- Qt中的Meta Type 包含兩種型別,每個型別都以一個整型ID來表示, 內建型別和使用者自定義型別(自定義型別對應的整型ID 從65536 即 QMetaType::User 開始):
1)內建型別:
corelib\kernel\qmetatype.h
// F is a tuple: (QMetaType::TypeName, QMetaType::TypeNameID, RealType)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_NON_VOID_TYPE(F)\
F(Bool, 1, bool) \
F(Int, 2, int) \
F(UInt, 3, uint) \
F(LongLong, 4, qlonglong) \
F(ULongLong, 5, qulonglong) \
F(Double, 6, double) \
F(Long, 32, long) \
F(Short, 33, short) \
F(Char, 34, char) \
F(Char16, 56, char16_t) \
F(Char32, 57, char32_t) \
F(ULong, 35, ulong) \
F(UShort, 36, ushort) \
F(UChar, 37, uchar) \
F(Float, 38, float) \
F(SChar, 40, signed char) \
F(Nullptr, 51, std::nullptr_t) \
F(QCborSimpleType, 52, QCborSimpleType) \
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_TYPE(F) \
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_NON_VOID_TYPE(F) \
F(Void, 43, void) \
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_POINTER(F) \
F(VoidStar, 31, void*) \
#if QT_CONFIG(easingcurve)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_EASINGCURVE(F)\
F(QEasingCurve, 29, QEasingCurve)
#else
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_EASINGCURVE(F)
#endif
#if QT_CONFIG(itemmodel)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_ITEMMODEL_CLASS(F)\
F(QModelIndex, 42, QModelIndex) \
F(QPersistentModelIndex, 50, QPersistentModelIndex)
#else
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_ITEMMODEL_CLASS(F)
#endif
#if QT_CONFIG(regularexpression)
# define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_REGULAR_EXPRESSION(F) \
F(QRegularExpression, 44, QRegularExpression)
#else
# define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_REGULAR_EXPRESSION(F)
#endif
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_CLASS(F)\
F(QChar, 7, QChar) \
F(QString, 10, QString) \
F(QByteArray, 12, QByteArray) \
F(QBitArray, 13, QBitArray) \
F(QDate, 14, QDate) \
F(QTime, 15, QTime) \
F(QDateTime, 16, QDateTime) \
F(QUrl, 17, QUrl) \
F(QLocale, 18, QLocale) \
F(QRect, 19, QRect) \
F(QRectF, 20, QRectF) \
F(QSize, 21, QSize) \
F(QSizeF, 22, QSizeF) \
F(QLine, 23, QLine) \
F(QLineF, 24, QLineF) \
F(QPoint, 25, QPoint) \
F(QPointF, 26, QPointF) \
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_EASINGCURVE(F) \
F(QUuid, 30, QUuid) \
F(QVariant, 41, QVariant) \
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_REGULAR_EXPRESSION(F) \
F(QJsonValue, 45, QJsonValue) \
F(QJsonObject, 46, QJsonObject) \
F(QJsonArray, 47, QJsonArray) \
F(QJsonDocument, 48, QJsonDocument) \
F(QCborValue, 53, QCborValue) \
F(QCborArray, 54, QCborArray) \
F(QCborMap, 55, QCborMap) \
F(Float16, 63, qfloat16) \
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_ITEMMODEL_CLASS(F)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_POINTER(F)\
F(QObjectStar, 39, QObject*)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_TEMPLATE(F)\
F(QVariantMap, 8, QVariantMap) \
F(QVariantList, 9, QVariantList) \
F(QVariantHash, 28, QVariantHash) \
F(QVariantPair, 58, QVariantPair) \
F(QByteArrayList, 49, QByteArrayList) \
F(QStringList, 11, QStringList) \
#if QT_CONFIG(shortcut)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_KEYSEQUENCE_CLASS(F)\
F(QKeySequence, 0x100b, QKeySequence)
#else
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_KEYSEQUENCE_CLASS(F)
#endif
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_GUI_CLASS(F)\
F(QFont, 0x1000, QFont) \
F(QPixmap, 0x1001, QPixmap) \
F(QBrush, 0x1002, QBrush) \
F(QColor, 0x1003, QColor) \
F(QPalette, 0x1004, QPalette) \
F(QIcon, 0x1005, QIcon) \
F(QImage, 0x1006, QImage) \
F(QPolygon, 0x1007, QPolygon) \
F(QRegion, 0x1008, QRegion) \
F(QBitmap, 0x1009, QBitmap) \
F(QCursor, 0x100a, QCursor) \
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_KEYSEQUENCE_CLASS(F) \
F(QPen, 0x100c, QPen) \
F(QTextLength, 0x100d, QTextLength) \
F(QTextFormat, 0x100e, QTextFormat) \
F(QTransform, 0x1010, QTransform) \
F(QMatrix4x4, 0x1011, QMatrix4x4) \
F(QVector2D, 0x1012, QVector2D) \
F(QVector3D, 0x1013, QVector3D) \
F(QVector4D, 0x1014, QVector4D) \
F(QQuaternion, 0x1015, QQuaternion) \
F(QPolygonF, 0x1016, QPolygonF) \
F(QColorSpace, 0x1017, QColorSpace) \
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_WIDGETS_CLASS(F)\
F(QSizePolicy, 0x2000, QSizePolicy) \
// F is a tuple: (QMetaType::TypeName, QMetaType::TypeNameID, AliasingType, "RealType")
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_ALIAS_TYPE(F)\
F(ULong, -1, ulong, "unsigned long") \
F(UInt, -1, uint, "unsigned int") \
F(UShort, -1, ushort, "unsigned short") \
F(UChar, -1, uchar, "unsigned char") \
F(LongLong, -1, qlonglong, "long long") \
F(ULongLong, -1, qulonglong, "unsigned long long") \
F(SChar, -1, signed char, "qint8") \
F(UChar, -1, uchar, "quint8") \
F(Short, -1, short, "qint16") \
F(UShort, -1, ushort, "quint16") \
F(Int, -1, int, "qint32") \
F(UInt, -1, uint, "quint32") \
F(LongLong, -1, qlonglong, "qint64") \
F(ULongLong, -1, qulonglong, "quint64") \
F(QVariantList, -1, QVariantList, "QList<QVariant>") \
F(QVariantMap, -1, QVariantMap, "QMap<QString,QVariant>") \
F(QVariantHash, -1, QVariantHash, "QHash<QString,QVariant>") \
F(QVariantPair, -1, QVariantPair, "QPair<QVariant,QVariant>") \
F(QByteArrayList, -1, QByteArrayList, "QList<QByteArray>") \
F(QStringList, -1, QStringList, "QList<QString>") \
#define QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_TYPE(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_TYPE(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_POINTER(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_CLASS(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_POINTER(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_TEMPLATE(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_GUI_CLASS(F)\
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_WIDGETS_CLASS(F)\
#define QT_DEFINE_METATYPE_ID(TypeName, Id, Name) \
TypeName = Id,
#define QT_FOR_EACH_AUTOMATIC_TEMPLATE_1ARG(F) \
F(QList) \
F(QQueue) \
F(QStack) \
F(QSet) \
/*end*/
#define QT_FOR_EACH_AUTOMATIC_TEMPLATE_2ARG(F) \
F(QHash, class) \
F(QMap, class)
#define QT_FOR_EACH_AUTOMATIC_TEMPLATE_SMART_POINTER(F) \
F(QSharedPointer) \
F(QWeakPointer) \
F(QPointer)
class Q_CORE_EXPORT QMetaType {
public:
#ifndef Q_QDOC
// The code that actually gets compiled.
enum Type {
// these are merged with QVariant
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_TYPE(QT_DEFINE_METATYPE_ID)
FirstCoreType = Bool,
LastCoreType = Float16,
FirstGuiType = QFont,
LastGuiType = QColorSpace,
FirstWidgetsType = QSizePolicy,
LastWidgetsType = QSizePolicy,
HighestInternalId = LastWidgetsType,
QReal = sizeof(qreal) == sizeof(double) ? Double : Float,
UnknownType = 0,
User = 65536
};
#else
// If we are using QDoc it fakes the Type enum looks like this.
enum Type {
UnknownType = 0, Bool = 1, Int = 2, UInt = 3, LongLong = 4, ULongLong = 5,
Double = 6, Long = 32, Short = 33, Char = 34, ULong = 35, UShort = 36,
UChar = 37, Float = 38,
VoidStar = 31,
QChar = 7, QString = 10, QStringList = 11, QByteArray = 12,
QBitArray = 13, QDate = 14, QTime = 15, QDateTime = 16, QUrl = 17,
QLocale = 18, QRect = 19, QRectF = 20, QSize = 21, QSizeF = 22,
QLine = 23, QLineF = 24, QPoint = 25, QPointF = 26,
QEasingCurve = 29, QUuid = 30, QVariant = 41, QModelIndex = 42,
QPersistentModelIndex = 50, QRegularExpression = 44,
QJsonValue = 45, QJsonObject = 46, QJsonArray = 47, QJsonDocument = 48,
QByteArrayList = 49, QObjectStar = 39, SChar = 40,
Void = 43,
Nullptr = 51,
QVariantMap = 8, QVariantList = 9, QVariantHash = 28, QVariantPair = 58,
QCborSimpleType = 52, QCborValue = 53, QCborArray = 54, QCborMap = 55,
Char16 = 56, Char32 = 57,
Int128 = 59, UInt128 = 60, Float128 = 61, BFloat16 = 62, Float16 = 63,
// Gui types
QFont = 0x1000, QPixmap = 0x1001, QBrush = 0x1002, QColor = 0x1003, QPalette = 0x1004,
QIcon = 0x1005, QImage = 0x1006, QPolygon = 0x1007, QRegion = 0x1008, QBitmap = 0x1009,
QCursor = 0x100a, QKeySequence = 0x100b, QPen = 0x100c, QTextLength = 0x100d, QTextFormat = 0x100e,
QTransform = 0x1010, QMatrix4x4 = 0x1011, QVector2D = 0x1012,
QVector3D = 0x1013, QVector4D = 0x1014, QQuaternion = 0x1015, QPolygonF = 0x1016, QColorSpace = 0x1017,
// Widget types
QSizePolicy = 0x2000,
// Start-point for client-code types:
User = 65536
};
2)自定義型別,需要向customRegistry中註冊使用者自定義型別資訊:
#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, ARGS) \
QT_WARNING_PUSH \
QT_WARNING_DISABLE_CLANG("-Wunevaluated-expression") \
namespace { struct Q_QGS_ ## NAME { \
typedef TYPE QGS_Type; \
static void innerFunction(void *pointer) \
noexcept(noexcept(std::remove_cv_t<QGS_Type> ARGS)) \
{ \
new (pointer) QGS_Type ARGS; \
} \
}; } \
Q_CONSTINIT static QGlobalStatic<QtGlobalStatic::Holder<Q_QGS_ ## NAME>> NAME; \
QT_WARNING_POP
/**/
#define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(TYPE, NAME, ...) \
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC_WITH_ARGS(TYPE, NAME, (__VA_ARGS__))
Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(QMetaTypeCustomRegistry, customTypeRegistry)
宏定義替換後會得到一個靜態全域性變數 customTypeRegistry的宣告,型別為QGlobalStatic<QtGlobalStatic::Holder<Q_QGS_customTypeRegistry >>,
替換後的程式碼如下:
namespace
{
struct Q_QGS_customTypeRegistry
{
typedef TYPE QMetaTypeCustomRegistry;
static void innerFunction(void *pointer) noexcept(noexcept(QMetaTypeCustomRegistry ()))
{
new (pointer) QMetaTypeCustomRegistry() ;
}
};
}
Q_CONSTINIT static QGlobalStatic<QtGlobalStatic::Holder<Q_QGS_customTypeRegistry >> customTypeRegistry;
在QMetaTypeCustomRegistry類中提供了註冊自定義型別的介面:
struct QMetaTypeCustomRegistry
{
#if QT_VERSION < QT_VERSION_CHECK(7, 0, 0) && !defined(QT_BOOTSTRAPPED)
QMetaTypeCustomRegistry()
{
/* qfloat16 was neither a builtin, nor unconditionally registered
in QtCore in Qt <= 6.2.
Inserting it as an alias ensures that a QMetaType::id call
will get the correct built-in type-id (the interface pointers
might still not match, but we already deal with that case.
*/
aliases.insert("qfloat16", QtPrivate::qMetaTypeInterfaceForType<qfloat16>());
}
#endif
QReadWriteLock lock;
QList<const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *> registry;
QHash<QByteArray, const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *> aliases;
// index of first empty (unregistered) type in registry, if any.
int firstEmpty = 0;
int registerCustomType(const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *cti)
{
// we got here because cti->typeId is 0, so this is a custom meta type
// (not read-only)
auto ti = const_cast<QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *>(cti);
{
QWriteLocker l(&lock);
if (int id = ti->typeId.loadRelaxed())
return id;
QByteArray name =
#ifndef QT_NO_QOBJECT
QMetaObject::normalizedType
#endif
(ti->name);
if (auto ti2 = aliases.value(name)) {
const auto id = ti2->typeId.loadRelaxed();
ti->typeId.storeRelaxed(id);
return id;
}
aliases[name] = ti;
int size = registry.size();
while (firstEmpty < size && registry[firstEmpty])
++firstEmpty;
if (firstEmpty < size) {
registry[firstEmpty] = ti;
++firstEmpty;
} else {
registry.append(ti);
firstEmpty = registry.size();
}
ti->typeId.storeRelaxed(firstEmpty + QMetaType::User);
}
if (ti->legacyRegisterOp)
ti->legacyRegisterOp();
return ti->typeId.loadRelaxed();
};
.........
.........
.........
};
- 在訊號槽機制中,如果使用QueuedConnection連線型別,當訊號和槽中使用了自定義資料型別傳遞引數時需要首先註冊自定義資料型別,如:
qRegisterMetaType("Add");

至於為何需要註冊自定義型別,個人理解理由如下:
在QueuedConnection 連線方式下 訊號觸發時 並非 對 槽函式的同步呼叫,而是封裝一個QMetaCallEvent 以post方式放到receiver物件所附屬的執行緒對應的連線佇列中
等待後續EventLoop迴圈中對取對應的Event處理。訊號函式呼叫結束後 棧幀已經銷燬,無法在後續的Eventloop 迴圈中從棧中拿到對應的引數資料。
因此,比較自然的方法就是將要傳遞的函式引數儲存在 堆上,這樣不會隨訊號函式呼叫的結束而丟失要傳遞的引數。儲存在堆上的引數記憶體地址
存放在上述的MetaCallEvent物件中,這樣在後續迴圈中執行槽函式時可以獲取到需要的函式引數資料。
又由於Qt 針對訊號槽機制中傳遞引數為了更通用,因此建立連結的內部框架程式碼中 引數都是以 void* 型別來宣告的。
因此在傳遞給Qt框架原始碼時都將 使用者的資料強制轉換為了 void*。例如如下程式碼所示:

由於傳遞進去的是void* 型別的引數,因此要將 該引數 複製到 堆上儲存,這時就需要知道要複製多少個位元組。為了需要這個位元組大小資訊 ,
因此需要有個地方記錄,而記錄位元組大小的資訊就以QMetaType的形式存放在customTypeRegistry中。Qt框架中記錄了訊號和槽函式中引數個數,引數型別資訊。
在使用自定義資料型別前先註冊,註冊時會在登錄檔中給這個新的使用者自定義型別資訊分配一個 整型ID,同時會根據該資料型別是否是
non-trival class 為其宣告和定義copyCtr,moveCtr,dtor等
複製構造,移動構造,解構函式資訊。如下程式碼:
template<typename T>
struct QMetaTypeInterfaceWrapper
{
// if the type ID for T is known at compile-time, then we can declare
// the QMetaTypeInterface object const; otherwise, we declare it as
// non-const and the .typeId is updated by QMetaType::idHelper().
static constexpr bool IsConstMetaTypeInterface = !!BuiltinMetaType<T>::value;
using InterfaceType = std::conditional_t<IsConstMetaTypeInterface, const QMetaTypeInterface, NonConstMetaTypeInterface>;
static inline InterfaceType metaType = {
/*.revision=*/ QMetaTypeInterface::CurrentRevision,
/*.alignment=*/ alignof(T),
/*.size=*/ sizeof(T),
/*.flags=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::Flags,
/*.typeId=*/ BuiltinMetaType<T>::value,
/*.metaObjectFn=*/ MetaObjectForType<T>::metaObjectFunction,
/*.name=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getName(),
/*.defaultCtr=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getDefaultCtr(),
/*.copyCtr=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getCopyCtr(),
/*.moveCtr=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getMoveCtr(),
/*.dtor=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getDtor(),
/*.equals=*/ QEqualityOperatorForType<T>::equals,
/*.lessThan=*/ QLessThanOperatorForType<T>::lessThan,
/*.debugStream=*/ QDebugStreamOperatorForType<T>::debugStream,
/*.dataStreamOut=*/ QDataStreamOperatorForType<T>::dataStreamOut,
/*.dataStreamIn=*/ QDataStreamOperatorForType<T>::dataStreamIn,
/*.legacyRegisterOp=*/ QMetaTypeForType<T>::getLegacyRegister()
};
};
template<typename S>
class QMetaTypeForType
{
public:
static constexpr decltype(typenameHelper<S>()) name = typenameHelper<S>();
static constexpr unsigned Flags = QMetaTypeTypeFlags<S>::Flags;
static constexpr QMetaTypeInterface::DefaultCtrFn getDefaultCtr()
{
if constexpr (std::is_default_constructible_v<S> && !QTypeInfo<S>::isValueInitializationBitwiseZero) {
return [](const QMetaTypeInterface *, void *addr) { new (addr) S(); };
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
static constexpr QMetaTypeInterface::CopyCtrFn getCopyCtr()
{
if constexpr (std::is_copy_constructible_v<S> && !std::is_trivially_copy_constructible_v<S>) {
return [](const QMetaTypeInterface *, void *addr, const void *other) {
new (addr) S(*reinterpret_cast<const S *>(other));
};
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
static constexpr QMetaTypeInterface::MoveCtrFn getMoveCtr()
{
if constexpr (std::is_move_constructible_v<S> && !std::is_trivially_move_constructible_v<S>) {
return [](const QMetaTypeInterface *, void *addr, void *other) {
new (addr) S(std::move(*reinterpret_cast<S *>(other)));
};
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
static constexpr QMetaTypeInterface::DtorFn getDtor()
{
if constexpr (std::is_destructible_v<S> && !std::is_trivially_destructible_v<S>)
return [](const QMetaTypeInterface *, void *addr) {
reinterpret_cast<S *>(addr)->~S();
};
else
return nullptr;
}
}
在QCoreApplicationPrivate::sendPostedEvents中取出PostEvent包裝著的QMetaCallEvent後 先將其初始化給 QScopedPointer event_deleter(e),
這樣可以在sendPostedEvents函式返回後 透過棧銷燬event_deleter時呼叫其Cleanup 的cleanup來釋放資源,這裡採用的是QScopedPointerDeleter,
其cleanup行為就是delete pointer,引起會呼叫QMetaCallEvent的解構函式,進而呼叫其中儲存的引數的destroy函式,destroy函式中呼叫destruct,
其中呼叫了解構函式,然後呼叫了QMetaTypeDeleter仿函式物件,其實是呼叫全域性的operator delete ,
到此為止會將 queued_activate函式中 QMetaCallEvent為儲存訊號函式引數 在堆上申請的記憶體釋放完成了。
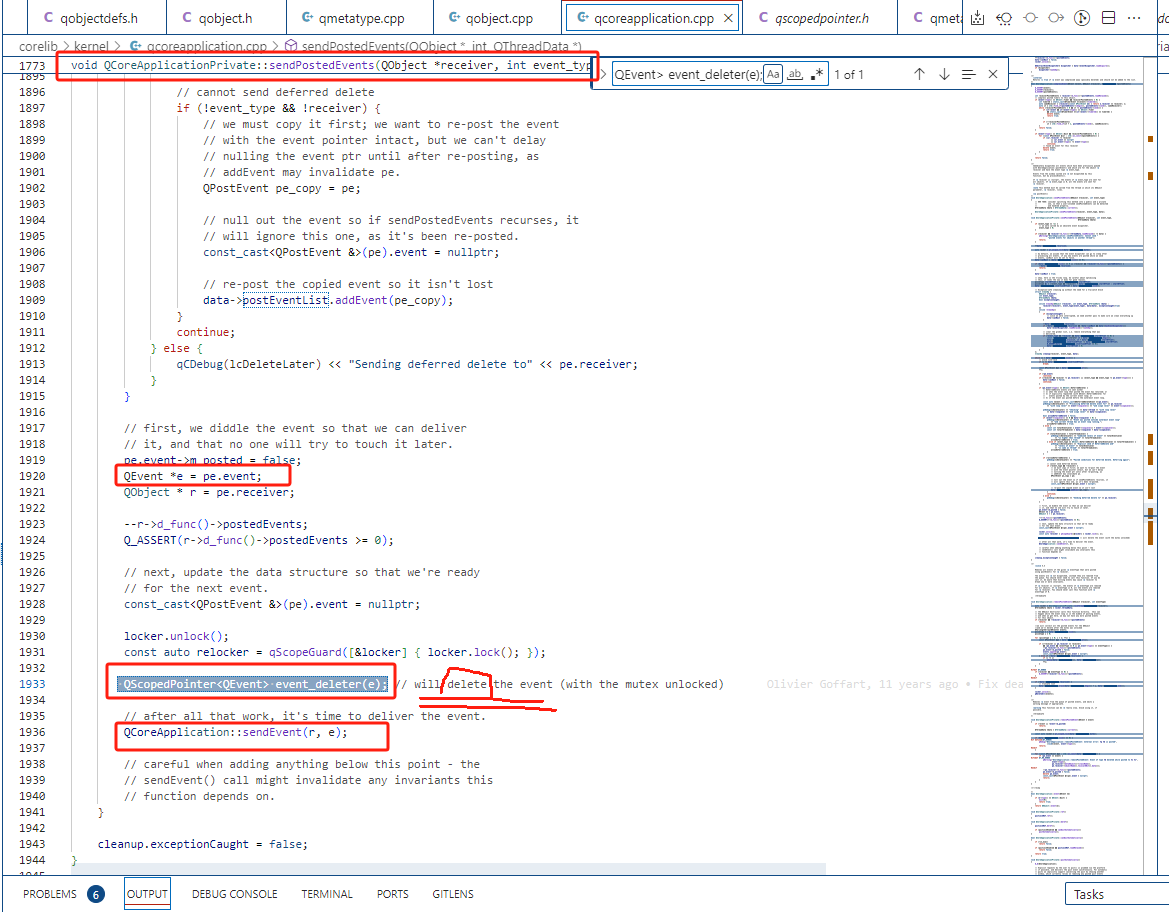
QScopedPointer<QEvent> event_deleter(e); // will delete the event (with the mutex unlocked)
/*!
template <typename T>
struct QScopedPointerDeleter
{
static inline void cleanup(T *pointer) noexcept
{
// Enforce a complete type.
// If you get a compile error here, read the section on forward declared
// classes in the QScopedPointer documentation.
typedef char IsIncompleteType[ sizeof(T) ? 1 : -1 ];
(void) sizeof(IsIncompleteType);
delete pointer;
}
void operator()(T *pointer) const noexcept
{
cleanup(pointer);
}
};
template <typename T, typename Cleanup = QScopedPointerDeleter<T> >
class QScopedPointer
{
public:
Q_NODISCARD_CTOR
explicit QScopedPointer(T *p = nullptr) noexcept : d(p)
{
}
inline ~QScopedPointer()
{
T *oldD = this->d;
Cleanup::cleanup(oldD);
}
......
};
\internal
*/
QMetaCallEvent::~QMetaCallEvent()
{
if (d.nargs_) {
QMetaType *t = types();
for (int i = 0; i < d.nargs_; ++i) {
if (t[i].isValid() && d.args_[i])
t[i].destroy(d.args_[i]);
}
if (reinterpret_cast<void *>(d.args_) != reinterpret_cast<void *>(prealloc_))
free(d.args_);
}
}
/*!
\fn void QMetaType::destroy(void *data) const
\since 5.0
Destroys the \a data, assuming it is of the type that this
QMetaType instance was created for.
\sa QMetaType::create()
*/
void QMetaType::destroy(void *data) const
{
if (data && isDestructible()) {
QtMetaTypePrivate::destruct(d_ptr, data);
QMetaTypeDeleter{d_ptr}(data);
}
}
inline void destruct(const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *iface, void *where)
{
Q_ASSERT(isDestructible(iface));
if (iface->dtor)
iface->dtor(iface, where);
}
struct QMetaTypeDeleter
{
const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *iface;
void operator()(void *data)
{
if (iface->alignment > __STDCPP_DEFAULT_NEW_ALIGNMENT__) {
operator delete(data, std::align_val_t(iface->alignment));
} else {
operator delete(data);
}
}
};



- 根據型別ID 查詢返回對應的QMetaTypeInterface資訊
static const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *interfaceForType(int typeId)
{
const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *iface = interfaceForTypeNoWarning(typeId);
if (!iface && typeId != QMetaType::UnknownType)
qWarning("Trying to construct an instance of an invalid type, type id: %i", typeId);
return iface;
}
static const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *interfaceForTypeNoWarning(int typeId)
{
const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *iface = nullptr;
if (typeId >= QMetaType::User) { //如果typeId >= 65536 屬於自定義資料型別,因此需要從登錄檔裡面查詢
if (customTypeRegistry.exists())
iface = customTypeRegistry->getCustomType(typeId);
} else { //typeId < 65536 屬於QT 自建型別資訊,從對應的moduleHelper中查詢
if (auto moduleHelper = qModuleHelperForType(typeId))
iface = moduleHelper->interfaceForType(typeId);
}
return iface;
}
static const struct : QMetaTypeModuleHelper
{
template<typename T, typename LiteralWrapper =
std::conditional_t<std::is_same_v<T, QString>, QLatin1StringView, const char *>>
static inline bool convertToBool(const T &source)
{
T str = source.toLower();
return !(str.isEmpty() || str == LiteralWrapper("0") || str == LiteralWrapper("false"));
}
const QtPrivate::QMetaTypeInterface *interfaceForType(int type) const override {
switch (type) {
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_TYPE(QT_METATYPE_CONVERT_ID_TO_TYPE)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_PRIMITIVE_POINTER(QT_METATYPE_CONVERT_ID_TO_TYPE)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_CLASS(QT_METATYPE_CONVERT_ID_TO_TYPE)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_POINTER(QT_METATYPE_CONVERT_ID_TO_TYPE)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_CORE_TEMPLATE(QT_METATYPE_CONVERT_ID_TO_TYPE)
default:
return nullptr;
}
}
..........................
..........................
..........................
} metatypeHelper = {};
Q_CONSTINIT Q_CORE_EXPORT const QMetaTypeModuleHelper *qMetaTypeGuiHelper = nullptr;
Q_CONSTINIT Q_CORE_EXPORT const QMetaTypeModuleHelper *qMetaTypeWidgetsHelper = nullptr;
static const QMetaTypeModuleHelper *qModuleHelperForType(int type)
{
if (type <= QMetaType::LastCoreType)
return &metatypeHelper;
if (type >= QMetaType::FirstGuiType && type <= QMetaType::LastGuiType)
return qMetaTypeGuiHelper;
else if (type >= QMetaType::FirstWidgetsType && type <= QMetaType::LastWidgetsType)
return qMetaTypeWidgetsHelper;
return nullptr;
}
===========================================================
C++ trivial和non-trivial建構函式及POD型別
今天看書看到侯捷的《STL原始碼剖析》裡提到trivial和non-trivial及POD型別,查了些資料理解了一下。
trivial意思是無意義,這個trivial和non-trivial是對類的四種函式來說的:
建構函式(ctor)
複製建構函式(copy)
賦值函式(assignment)
解構函式(dtor)
如果至少滿足下面3條裡的一條:
顯式(explict)定義了這四種函式。
類裡有非靜態非POD的資料成員。
有基類。
那麼上面的四種函式是non-trivial函式,比如叫non-trivial ctor、non-trivial copy…,也就是說有意義的函式,裡面有一下必要的操作,
比如類成員的初始化,釋放記憶體等。
那個POD意思是Plain Old Data,也就是C++的內建型別或傳統的C結構體型別。POD型別必然有trivial ctor/dtor/copy/assignment四種函式。
//整個T是POD型別
class T
{
//沒有顯式定義ctor/dtor/copy/assignemt所以都是trivial
int a; //POD型別
};
//整個T1是非POD型別
class T1
{
T1() //顯式定義了建構函式,所以是non-trivial ctor
{}
//沒有顯式定義ctor/dtor/copy/assignemt所以都是trivial
int a;//POD型別
std::string b; //非POD型別
};
那這有什麼用處呢?
如果這個類都是trivial ctor/dtor/copy/assignment函式,我們對這個類進行構造、析構、複製和賦值時可以採用最有效率的方法,不呼叫無所事事正真的那些ctor/dtor等,而直接採用記憶體操作如malloc()、memcpy()等提高效能,這也是SGI STL內部乾的事情。
比如STL的copy演算法最基本的想法是這樣的:
// 非POD過載指標數值
template <class T> void copy(T* source, T* destination, int n, __false_type)
{
// 省略異常處理
for (; n > 0; n--,source++,destination++)
{
// 呼叫source的複製建構函式
constructor(source, *destination);
}
}
// POD過載指標數值
template <class T> void copy(T* source, T* destination, int n, __false_type)
{
// 省略異常處理
memmove(source, destination, n);
}
當然實際的copy比這個複雜多了,有非常多的特化等,這個只是其中一方面而已。