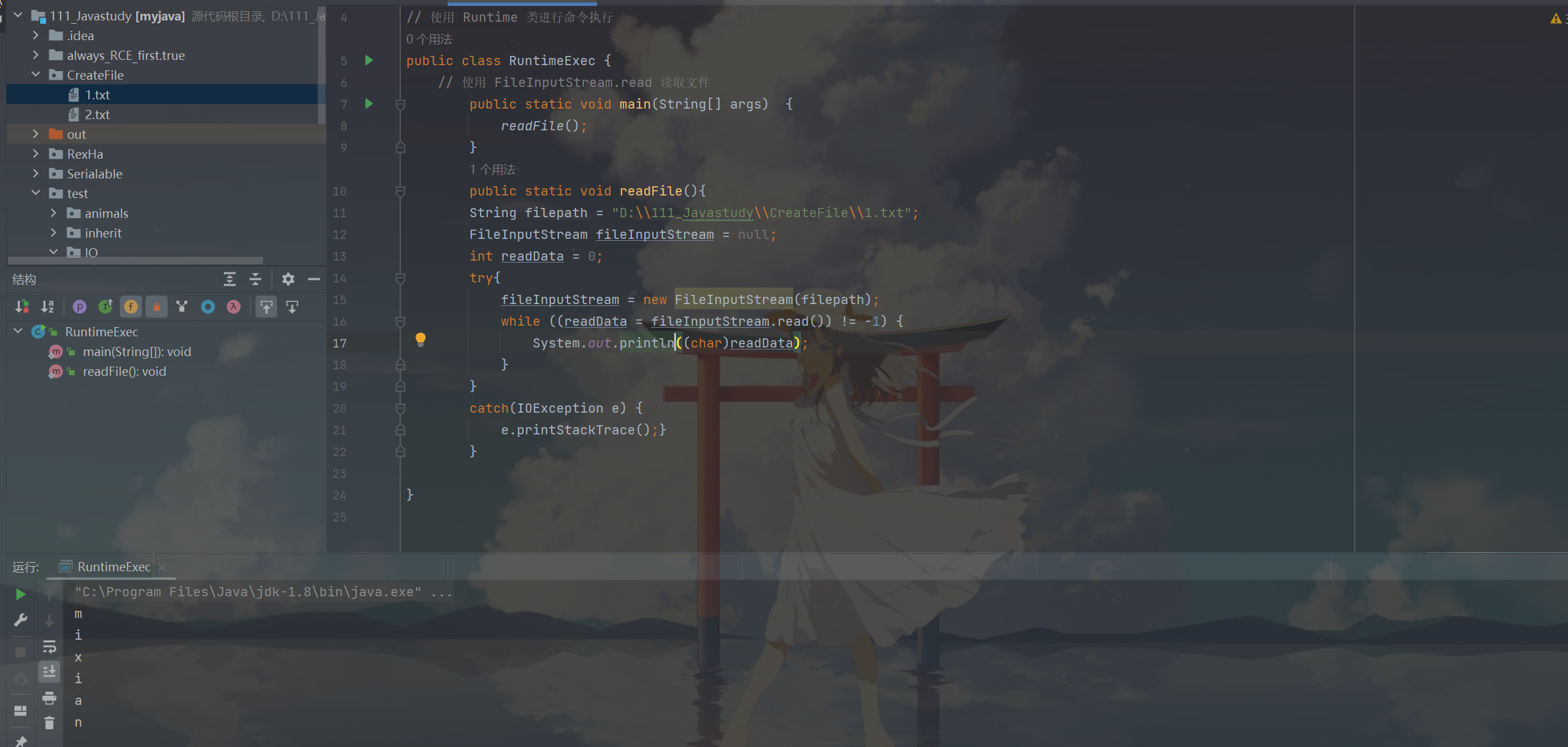
2. FileInputStream
read() 方法用來讀取資料
read() 方法到底是啥樣的呢,我們跳進去看看
read()
public int read() throws IOException
從此輸入流中讀取一個資料位元組。
如果沒有輸入可用,則此方法將阻塞。
指定者: 類 InputStream 中的 read
返回: 下一個資料位元組;如果已到達檔案末尾,則返回 -1。
丟擲: IOException - 如果發生 I/O 錯誤。
之前我們用 file 的一系列操作讀取過檔案的資訊,現在我們用 FileInputStream.read() 來讀取檔案內容。
package src.IOStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
// 使用 FileInputStream.read 讀取檔案
public class FileInputRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readFile();
}
public static void readFile(){
String filePath = "Serialable/src/IOStream/CreateForFile/new1.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
int readData = 0;
try{
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while((readData = fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)readData);
}
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try{
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
成功讀取到檔案內容,這裡有個小坑,若我們 sout 的時候進行了換行,則每一個字元都會經過換行。而如果不設定換行,才是正常的輸出。
也就是說System.out.print是正常輸出,System.out.println會自動換行
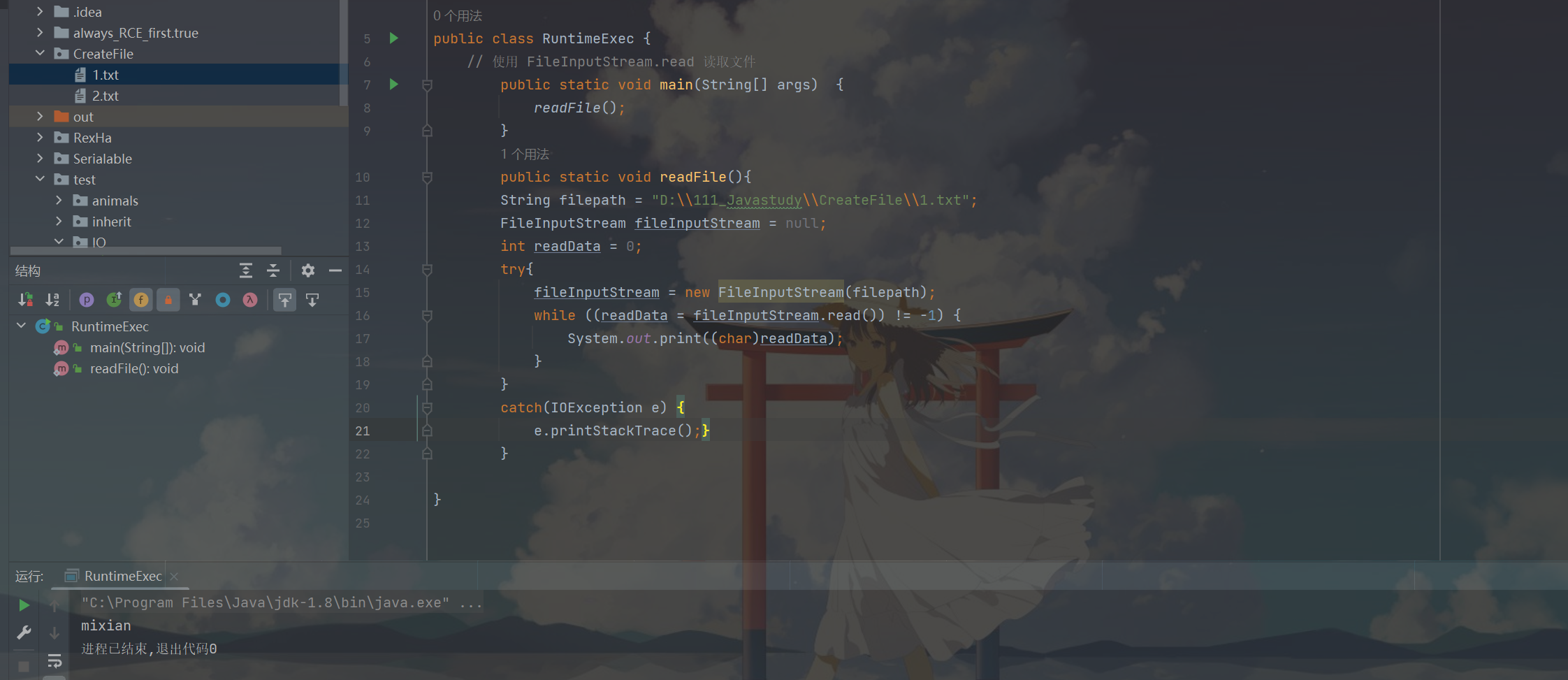
read(byte[] d) 方法用來返回位元組數
允許在方法中新增一個位元組陣列。
這種方式很有意思,當我們設定緩衝區的值為 8 時,若檔案中的字元長度超過了 8,則會換行輸出。這和上面的換行實際上是異曲同工。
再回到之前我們講的 Runtime 類進行命令執行的 Payload,在那裡,我們設定的 Cache 緩衝區的值為 1024.
read(byte[] d) 方法
package src.IOStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
// read(byte[] d) 方法,允許在方法中新增一個位元組陣列
public class FileInputRead02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readFile();
}
public static void readFile(){
String filePath = "Serialable/src/IOStream/CreateForFile/new1.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
byte[] cache = new byte[8]; // 設定緩衝區,緩衝區大小為 8 位元組
int readLen = 0;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while((readLen = fileInputStream.read(cache)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(cache, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
這裡的 while 會執行三次,會讀取檔案當中所有的字元。
3. FileOutputStream
往檔案裡面寫資料
簡單的 write(int b) 這裡先不提
write(byte[] b) 方法
write(byte[] b)
public void write(byte[] b)
throws IOException
將 b.length 個位元組從指定 byte 陣列寫入此檔案輸出流中。
覆蓋:
類 OutputStream 中的 write
引數:
b - 資料。
丟擲:
IOException - 如果發生 I/O 錯誤。
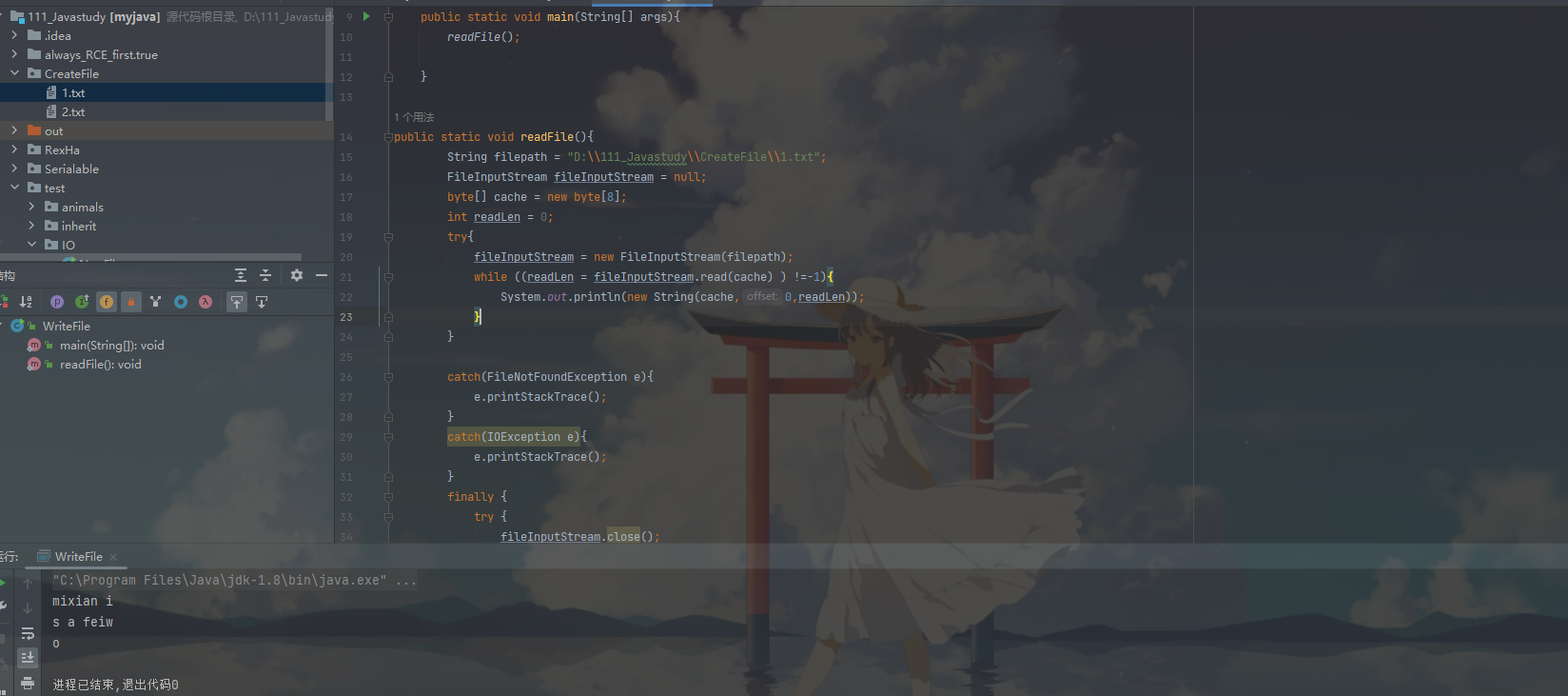
我們嘗試向檔案當中寫入資料,這裡寫程式碼的時候小心一點,容易踩坑的。
package test.IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args){
readFile();
}
public static void readFile(){
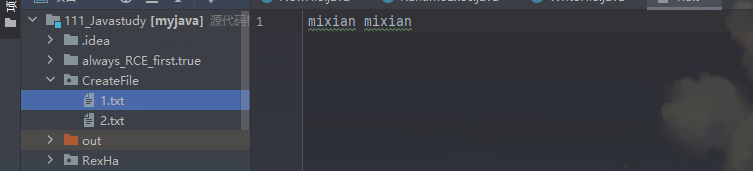
String filepath = "D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile\\1.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
String content = "mixian mixian";
try{
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filepath);
//需要將content轉換為byte型別
fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 方法
- 將指定 byte 陣列中從偏移量 off 開始的 len 個位元組寫入此檔案輸出流。
這裡的長度一定要與輸入的字元相等。
package test.IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args){
readFile();
}
public static void readFile(){
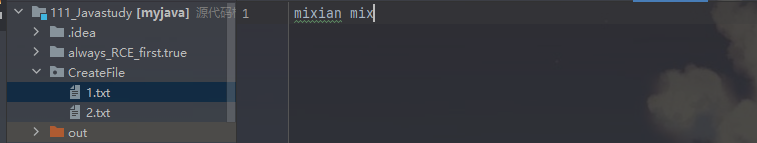
String filepath = "D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile\\1.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
String content = "mixian mixian";
try{
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filepath);
fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes(),0,10);
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
這裡僅輸出10字元導致1.txt寫入內容不全
追加寫入
如果想要寫入的資料不被覆蓋,可以設定 FileOutputStream 的構造方法 append 引數設定為 true
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
// 設定追加寫入
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true);
4. 檔案複製 ———— input output 結合
利用前文講的 fileInputStream 和 fileOutputStream 進行檔案複製。
原理上來說,先將檔案的內容(注意,其實圖片當中也是內容,這個內容不光是文字!) 讀取出來,再寫入新的檔案當中。
package test.IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
copyFile();
}
public static void copyFile() {
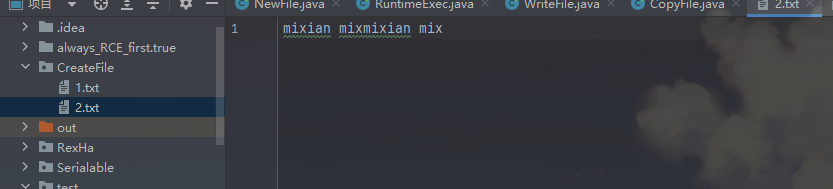
String oldfile = "D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile\\1.txt";
String newfile = "D:\\111_Javastudy\\CreateFile\\2.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try{
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(oldfile);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newfile);
byte[] cache = new byte[1024];
int readLen = 0;
while((readLen = fileInputStream.read(cache)) != -1){
fileOutputStream.write(cache,0 ,readLen);
}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){e.printStackTrace();}
catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
5. FileReader
public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader
用來讀取字元檔案的便捷類。此類的構造方法假定預設字元編碼和預設位元組緩衝區大小都是適當的。要自己指定這些值,可以先在 FileInputStream 上構造一個 InputStreamReader。
FileReader 用於讀取字元流。要讀取原始位元組流,請考慮使用 FileInputStream。
下方測試程式碼將會將 Serialable/src/IOStream/CreateForFile/new1.txt 中的 new1.tx 檔案列印輸出至控制檯:
package src.IOStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
// 讀取檔案的字元流
public class FileReaderPrint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readFile();
}
public static void readFile(){
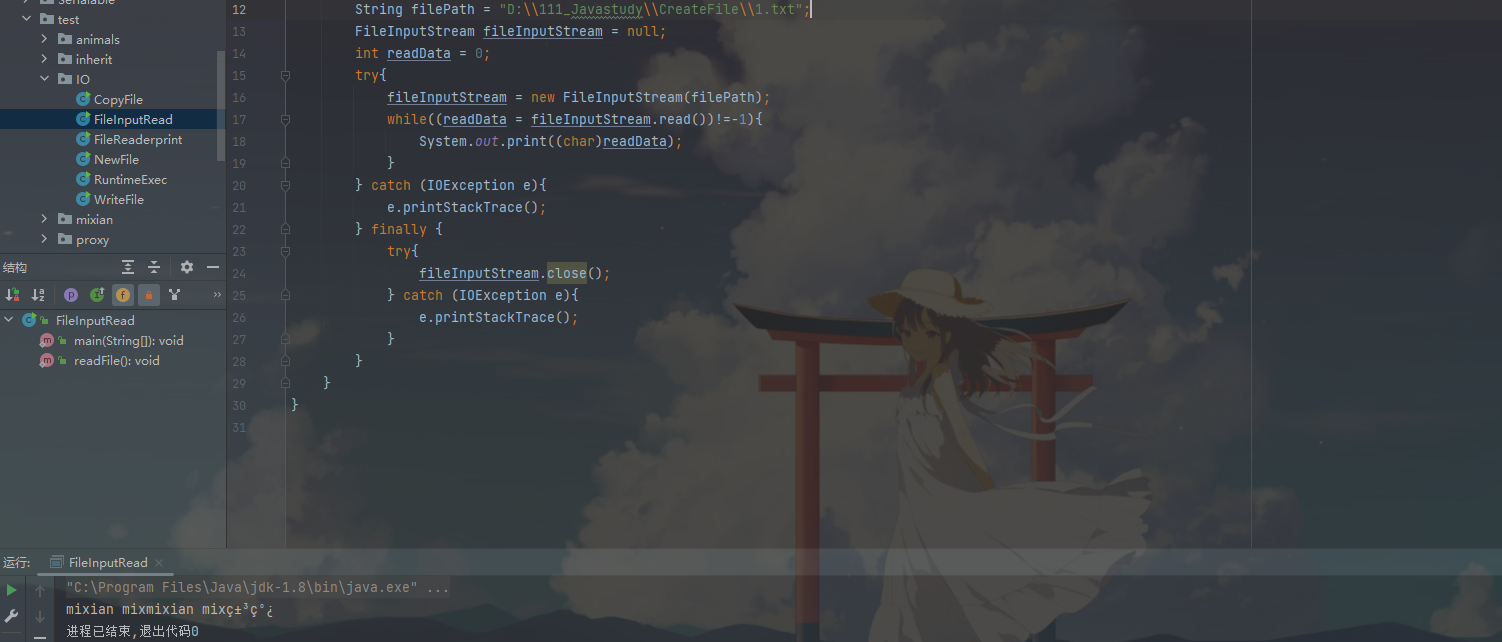
String filePath = "Serialable/src/IOStream/CreateForFile/new1.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
int readLen = 0;
char[] cache = new char[8];
while ((readLen = fileReader.read(cache))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(cache, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
-
FileReader 將會一個一個字元讀取,因此可以不亂碼輸出中文