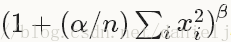如何在Caffe中配置每一個層的結構
【原文:http://demo.netfoucs.com/danieljianfeng/article/details/42929283】
最近剛在電腦上裝好Caffe,由於神經網路中有不同的層結構,不同型別的層又有不同的引數,所有就根據Caffe官網的說明文件做了一個簡單的總結。
1. Vision Layers
1.1 卷積層(Convolution)
型別:CONVOLUTION
例子
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "conv1" type: CONVOLUTION bottom: "data" top: "conv1" blobs_lr: 1 # learning rate multiplier for the filters blobs_lr: 2 # learning rate multiplier for the biases weight_decay: 1 # weight decay multiplier for the filters weight_decay: 0 # weight decay multiplier for the biases convolution_param { num_output: 96 # learn 96 filters kernel_size: 11 # each filter is 11x11 stride: 4 # step 4 pixels between each filter application weight_filler { type: "gaussian" # initialize the filters from a Gaussian std: 0.01 # distribution with stdev 0.01 (default mean: 0) } bias_filler { type: "constant" # initialize the biases to zero (0) value: 0 } }}</span>
blobs_lr: 學習率調整的引數,在上面的例子中設定權重學習率和執行中求解器給出的學習率一樣,同時是偏置學習率為權重的兩倍。
weight_decay:
卷積層的重要引數
必須引數:
num_output (c_o):過濾器的個數
kernel_size (or kernel_h and kernel_w):過濾器的大小
可選引數:
weight_filler [default type: 'constant' value: 0]:引數的初始化方法
bias_filler:偏置的初始化方法
bias_term [default true]:指定是否是否開啟偏置項
pad (or pad_h and pad_w) [default 0]:指定在輸入的每一邊加上多少個畫素
stride (or stride_h and stride_w) [default 1]:指定過濾器的步長
group (g) [default 1]: If g > 1, we restrict the connectivityof each filter to a subset of the input. Specifically, the input and outputchannels are separated into g groups, and the ith output group channels will beonly connected to the ith input group channels.
通過卷積後的大小變化:
輸入:n * c_i * h_i * w_i
輸出:n * c_o * h_o * w_o,其中h_o = (h_i + 2 * pad_h - kernel_h) /stride_h + 1,w_o通過同樣的方法計算。
1.2 池化層(Pooling)
型別:POOLING
例子
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "pool1" type: POOLING bottom: "conv1" top: "pool1" pooling_param { pool: MAX kernel_size: 3 # pool over a 3x3 region stride: 2 # step two pixels (in the bottom blob) between pooling regions }}</span>卷積層的重要引數
必需引數:
kernel_size (or kernel_h and kernel_w):過濾器的大小
可選引數:
pool [default MAX]:pooling的方法,目前有MAX, AVE, 和STOCHASTIC三種方法
pad (or pad_h and pad_w) [default 0]:指定在輸入的每一遍加上多少個畫素
stride (or stride_h and stride_w) [default1]:指定過濾器的步長
通過池化後的大小變化:
輸入:n * c_i * h_i * w_i
輸出:n * c_o * h_o * w_o,其中h_o = (h_i + 2 * pad_h - kernel_h) /stride_h + 1,w_o通過同樣的方法計算。
1.3 Local Response Normalization (LRN)
型別:LRN
Local ResponseNormalization是對一個區域性的輸入區域進行的歸一化(啟用a被加一個歸一化權重(分母部分)生成了新的啟用b),有兩種不同的形式,一種的輸入區域為相鄰的channels(cross channel LRN),另一種是為同一個channel內的空間區域(within channel LRN)
計算公式:對每一個輸入除以
可選引數:
local_size [default 5]:對於cross channel LRN為需要求和的鄰近channel的數量;對於within channel LRN為需要求和的空間區域的邊長
alpha [default 1]:scaling引數
beta [default 5]:指數
norm_region [default ACROSS_CHANNELS]: 選擇哪種LRN的方法ACROSS_CHANNELS 或者WITHIN_CHANNEL
2. Loss Layers
深度學習是通過最小化輸出和目標的Loss來驅動學習。
2.1 Softmax
型別: SOFTMAX_LOSS2.2 Sum-of-Squares / Euclidean
型別: EUCLIDEAN_LOSS
2.3 Hinge / Margin
型別: HINGE_LOSS例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"># L1 Normlayers { name: "loss" type: HINGE_LOSS bottom: "pred" bottom: "label"}# L2 Normlayers { name: "loss" type: HINGE_LOSS bottom: "pred" bottom: "label" top: "loss" hinge_loss_param { norm: L2 }}</span>
可選引數:
norm [default L1]: 選擇L1或者 L2範數
輸入:
n * c * h * wPredictions
n * 1 * 1 * 1Labels
輸出
1 * 1 * 1 * 1Computed Loss
2.4 Sigmoid Cross-Entropy
型別:SIGMOID_CROSS_ENTROPY_LOSS2.5 Infogain
型別:INFOGAIN_LOSS2.6 Accuracy and Top-k
型別:ACCURACY 用來計算輸出和目標的正確率,事實上這不是一個loss,而且沒有backward這一步。
3. 激勵層(Activation / Neuron Layers)
一般來說,激勵層是element-wise的操作,輸入和輸出的大小相同,一般情況下就是一個非線性函式。
3.1 ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU
型別: RELU例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "relu1" type: RELU bottom: "conv1" top: "conv1"}</span>
可選引數:
negative_slope [default 0]:指定輸入值小於零時的輸出。
ReLU是目前使用做多的激勵函式,主要因為其收斂更快,並且能保持同樣效果。
標準的ReLU函式為max(x, 0),而一般為當x > 0時輸出x,但x <= 0時輸出negative_slope。RELU層支援in-place計算,這意味著bottom的輸出和輸入相同以避免記憶體的消耗。
3.2 Sigmoid
型別: SIGMOID例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "encode1neuron" bottom: "encode1" top: "encode1neuron" type: SIGMOID}</span>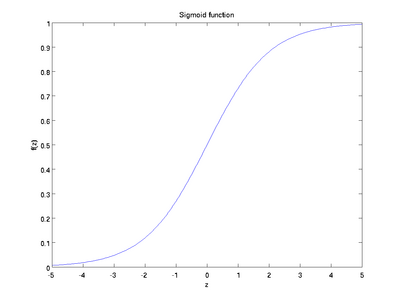
3.3 TanH / Hyperbolic Tangent
型別: TANH例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "encode1neuron" bottom: "encode1" top: "encode1neuron" type: SIGMOID}</span>
TANH層通過 tanh(x) 計算每一個輸入x的輸出,函式如下圖。
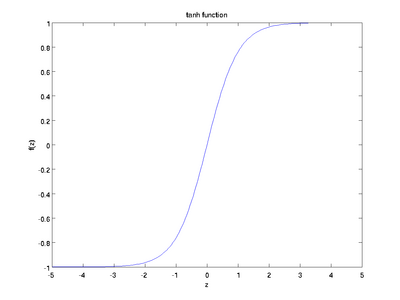
3.3 Absolute Value
型別: ABSVAL例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "layer" bottom: "in" top: "out" type: ABSVAL}</span>
3.4 Power
型別: POWER例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "layer" bottom: "in" top: "out" type: POWER power_param { power: 1 scale: 1 shift: 0 }}</span>POWER層通過 (shift + scale * x) ^ power計算每一個輸入x的輸出。
3.5 BNLL
型別: BNLL例子:
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "layer" bottom: "in" top: "out" type: BNLL}</span>BNLL (binomial normal log likelihood) 層通過 log(1 + exp(x)) 計算每一個輸入x的輸出。
4. 資料層(Data Layers)
資料通過資料層進入Caffe,資料層在整個網路的底部。資料可以來自高效的資料庫(LevelDB 或者 LMDB),直接來自記憶體。如果不追求高效性,可以以HDF5或者一般影象的格式從硬碟讀取資料。
4.1 Database
型別:DATA
必須引數:
source:包含資料的目錄名稱
batch_size:一次處理的輸入的數量
可選引數:
rand_skip:在開始的時候從輸入中跳過這個數值,這在非同步隨機梯度下降(SGD)的時候非常有用
backend [default LEVELDB]: 選擇使用 LEVELDB 或者 LMDB
4.2 In-Memory
型別: MEMORY_DATA必需引數:batch_size, channels, height, width: 指定從記憶體讀取資料的大小The memory data layer reads data directly from memory, without copying it. In order to use it, one must call MemoryDataLayer::Reset (from C++) or Net.set_input_arrays (from Python) in order to specify a source of contiguous data (as 4D row major array), which is read one batch-sized chunk at a time.
4.3 HDF5 Input
型別: HDF5_DATA必要引數:source:需要讀取的檔名batch_size:一次處理的輸入的數量
4.4 HDF5 Output
型別: HDF5_OUTPUT必要引數:file_name: 輸出的檔名HDF5的作用和這節中的其他的層不一樣,它是把輸入的blobs寫到硬碟
4.5 Images
型別: IMAGE_DATA必要引數:source: text檔案的名字,每一行給出一張圖片的檔名和labelbatch_size: 一個batch中圖片的數量可選引數:rand_skip:在開始的時候從輸入中跳過這個數值,這在非同步隨機梯度下降(SGD)的時候非常有用shuffle [default false]new_height, new_width: 把所有的影象resize到這個大小
4.6 Windows
型別:WINDOW_DATA4.7 Dummy
型別:DUMMY_DATADummy 層用於development 和debugging。具體引數DummyDataParameter。
5. 一般層(Common Layers)
5.1 全連線層Inner Product
型別:INNER_PRODUCT例子:<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "fc8" type: INNER_PRODUCT blobs_lr: 1 # learning rate multiplier for the filters blobs_lr: 2 # learning rate multiplier for the biases weight_decay: 1 # weight decay multiplier for the filters weight_decay: 0 # weight decay multiplier for the biases inner_product_param { num_output: 1000 weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 } bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 } } bottom: "fc7" top: "fc8"}</span>必要引數:
num_output (c_o):過濾器的個數
可選引數:
weight_filler [default type: 'constant' value: 0]:引數的初始化方法
bias_filler:偏置的初始化方法
bias_term [default true]:指定是否是否開啟偏置項
通過全連線層後的大小變化:
輸入:n * c_i * h_i * w_i
輸出:n * c_o * 1 *1
5.2 Splitting
型別:SPLITSplitting層可以把一個輸入blob分離成多個輸出blobs。這個用在當需要把一個blob輸入到多個輸出層的時候。5.3 Flattening
型別:FLATTENFlattening是把一個輸入的大小為n * c * h * w變成一個簡單的向量,其大小為 n * (c*h*w) * 1 * 1。5.4 Concatenation
型別:CONCAT例子:<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">layers { name: "concat" bottom: "in1" bottom: "in2" top: "out" type: CONCAT concat_param { concat_dim: 1 }}</span>
可選引數:
concat_dim [default 1]:0代表連結num,1代表連結channels
通過全連線層後的大小變化:
輸入:從1到K的每一個blob的大小n_i * c_i * h * w
輸出:
如果concat_dim = 0: (n_1 + n_2 + ... + n_K) *c_1 * h * w,需要保證所有輸入的c_i 相同。
如果concat_dim = 1: n_1 * (c_1 + c_2 + ... +c_K) * h * w,需要保證所有輸入的n_i 相同。
通過Concatenation層,可以把多個的blobs連結成一個blob。
5.5 Slicing
The SLICE layer is a utility layer that slices an input layer to multiple output layers along a given dimension (currently num or channel only) with given slice indices.5.6 Elementwise Operations
型別:ELTWISE5.7 Argmax
型別:ARGMAX5.8 Softmax
型別:SOFTMAX5.9 Mean-Variance Normalization
型別:MVN
6. 參考
Caffe相關文章
- Caffe程式碼結構
- caffe的基本資料結構資料結構
- caffe學習(1)caffe模型三種結構模型
- 總結!計網分層 每層任務 每層協議協議
- 如何在構圖中建立層次結構流程才有節奏和平衡感
- caffe 網路結構幾個部分簡單介紹
- caffe study - 資料結構(1)資料結構
- (2)caffe總結之目錄結構
- pytorch模型結構視覺化,可顯示每層的尺寸PyTorch模型視覺化
- 計算機網路的七層結構、五層結構和四層結構計算機網路
- (4)caffe總結之視覺層及引數視覺
- (6)caffe總結之其它常用層及引數
- ubuntu 16.04中CAFFE配置步驟Ubuntu
- (8)caffe總結之solver及其配置
- 【Caffe篇】--Caffe solver層從初始到應用
- caffe層解讀系列——BatchNormBATORM
- caffe study- AlexNet 之結構篇
- 【演算法】輸入一顆二元樹,從上往下按層列印樹的每個結點,同一層中按照從左往右的順序列印演算法
- js 獲取 table 中的每一個tdJS
- ECshop 每個資料庫表結構說明資料庫
- 用一個專案把控制層、業務層、持久層說明白了,每一句話都講的很清楚
- 每個月的sql引數配置SQL
- caffe整體框架的學習的部落格,這個部落格山寨了一個caffe框架框架
- 聊聊經典資料結構HashMap,逐行分析每一個關鍵點資料結構HashMap
- caffe中各種cblas的函式使用總結函式
- C#中類和結構的一個區別...C#
- 【Caffe篇】--Caffe從入門到初始及各層介紹
- 給每一個結點新增向右的next指標結點指標
- 一個統一的連結串列結構 (轉)
- Django工程的分層結構Django
- dump index 的層次結構Index
- golang map的底層結構Golang
- 每週一資料結構之連結串列(Kotlin描述)資料結構Kotlin
- javascript如何遍歷陣列中的每一個元素JavaScript陣列
- 談一談資料域層次結構
- Caffe中的優化方法優化
- 儲存器的層次結構
- 如何在Java中返回樹形結構 最佳實踐Java