neutron是openstack的一個重要模組,也是比較難以理解和debug的模組之一。
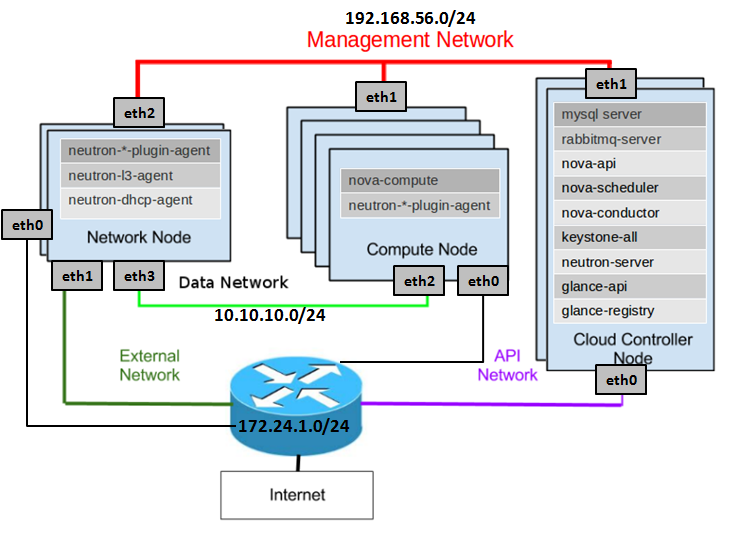
我這裡安裝如圖安裝了經典的三個節點的Havana的Openstack
圖1
分三個網路:
- External Network/API Network,這個網路是連線外網的,無論是使用者呼叫Openstack的API,還是建立出來的虛擬機器要訪問外網,或者外網要ssh到虛擬機器,都需要通過這個網路
- Data Network,資料網路,虛擬機器之間的資料傳輸通過這個網路來進行,比如一個虛擬機器要連線另一個虛擬機器,虛擬機器要連線虛擬的路由都是通過這個網路來進行
- Management Network,管理網路,Openstack各個模組之間的互動,連線資料庫,連線Message Queue都是通過這個網路來。
將這三個網路隔離,一方面是安全的原因,在虛擬機器裡面,無論採取什麼手段,干擾的都緊緊是Data Network,都不可能訪問到我的資料庫,一方面是流量分離,Management Network的流量不是很大的,而且一般都會比較優雅的使用,而Data network和External Network就需要進行流量控制的策略。
我的這個網路結構有些奇怪,除了Controller節點是兩張網路卡之外,其他的都多了一張網路卡連線到external network,這個網路卡是用來做apt-get的,因為Compute Node按說是沒有網路卡連線到外網的,為了apt-get新增了eth0,Network Node雖然有一個網路卡eth1是連線外網的,然而在neutron配置好之前,這個網路卡通常是沒有IP的,為了apt-get也新增了eth0,有人說可以通過新增route規則都通過Controller連線外網,但是對於初學的人,這個樣比較容易操作。
neutron是用來建立虛擬網路的,所謂虛擬網路,就是虛擬機器啟動的時候會有一個虛擬網路卡,虛擬網路卡會連線到虛擬的switch上,虛擬的switch連線到虛擬的router上,虛擬的router最終和物理網路卡聯通,從而虛擬網路和物理網路聯通起來。
neutron分成多個模組分佈在三個節點上。
Controller節點:
- neutron-server,用於接受API請求建立網路,子網,路由器等,然而建立的這些東西僅僅是一些資料結構在資料庫裡面
Network節點:
- neutron-l3-agent,用於建立和管理虛擬路由器,當neutron-server將路由器的資料結構建立好,它是做具體的事情的,真正的呼叫命令列將虛擬路由器,路由表,namespace,iptables規則全部建立好
- neutron-dhcp-agent,用於建立和管理虛擬DHCP Server,每個虛擬網路都會有一個DHCP Server,這個DHCP Server為這個虛擬網路裡面的虛擬機器提供IP
- neutron-openvswith-plugin-agent,這個是用於建立虛擬的L2的switch的,在Network節點上,Router和DHCP Server都會連線到二層的switch上
Compute節點:
- neutron-openvswith-plugin-agent,這個是用於建立虛擬的L2的switch的,在Compute節點上,虛擬機器的網路卡也是連線到二層的switch上
圖2
當我們搭建好了Openstack,然後建立好了tenant後,我們會為這個tenant建立一個網路。
#!/bin/bash
TENANT_NAME="openstack"
TENANT_NETWORK_NAME="openstack-net"
TENANT_SUBNET_NAME="${TENANT_NETWORK_NAME}-subnet"
TENANT_ROUTER_NAME="openstack-router"
FIXED_RANGE="192.168.0.0/24"
NETWORK_GATEWAY="192.168.0.1"
PUBLIC_GATEWAY="172.24.1.1"
PUBLIC_RANGE="172.24.1.0/24"
PUBLIC_START="172.24.1.100"
PUBLIC_END="172.24.1.200"
TENANT_ID=$(keystone tenant-list | grep " $TENANT_NAME " | awk '{print $2}')
(1) TENANT_NET_ID=$(neutron net-create --tenant_id $TENANT_ID $TENANT_NETWORK_NAME --provider:network_type gre --provider:segmentation_id 1 | grep " id " | awk '{print $4}')
(2) TENANT_SUBNET_ID=$(neutron subnet-create --tenant_id $TENANT_ID --ip_version 4 --name $TENANT_SUBNET_NAME $TENANT_NET_ID $FIXED_RANGE --gateway $NETWORK_GATEWAY --dns_nameservers list=true 8.8.8.8 | grep " id " | awk '{print $4}')
(3) ROUTER_ID=$(neutron router-create --tenant_id $TENANT_ID $TENANT_ROUTER_NAME | grep " id " | awk '{print $4}')
(4) neutron router-interface-add $ROUTER_ID $TENANT_SUBNET_ID
(5) neutron net-create public --router:external=True
(6) neutron subnet-create --ip_version 4 --gateway $PUBLIC_GATEWAY public $PUBLIC_RANGE --allocation-pool start=$PUBLIC_START,end=$PUBLIC_END --disable-dhcp --name public-subnet
(7) neutron router-gateway-set ${TENANT_ROUTER_NAME} public
圖3
- 為這個Tenant建立一個private network,不同的private network是需要通過VLAN tagging進行隔離的,互相之間broadcast不能到達,這裡我們用的是GRE模式,也需要一個類似VLAN ID的東西,稱為Segment ID
- 建立一個private network的subnet,subnet才是真正配置IP網段的地方,對於私網,我們常常用192.168.0.0/24這個網段
- 為這個Tenant建立一個Router,才能夠訪問外網
- 將private network連線到Router上
- 建立一個External Network
- 建立一個Exernal Network的Subnet,這個外網邏輯上代表了我們資料中心的物理網路,通過這個物理網路,我們可以訪問外網。因而PUBLIC_GATEWAY應該設為資料中心裡面的Gateway, PUBLIC_RANGE也應該和資料中心的物理網路的CIDR一致,否則連不通,而之所以設定PUBLIC_START和PUBLIC_END,是因為在資料中心中,不可能所有的IP地址都給Openstack使用,另外可能搭建了VMware Vcenter,可能有物理機器,僅僅分配一個區間給Openstack來用。
- 將Router連線到External Network
經過這個流程,從虛擬網路,到物理網路就邏輯上聯通了。
建立完畢網路,如果不建立虛擬機器,我們還是發現neutron的agent還是做了很多工作的,建立了很多的虛擬網路卡和switch
在Compute節點上:
root@ComputeNode:~# ip addr
1: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:49:5c:41 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.24.1.124/22 brd 16.158.167.255 scope global eth0
2: eth2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:8e:42:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.56.124/24 brd 192.168.56.255 scope global eth2
3: eth3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:68:92:ce brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.10.10.124/24 brd 10.10.10.255 scope global eth3
4: br-int: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether d6:2a:96:12:4a:49 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: br-tun: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether a2:ee:75:bd:af:4a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: qvof5da998c-82: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether c2:7e:50:de:8c:c5 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: qvbf5da998c-82: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether c2:33:73:40:8f:e0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@ComputeNode:~# ovs-vsctl show
39f69272-17d4-42bf-9020-eecc9fe8cde6
Bridge br-int
Port patch-tun
Interface patch-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-int}
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Bridge br-tun
Port patch-int
Interface patch-int
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-tun}
Port "gre-1"
Interface "gre-1"
type: gre
options: {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.10.10.124", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.10.10.121"}
Port br-tun
Interface br-tun
type: internal
ovs_version: "1.10.2"
在Network Node上:
root@NetworkNode:~# ip addr
1: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:22:8a:7a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.24.1.121/22 brd 172.24.1.255 scope global eth0
2: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:f1:31:81 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:56:7b:8a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.56.121/24 brd 192.168.56.255 scope global eth2
4: eth3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:26:bc:84 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.10.10.121/24 brd 10.10.10.255 scope global eth3
5: br-ex: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether 08:00:27:f1:31:81 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.24.1.8/24 brd 172.24.1.255 scope global br-ex
6: br-int: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether 22:fe:f1:9b:29:4b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: br-tun: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether c6:ea:94:ff:23:41 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@NetworkNode:~# ip netns
qrouter-b2510953-1ae4-4296-a628-1680735545ac
qdhcp-96abd26b-0a2f-448b-b92c-4c98b8df120b
root@NetworkNode:~# ip netns exec qrouter-b2510953-1ae4-4296-a628-1680735545ac ip addr
8: qg-97040ca3-2c: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether fa:16:3e:26:57:e3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.24.1.100/24 brd 172.24.1.255 scope global qg-97040ca3-2c
11: qr-e8b97930-ac: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether fa:16:3e:43:ef:16 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.1/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global qr-e8b97930-ac
root@NetworkNode:~# ip netns exec qdhcp-96abd26b-0a2f-448b-b92c-4c98b8df120b ip addr
9: tapde5739e1-95: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/ether fa:16:3e:19:8c:67 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.2/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global tapde5739e1-95
inet 169.254.169.254/16 brd 169.254.255.255 scope global tapde5739e1-95
root@NetworkNode:~# ovs-vsctl show
d5d5847e-1c9e-4770-a68c-7a695b7b95cd
Bridge br-ex
Port "qg-97040ca3-2c"
Interface "qg-97040ca3-2c"
type: internal
Port "eth1"
Interface "eth1"
Port br-ex
Interface br-ex
type: internal
Bridge br-int
Port patch-tun
Interface patch-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-int}
Port "tapde5739e1-95"
tag: 1
Interface "tapde5739e1-95"
type: internal
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Port "qr-e8b97930-ac"
tag: 1
Interface "qr-e8b97930-ac"
type: internal
Bridge br-tun
Port patch-int
Interface patch-int
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-tun}
Port "gre-2"
Interface "gre-2"
type: gre
options: {in_key=flow, local_ip="10.10.10.121", out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.10.10.124"}
Port br-tun
Interface br-tun
type: internal
ovs_version: "1.10.2"
這時候如果我們建立一個虛擬機器在這個網路裡面,在Compute Node多了下面的網路卡:
13: qvof5da998c-82: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether c2:7e:50:de:8c:c5 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
14: qvbf5da998c-82: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether c2:33:73:40:8f:e0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
15: qbr591d8cc4-df: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP
link/ether f2:d9:f0:d5:48:c8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
16: qvo591d8cc4-df: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether e2:58:d4:dc:b5:16 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
17: qvb591d8cc4-df: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master qbr591d8cc4-df state UP qlen 1000
link/ether f2:d9:f0:d5:48:c8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
18: tap591d8cc4-df: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master qbr591d8cc4-df state UNKNOWN qlen 500
link/ether fe:16:3e:6e:ba:d0 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
如果我們按照ovs-vsctl show的網路卡橋接關係,變可以畫出下面的圖
圖4
當然如果你配的不是GRE而是VLAN的話,便有下面這個著名的複雜的圖。
在network Node上:
圖5
在Compute Node上:
圖6
當看到這裡,很多人腦袋就大了,openstack為什麼要建立這麼多的虛擬網路卡,他們之間什麼關係,這些dl_vlan, mod_vlan_vid都是什麼東東啊?
這些網路卡看起來複雜,卻是各有用處,這種虛擬網路拓撲,正是我們經常使用的物理網路的拓撲結構。
我們先來回到一個最最熟悉不過的場景,我們的大學寢室,當時我們還買不起路由器,所以一般採取的方法如下圖所示:
寢室長的機器上弄兩張網路卡,寢室買一個HUB,其他人的電腦都接到HUB上,寢室長的電腦的兩張網路卡一張對外連線網路,一張對內連線HUB。寢室長的電腦其實充當的便是路由器的作用。
後來條件好了,路由器也便宜了,所以很多家庭也是類似的拓撲結構,只不過將Computer1和switch合起來,變成了一個路由器,路由器也是有多個口一個連線WLAN,一個連線LAN。
圖7
現在我們想象一個寢室變成了一臺物理機Hypervisor,所有的電腦都變成了虛擬機器,就成了下面的樣子。
圖8
我們先忽略qbr和DHCP Server,以及namespace。
br-int就是寢室裡面的HUB,所有虛擬機器都會連線到這個switch上,虛擬機器之間的相互通訊就是通過br-int來的。
Router就是你們寢室長的電腦,一邊接在br-int上,一邊接在對外的網口上,br-ex/eth0外面就是我們的物理網路。
為什麼會有個DHCP Server呢,是同一個private network裡的虛擬機器得到IP都是通過這個DHCP Server來的,這個DHCP Server也是連線到br-int上和虛擬機器進行通訊。
為什麼會有qbr呢,這是和security group的概念有關,openstack中的security group開通哪些埠,遮蔽哪些埠是用iptables來實現的,然而br-int這些虛擬bridge都是openvswitch建立的,openvswitch的kernel mode和netfilter的kernel mode不相容,一個IP包進來要麼走iptables的規則進行處理,要麼走openvswitch的規則進行處理,通過上面的複雜的圖我們可以看到,br-int上面有很多openvswitch的規則,比如vlan tag等,所以iptables必須要另外建立一個linux bridge來做,因而有了qbr,在瞭解拓撲結構的時候,可以將qbr忽略,看成VM直接連線到br-int上就可以了。
為什麼會有namespace呢,java的namespace是為了相同的類名,不同的namespace,顯然是不同的類。openstack也想做到這一點,不同的tenant都想建立自己的router和private network,彼此不知道別人指定了哪些網段,很有可能兩個tenant都指定了192.168.0.0/24,這樣不同的private network的路由表,DHCP Server就需要隔離,不然就亂了,因而有了namespace。
上面的圖其實就是單節點的openstack的網路結構,雖然複雜,但是就是把我們家裡的,或者寢室裡面的物理機搬到一個Hypervisor上了,其結構就不難理解了。
當然單節點的openstack不過是個測試環境,compute節點和network節點也是要分開的,如圖4,每個機器上都有了自己的br-int。
但是對於虛擬機器和虛擬Router來講,他們仍然覺得他們是連線到了一個大的L2的br-int上,通過這個br-int相互通訊的,他們感受不到br-int下面的虛擬網路卡br-tun。所以對於多節點結構,我們可以想象br-int是一個大的,橫跨所有的compute和network節點的二層switch,虛擬機器之間的通訊以及虛擬機器和Router的通訊,就像在一個寢室一樣的。
然而br-int畢竟被物理的割開了,需要有一種方式將他們串聯起來,openstack提供了多種方式,圖4中是用GRE tunnel將不同機器的br-int連線起來,圖5圖6是通過VLAN將br-int連線起來,當然還可以使用vxlan。
這就是為什麼openstack有了br-int這個bridge,但是不把所有的openvswitch的規則都在它上面實現。就是為了提供這種靈活性,對於虛擬機器來講,看到的是一大整個br-int,不同機器的br-int可以有多種方式連線,這在br-int下面的網路卡上面實現。
如果有不同的Tenant,建立了不同的private network,為了在data network上對包進行隔離,建立private network的時候,需要指定vlanid或者segmentid。
從ovs-vsctl show我們可以看到,不同的tenant的private network上建立的虛擬機器,連線到br-int上的時候是帶tag的,所以不同tenant的虛擬機器,即便連線到同一個br-int上,因為tag不同,也是不能相互通訊的,然而同一個機器上的tag的計數是僅在本機有效的,並不使用我們建立private network的時候指定的全域性唯一的vlanid或者segmentid,一個compute節點上的br-int上的tag 1和另一臺compute節點上的br-int的tag1很可能是兩碼事。全域性的vlanid和segmentid僅僅在br-int以下的虛擬網路卡和物理網路中使用,虛擬機器所有能看到的東西,到br-int為止,看不到打通br-int所要使用的vlanid和segmentid。
從區域性有效的taging到全域性有效的vlanid或者segmentid的轉換,都是通過openvswitch的規則,在br-tun或者br-eth1上實現。
我們可以用下面的命令看一下這個規則:
在Compute節點上:
private network “openstack-net”的tag在這臺機器上是2,而我們建立的時候的segmentid設定的是1
Bridge br-int
Port patch-tun
Interface patch-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-int}
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Port "qvo591d8cc4-df"
tag: 2
Interface "qvo591d8cc4-df"
root@ComputeNodeCliu8:~# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-tun
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
//in_port=1是指包是從patch-int,也即是從虛擬機器來的,所以是傳送規則,跳轉到table1
cookie=0x0, duration=77419.191s, table=0, n_packets=22, n_bytes=2136, idle_age=6862, hard_age=65534, priority=1,in_port=1 actions=resubmit(,1)
//in_port=2是指包是從GRE來的,也即是從物理網路來的,所以是接收規則,跳轉到table2
cookie=0x0, duration=77402.19s, table=0, n_packets=3, n_bytes=778, idle_age=6867, hard_age=65534, priority=1,in_port=2 actions=resubmit(,2)
cookie=0x0, duration=77418.403s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
//multicast,跳轉到table21
cookie=0x0, duration=77416.63s, table=1, n_packets=21, n_bytes=2094, idle_age=6862, hard_age=65534, priority=0,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,21)
//unicast,跳轉到table 20
cookie=0x0, duration=77417.389s, table=1, n_packets=1, n_bytes=42, idle_age=6867, hard_age=65534, priority=0,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,20)
//這是接收規則的延續,如果接收的tun_id=0x1則轉換為本地的tag,mod_vlan_vid:2,跳轉到table 10
cookie=0x0, duration=6882.254s, table=2, n_packets=3, n_bytes=778, idle_age=6867, priority=1,tun_id=0x1 actions=mod_vlan_vid:2,resubmit(,10)
cookie=0x0, duration=77415.638s, table=2, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=77414.432s, table=3, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=77412.825s, table=10, n_packets=3, n_bytes=778, idle_age=6867, hard_age=65534, priority=1 actions=learn(table=20,hard_timeout=300,priority=1,NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[0..11],NXM_OF_ETH_DST[]=NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[],load:0->NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[],load:NXM_NX_TUN_ID[]->NXM_NX_TUN_ID[],output:NXM_OF_IN_PORT[]),output:1
cookie=0x0, duration=77411.549s, table=20, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,21)
//這是傳送規則的延續,如果接收到的dl_vlan=2,則轉換為物理網路的segmentid=1,set_tunnel:0x1
cookie=0x0, duration=6883.119s, table=21, n_packets=10, n_bytes=1264, idle_age=6862, priority=1,dl_vlan=2 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x1,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=77410.56s, table=21, n_packets=11, n_bytes=830, idle_age=6885, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
在Network節點上:
Bridge br-int
Port patch-tun
Interface patch-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=patch-int}
Port "tapde5739e1-95"
tag: 1
Interface "tapde5739e1-95"
type: internal
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Port "qr-e8b97930-ac"
tag: 1
Interface "qr-e8b97930-ac"
type: internal
非常相似的規則。
root@NetworkNodeCliu8:~# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-tun
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
//in_port=1是指包是從patch-int,也即是從虛擬機器來的,所以是傳送規則,跳轉到table1
cookie=0x0, duration=73932.142s, table=0, n_packets=12, n_bytes=1476, idle_age=3380, hard_age=65534, priority=1,in_port=1 actions=resubmit(,1)
cookie=0x0, duration=73914.323s, table=0, n_packets=9, n_bytes=1166, idle_age=3376, hard_age=65534, priority=1,in_port=2 actions=resubmit(,2)
cookie=0x0, duration=73930.934s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
//multicast,跳轉到table21
cookie=0x0, duration=73928.59s, table=1, n_packets=6, n_bytes=468, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,21)
//unicast,跳轉到table20
cookie=0x0, duration=73929.695s, table=1, n_packets=3, n_bytes=778, idle_age=3380, hard_age=65534, priority=0,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,20)
//這是接收規則的延續,如果接收的tun_id=0x1則轉換為本地的tag,mod_vlan_vid:1,跳轉到table 10
cookie=0x0, duration=73906.864s, table=2, n_packets=9, n_bytes=1166, idle_age=3376, hard_age=65534, priority=1,tun_id=0x1 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,resubmit(,10)
cookie=0x0, duration=73927.542s, table=2, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=73926.403s, table=3, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop
cookie=0x0, duration=73925.611s, table=10, n_packets=9, n_bytes=1166, idle_age=3376, hard_age=65534, priority=1 actions=learn(table=20,hard_timeout=300,priority=1,NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[0..11],NXM_OF_ETH_DST[]=NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[],load:0->NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[],load:NXM_NX_TUN_ID[]->NXM_NX_TUN_ID[],output:NXM_OF_IN_PORT[]),output:1
cookie=0x0, duration=73924.858s, table=20, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,21)
//這是傳送規則的延續,如果接收到的dl_vlan=1,則轉換為物理網路的segmentid=1,set_tunnel:0x1
cookie=0x0, duration=73907.657s, table=21, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=1,dl_vlan=1 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x1,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=73924.117s, table=21, n_packets=6, n_bytes=468, idle_age=65534, hard_age=65534, priority=0 actions=drop