棧在表示式求值中的應用
一. 棧ADT
首先我們使用java來實現棧ADT,這裡不使用java提供的Stack類, 而是使用ArrayList來實現,具體看程式碼:
public class MyStack {
public ArrayList<String> stack = new ArrayList<String>();
public String pop()
{
int index = stack.size()-1;
String str = stack.get(index);
stack.remove(index);
return str;
}
public String peek()
{
int index = stack.size()-1;
return stack.get(index);
}
public void push(String value)
{
stack.add(value);
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public int length()
{
return stack.size();
}
}二. 逆波蘭式
表示式求值首先需要用將表示式轉換成字尾表示式(由中綴表示式轉成字尾表達(逆波蘭式))。字尾表達在計算時就不需要考慮符號的優先順序。
1、利用棧來實現
/**
*
* @param expr
* @return
* 從左到右遍歷中綴表示式的每個數字和符號,若是數字就輸出,即成為字尾表示式的一部分;
* 若是符號,則判斷其與棧頂符號的優先順序,是右括號或優先順序低於找頂符號(乘除優先加減)則棧頂元素依次出找並輸出,並將當前符號進棧,
* 若優先順序高於棧頂符合,將當前符號進棧,一直到最終輸出字尾表示式為止。
*/
public static String convert_suffix_expr(String expr) {
String result = "", top = "";
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9].*");
String[] str = expr.split(" ");
for (String string : str) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(string);
boolean b = matcher.matches();
if (b) { //如果是數字
result += string + " ";
} else {
if (al.size() > 0) {
top = al.get(al.size() - 1);
}
if (string.equals(")")) {
do {
if (!(al.get(al.size() - 1).equals("("))) {
result += al.get(al.size() - 1) + " ";
al.remove(al.size() - 1);
}
} while (al.size() > 0
&& !al.get(al.size() - 1).equals("("));
al.remove(al.size() - 1);
} else if (string.equals("(") || string.equals("*")
|| string.equals("/")) {
al.add(string);
} else {
if (top.equals("*") || top.equals("/")) {
do {
result += al.get(al.size() - 1) + " ";
al.remove(al.size() - 1);
} while (al.size() > 0);
al.add(string);
} else { //處理+,-
al.add(string);
}
}
}
}
while (al.size() > 0) {
result += al.get(al.size() - 1) + " ";
al.remove(al.size() - 1);
}
return result;
}2、利用語法樹來實現
先把中綴表示式用二叉樹表示出來,再後序遍歷該二叉樹就得到相應的字尾表示式了。
a.中綴表示式用二叉樹表示
一般情況下並不能由一箇中綴表示式得到一個唯一的二叉樹,但是若由二叉樹來表示表示式,葉子節點必須是運算元,非葉子節點是操作符,所以能夠確定一個二叉樹:轉化過程如下:
按照優先順序加上括號,得到:( 8 - ( (3 + 5) * ( 5 - (6 / 2) ) ) )
然後從最外層括號開始,依次轉化成二叉樹
1) 根是- ,左子樹8,右子樹( (3 + 5) * ( 5 - (6 / 2) ) )
2) 右子樹的根*,右子樹的左子樹(3 + 5),右子樹的右子樹( 5 - (6 / 2) )
3) (3 + 5)的根+,左子樹3 ,右子樹5
4) ( 5 - (6 / 2) )的根-,左子樹5,右子樹(6 / 2)
5) (6 / 2)的根/,左子樹6,右子樹2
b. 樹的遍歷
下面是對圖中樹的遍歷
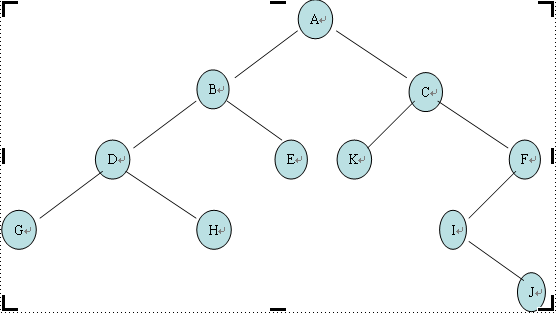
這裡的順序針對的是非葉子節點
先序遍歷:A B D G H E C K F I J
中序遍歷:G D H B E A K C I J F
後序遍歷:G H D E B K J I F C A
3、加括號法(在草稿上手工轉換)
三. 表示式求值
最後我們通過棧來求取表示式的值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = convert_suffix_expr("8 - ( ( 3 + 5 ) * ( 5 - ( 6 / 2 ) ) ) ");
// System.out.println(expression);
String[] str = expression.split(" ");
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++)
{
if (i<2)
{
myStack.push(str[i]);
}else
{
if ("+".equals(str[i]))
{
String value1 = myStack.pop();
String value2 = myStack.pop();
int result = Integer.parseInt(value1)+Integer.parseInt(value2);
myStack.push(String.valueOf(result));
}else if ("-".equals(str[i]) )
{
String value1 = myStack.pop();
String value2 = myStack.pop();
int result = Integer.parseInt(value2)-Integer.parseInt(value1);
myStack.push(String.valueOf(result));
}else if ("*".equals(str[i]) )
{
String value1 = myStack.pop();
String value2 = myStack.pop();
int result = Integer.parseInt(value1)*Integer.parseInt(value2);
myStack.push(String.valueOf(result));
}else if ("/".equals(str[i]) )
{
String value1 = myStack.pop();
String value2 = myStack.pop();
int result = Integer.parseInt(value2)/Integer.parseInt(value1);
myStack.push(String.valueOf(result));
}
else
{
myStack.push(str[i]);
}
}
}
if (!myStack.isEmpty())
{
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
}
}- 將中綴表示式轉化為字尾表示式(棧用來進出運算的符號)。
- 將字尾表示式進行運算得出結果(棧用來進出運算的數字)。
相關文章
- 【資料結構】棧的應用——中綴表示式求值(c++)資料結構C++
- 使用棧實現表示式求值,運用棧計算
- 【資料結構】棧的應用---四則運算表示式求值(中綴表示式與字尾表示式轉換)資料結構
- 資料結構學習(C++)——棧應用(表示式求值) (轉)資料結構C++
- 逆波蘭表示式求值——棧與佇列佇列
- 棧的應用——表示式求和
- 棧的應用---字尾表示式
- 表示式計算(棧的應用)
- 3.2.5 表示式求值
- 4、逆波蘭表示式求值——棧(java資料結構)Java資料結構
- 利用 Lambda 表示式實現 Java 中的惰性求值Java
- 利用Lambda表示式進行Java中的惰性求值Java
- 正規表示式在iOS開發中的應用iOS
- Java表示式求值引擎 - AviatorJava
- Java中Lambda表示式的應用Java
- 表示式計算 用棧完成
- 正規表示式在PHP裡的應用PHP
- 字尾表示式的求值的演算法演算法
- CF552E 字串 表示式求值字串
- 正規表示式在iOS中的運用iOS
- JDK1.8中Lambda表示式的應用JDK
- 資訊學奧賽複賽複習09-CSP-J2020-03表示式求值前置知識點-中綴表示式求值、摸運算、模運算性質、棧
- Lambda 表示式的應用
- 演算法手記(2)Dijkstra雙棧算術表示式求值演算法演算法
- 逆波蘭表示式求值 golang VS pythonGolangPython
- 一種簡易的表示式求值演算法演算法
- 正規表示式的應用
- 力扣-150. 逆波蘭表示式求值力扣
- mapboxgl 中插值表示式的應用場景
- Python中lambda表示式的語法與應用Python
- 使用棧結構計算中綴表示式
- rem在響應式佈局中的應用REM
- LeetCode-150- 逆波蘭表示式求值LeetCode
- Leetcode——150. 逆波蘭表示式求值LeetCode
- Render函式在Vue多頁面應用中的應用函式Vue
- 棧(2)--棧的應用
- 正規表示式在Java中的使用Java
- 算數表示式求值--c語言課程設計C語言
