C++弱引用智慧指標weak_ptr的用處
weak_ptr也是一個引用計數型智慧指標,但是它不增加物件的引用計數,即弱引用。與之相對,shared_ptr是強引用,只要有一個指向物件的shared_ptr存在,該物件就不會析構,直到指向物件的最後一個shared_ptr析構或reset()時才會被銷燬。
利用weak_ptr,我們可以解決常見的空懸指標問題以及迴圈引用問題。
空懸指標問題
什麼是空懸指標?考慮以下這種情況:
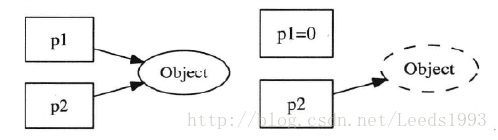
有兩個指標p1和p2,指向堆上的同一個物件Object,p1和p2位於不同的執行緒中。假設執行緒A通過p1指標將物件銷燬了(儘管把p1置為了NULL),那p2就成了空懸指標。這是一種典型的C/C++記憶體錯誤。
使用weak_ptr能夠幫我們輕鬆解決上述的空懸指標問題。
weak_ptr不控制物件的生命期,但是它知道物件是否還活著。如果物件還活著,那麼它可以提升為有效的shared_ptr(提升操作通過lock()函式獲取所管理物件的強引用指標);如果物件已經死了,提升會失敗,返回一個空的shared_ptr。示例程式碼如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
int main()
{
// OLD, problem with dangling pointer
// PROBLEM: ref will point to undefined data!
int* ptr = new int(10);
int* ref = ptr;
delete ptr;
// NEW
// SOLUTION: check expired() or lock() to determine if pointer is valid
// empty definition
std::shared_ptr<int> sptr;
// takes ownership of pointer
sptr.reset(new int);
*sptr = 10;
// get pointer to data without taking ownership
std::weak_ptr<int> weak1 = sptr;
// deletes managed object, acquires new pointer
sptr.reset(new int);
*sptr = 5;
// get pointer to new data without taking ownership
std::weak_ptr<int> weak2 = sptr;
// weak1 is expired!
if(auto tmp = weak1.lock())
std::cout << *tmp << '\n';
else
std::cout << "weak1 is expired\n";
// weak2 points to new data (5)
if(auto tmp = weak2.lock())
std::cout << *tmp << '\n';
else
std::cout << "weak2 is expired\n";
}迴圈引用問題
一種迴圈引用的情況如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Parent;
class Child;
typedef shared_ptr<Parent> parent_ptr;
typedef shared_ptr<Child> child_ptr;
class Parent
{
public:
~Parent() {
cout << "~Parent()" << endl;
}
public:
child_ptr children;
};
class Child
{
public:
~Child() {
cout << "~Child()" << endl;
}
public:
parent_ptr parent;
};
int main()
{
parent_ptr father(new Parent);
child_ptr son(new Child);
// 父子互相引用
father->children = son;
son->parent = father;
cout << father.use_count() << endl; // 引用計數為2
cout << son.use_count() << endl; // 引用計數為2
return 0;
}如上程式碼,將在程式退出前,father的引用計數為2,son的計數也為2,退出時,shared_ptr所作操作就是簡單的將計數減1,如果為0則釋放,顯然,這個情況下,引用計數不為0,於是造成father和son所指向的記憶體得不到釋放,導致記憶體洩露。
使用weak_ptr可以打破這樣的迴圈引用。由於弱引用不更改引用計數,類似普通指標,只要把迴圈引用的一方使用弱引用,即可解除迴圈引用。
以上述程式碼為例,只要把Child類的程式碼修改為如下即可:
class Child
{
public:
~Child() {
cout << "~Child()" << endl;
}
public:
weak_ptr<Parent> parent;
};最後值得一提的是,雖然通過弱引用指標可以有效的解除迴圈引用,但這種方式必須在能預見會出現迴圈引用的情況下才能使用,即這個僅僅是一種編譯期的解決方案,如果程式在執行過程中出現了迴圈引用,還是會造成記憶體洩漏的。因此,不要認為只要使用了智慧指標便能杜絕記憶體洩漏。
參考資料:
When is std::weak_ptr useful?
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/12030650/when-is-stdweak-ptr-useful
相關文章
- c++動態記憶體智慧指標及weak_ptr用法的理解C++記憶體指標
- C、C++用指標引用的差異C++指標
- java的引用:用C++/C的引用和指標去理解JavaC++指標
- C++引用和指標C++指標
- C++中的指標與引用C++指標
- [C++]指標和引用(一)C++指標
- [C++]指標和引用(二)C++指標
- [C++]指標和引用(三)C++指標
- [C++]指標和引用(四)C++指標
- C++智慧指標學習——小談引用計數C++指標
- C++指標與引用的區別C++指標
- c++ 類的函式引用 指標C++函式指標
- 詳解c++指標的指標和指標的引用C++指標
- 【c++】智慧指標C++指標
- C++智慧指標C++指標
- C++引用比指標的好處C++指標
- C++ 用智慧指標這樣包裝 this 指標是否可行C++指標
- ARC中強指標與弱指標指標
- 「C++」理解智慧指標C++指標
- c++指標傳遞與引用傳遞C++指標
- C++14 智慧指標unique_ptr、shared_ptr、weak_ptrC++指標
- C++中const與指標、引用的總結C++指標
- C++中的指標與引用詳細解讀C++指標
- C++智慧指標之shared_ptr與右值引用(詳細)C++指標
- C++進階(智慧指標)C++指標
- C++ 智慧指標詳解C++指標
- 指標與引用指標
- nim的引用和指標指標
- 智慧指標引用計數變化學習指標
- C++筆記(11) 智慧指標C++筆記指標
- c++ 智慧指標用法詳解C++指標
- C++智慧指標簡單剖析C++指標
- c++ auto_ptr 智慧指標C++指標
- 【C++智慧指標 auto_ptr】C++指標
- 1.0 - 指標和引用指標
- C++ 引用和指標:記憶體地址、建立方法及應用解析C++指標記憶體
- 引用的底層為指標指標
- 指標和引用的區別指標