muduo網路庫學習筆記(10):定時器的實現
傳統的Reactor通過控制select和poll的等待時間來實現定時,而現在在Linux中有了timerfd,我們可以用和處理IO事件相同的方式來處理定時,程式碼的一致性更好。
為什麼選擇timerfd
常見的定時函式有如下幾種:
sleep
alarm
usleep
nanosleep
clock_nanosleep
getitimer / setitimer
timer_create / timer_settime / timer_gettime / timer_delete
timerfd_create / timerfd_gettime / timerfd_settime
我們之所以選擇timerfd,是因為:
1.sleep / alarm / usleep 在實現時有可能用了訊號 SIGALRM,在多執行緒程式中處理訊號是個相當麻煩的事情,應當儘量避免。
2.nanosleep 和 clock_nanosleep 是執行緒安全的,但是在非阻塞網路程式設計中,絕對不能用讓執行緒掛起的方式來等待一段時間,程式會失去響應。正確的做法是註冊一個時間回撥函式。
3.getitimer 和 timer_create 也是用訊號來傳遞超時,在多執行緒程式中也會有麻煩。
4.timer_create 可以指定訊號的接收方是程式還是執行緒,算是一個進步,不過在訊號處理函式(signal handler)能做的事情實在很受限。
5.timerfd_create 把時間變成了一個檔案描述符,該“檔案”在定時器超時的那一刻變得可讀,這樣就能很方便地融入到 select/poll 框架中,用統一的方式來處理 IO 事件和超時事件,這也正是 Reactor 模式的長處。
timerfd相關函式介紹:
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
/**
* 此函式用於建立一個定時器檔案
* 引數clockid可以是CLOCK_MONOTONIC或者CLOCK_REALTIME
* 引數flags可以是0或者TFD_CLOEXEC/TFD_NONBLOCK
* 函式返回值是一個檔案控制程式碼fd
*/
int timerfd_create(int clockid, int flags);
/**
* 此函式用於設定新的超時時間,並開始計時
* 引數fd是timerfd_create返回的檔案控制程式碼
* 引數flags為TFD_TIMER_ABSTIME(1)代表設定的是絕對時間;為0代表相對時間
* 引數new_value為需要設定的超時和間隔時間
* 引數old_value為定時器這次設定之前的超時時間
* 函式返回0代表設定成功
*/
int timerfd_settime(int fd, int flags, const struct itimerspec *new_value, struct itimerspec *old_value);
/**
* 此函式用於獲得定時器距離下次超時還剩下的時間
* 如果呼叫時定時器已經到期,並且該定時器處於迴圈模式
* 即設定超時時間時struct itimerspec::it_interval不為0
* 那麼呼叫此函式之後定時器重新開始計時
*/
int timerfd_gettime(int fd, struct itimerspec *curr_value);
itimerspec結構體;
struct itimerspec {
struct timespec it_interval; // interval for periodic timer
struct timespec it_value; // initial expiration
};
struct timespec {
time_t tv_sec; // seconds
long tv_nsec; // nano-seconds
};muduo定時器的實現
muduo的定時器功能由三個class實現,TimerId、Timer、TimerQueue,使用者只能看到第一個class,另外兩個都是內部實現細節。
TimerId被設計用來取消Timer的,它的結構很簡單,只有一個Timer指標和其序列號。其中還宣告瞭TimerQueue為其友元,可以操作其私有資料。
Timer是對定時器的高層次抽象,封裝了定時器的一些引數,例如超時回撥函式、超時時間、超時時間間隔、定時器是否重複、定時器的序列號。其函式大都是設定這些引數,run()用來呼叫回撥函式,restart()用來重啟定時器(如果設定為重複)。
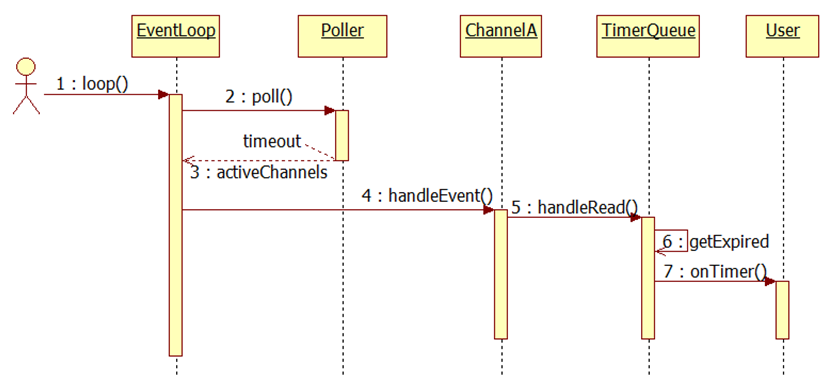
重點介紹一下TimerQueue類。
TimerQueue class
TimerQueue的介面很簡單,只有兩個函式addTimer()和cancel()。它的內部有channel,和timerfd相關聯。新增新的Timer後,在超時後,timerfd可讀,會處理channel事件,之後呼叫Timer的回撥函式;在timerfd的事件處理後,還會檢查一遍超時定時器,如果其屬性為重複還會再次新增到定時器集合中。
時序圖:
(1)TimerQueue資料結構的選擇
TimerQueue需要高效地組織目前尚未到期的Timer,能快速地根據當前時間找到已經到期的Timer,也要能高效地新增和刪除Timer。因而可以用二叉搜尋樹(例如std::set/std::map),把Timer按到期時間先後排好序,其操作的複雜度是O(logN),但我們使用時還要處理兩個Timer到期時間相同的情況(map不支援key相同的情況),做法如下:
// 兩種型別的set,一種按時間戳排序,一種按Timer的地址排序
// 實際上,這兩個set儲存的是相同的定時器列表
typedef std::pair<Timestamp, Timer*> Entry;
typedef std::set<Entry> TimerList;
typedef std::pair<Timer*, int64_t> ActiveTimer;
typedef std::set<ActiveTimer> ActiveTimerSet;(2)程式碼分析
檔名:TimerQueue.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H
#define MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <muduo/base/Mutex.h>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
#include <muduo/net/Callbacks.h>
#include <muduo/net/Channel.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class EventLoop;
class Timer;
class TimerId;
class TimerQueue : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
TimerQueue(EventLoop* loop);
~TimerQueue();
// 一定是執行緒安全的,可以跨執行緒呼叫。通常情況下被其它執行緒呼叫。
TimerId addTimer(const TimerCallback& cb,
Timestamp when,
double interval);
void cancel(TimerId timerId);
private:
// FIXME: use unique_ptr<Timer> instead of raw pointers.
// unique_ptr是C++ 11標準的一個獨享所有權的智慧指標
// 無法得到指向同一物件的兩個unique_ptr指標
// 但可以進行移動構造與移動賦值操作,即所有權可以移動到另一個物件(而非拷貝構造)
typedef std::pair<Timestamp, Timer*> Entry;
typedef std::set<Entry> TimerList;
typedef std::pair<Timer*, int64_t> ActiveTimer;
typedef std::set<ActiveTimer> ActiveTimerSet;
// 以下成員函式只可能在其所屬的I/O執行緒中呼叫,因而不必加鎖。
// 伺服器效能殺手之一是鎖競爭,所以要儘可能少用鎖
void addTimerInLoop(Timer* timer);
void cancelInLoop(TimerId timerId);
// called when timerfd alarms
void handleRead();
// 返回超時的定時器列表
std::vector<Entry> getExpired(Timestamp now);
void reset(const std::vector<Entry>& expired, Timestamp now);
bool insert(Timer* timer);
EventLoop* loop_; // 所屬的EventLoop
const int timerfd_;
Channel timerfdChannel_;
TimerList timers_; // timers_是按到期時間排序
// for cancel()
// timers_與activeTimers_儲存的是相同的資料
// timers_是按到期時間排序,activeTimers_是按物件地址排序
ActiveTimerSet activeTimers_;
bool callingExpiredTimers_; // 是否正在處理超時事件
ActiveTimerSet cancelingTimers_; // 儲存的是被取消的定時器
};
}
}
#endif //MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H檔名:TimerQueue.cc
#define __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS
#include <muduo/net/TimerQueue.h>
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/Timer.h>
#include <muduo/net/TimerId.h>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
namespace detail
{
// 建立定時器,用到了timerfd_create()
int createTimerfd()
{
int timerfd = ::timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC,
TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
if (timerfd < 0)
{
LOG_SYSFATAL << "Failed in timerfd_create";
}
return timerfd;
}
// 計算超時時刻與當前時間的時間差
struct timespec howMuchTimeFromNow(Timestamp when)
{
int64_t microseconds = when.microSecondsSinceEpoch()
- Timestamp::now().microSecondsSinceEpoch();
// 精確度沒有設定那麼高,所以小於100ms時都置為100
if (microseconds < 100)
{
microseconds = 100;
}
struct timespec ts;
ts.tv_sec = static_cast<time_t>(
microseconds / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
ts.tv_nsec = static_cast<long>(
(microseconds % Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond) * 1000);
return ts;
}
// 處理超時事件。超時後,timerfd變為可讀
void readTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp now)
{
uint64_t howmany; // howmany為超時次數
ssize_t n = ::read(timerfd, &howmany, sizeof howmany);
LOG_TRACE << "TimerQueue::handleRead() " << howmany << " at " << now.toString();
if (n != sizeof howmany)
{
LOG_ERROR << "TimerQueue::handleRead() reads " << n << " bytes instead of 8";
}
}
// 重置定時器的超時時間,用到了timerfd_settime()
void resetTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp expiration)
{
// wake up loop by timerfd_settime()
struct itimerspec newValue;
struct itimerspec oldValue;
bzero(&newValue, sizeof newValue);
bzero(&oldValue, sizeof oldValue);
newValue.it_value = howMuchTimeFromNow(expiration);
int ret = ::timerfd_settime(timerfd, 0, &newValue, &oldValue);
if (ret)
{
LOG_SYSERR << "timerfd_settime()";
}
}
}
}
}
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
using namespace muduo::net::detail;
// 建構函式
TimerQueue::TimerQueue(EventLoop* loop)
: loop_(loop),
timerfd_(createTimerfd()), // 建立timerfd
timerfdChannel_(loop, timerfd_), // timerfd關聯的channel
timers_(),
callingExpiredTimers_(false)
{
timerfdChannel_.setReadCallback(
boost::bind(&TimerQueue::handleRead, this));
// we are always reading the timerfd, we disarm it with timerfd_settime.
timerfdChannel_.enableReading(); // timerfd對應的channel監聽事件為可讀事件
}
// 解構函式
TimerQueue::~TimerQueue()
{
::close(timerfd_);
// do not remove channel, since we're in EventLoop::dtor();
for (TimerList::iterator it = timers_.begin();
it != timers_.end(); ++it)
{
delete it->second; // 手動釋放Timer*
}
}
// 新增新的定時器
TimerId TimerQueue::addTimer(const TimerCallback& cb,
Timestamp when,
double interval)
{
Timer* timer = new Timer(cb, when, interval);
addTimerInLoop(timer);
return TimerId(timer, timer->sequence());
}
// 取消定時器
void TimerQueue::cancel(TimerId timerId)
{
cancelInLoop(timerId);
}
// 新增定時器時實際呼叫了addTimerInLoop()
void TimerQueue::addTimerInLoop(Timer* timer)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
// 插入一個定時器,有可能會使得最早到期的定時器發生改變
bool earliestChanged = insert(timer);
if (earliestChanged)
{
// 重置定時器的超時時刻(timerfd_settime)
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, timer->expiration());
}
}
// 取消定時器時實際呼叫了cancelInLoop()
void TimerQueue::cancelInLoop(TimerId timerId)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
ActiveTimer timer(timerId.timer_, timerId.sequence_); // 要取消的定時器timer
// 查詢該定時器
ActiveTimerSet::iterator it = activeTimers_.find(timer);
// 要取消的在當前啟用的Timer集合中
if (it != activeTimers_.end())
{
size_t n = timers_.erase(Entry(it->first->expiration(), it->first)); // 從timers_中移除
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
delete it->first; // FIXME:如果用了unique_ptr,這裡就不需要手動刪除了
activeTimers_.erase(it); // 從activeTimers_中移除
}
// 如果正在執行超時定時器的回撥函式,則加入到cancelingTimers集合中
else if (callingExpiredTimers_)
{
cancelingTimers_.insert(timer);
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
}
void TimerQueue::handleRead()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
readTimerfd(timerfd_, now); // 讀timerfd
// 獲取該時刻之前所有的定時器列表(即超時定時器列表)
std::vector<Entry> expired = getExpired(now);
callingExpiredTimers_ = true;
cancelingTimers_.clear();
for (std::vector<Entry>::iterator it = expired.begin();
it != expired.end(); ++it)
{
// 這裡回撥定時器處理函式
it->second->run();
}
callingExpiredTimers_ = false;
// 把重複的定時器重新加入到定時器中
reset(expired, now);
}
// rvo即Return Value Optimization
// 是一種編譯器優化技術,可以把通過函式返回建立的臨時物件給”去掉”
// 然後達到少呼叫拷貝構造的操作,從而提高效能
std::vector<TimerQueue::Entry> TimerQueue::getExpired(Timestamp now)
{
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
std::vector<Entry> expired;
// UINTPTR_MAX表示最大的地址
Entry sentry(now, reinterpret_cast<Timer*>(UINTPTR_MAX));
// 返回第一個未到期的Timer的迭代器
// lower_bound的含義是返回第一個值>=sentry的元素的iterator
// 即*end >= sentry,從而end->first > now
// 注意:此處是>,而不是>=
TimerList::iterator end = timers_.lower_bound(sentry);
assert(end == timers_.end() || now < end->first);
// 將[begin end)區間的元素(到期的)追加到expired末尾
std::copy(timers_.begin(), end, back_inserter(expired));
// 從timers_中移除到期的定時器
timers_.erase(timers_.begin(), end);
// 從activeTimers_中移除到期的定時器
for (std::vector<Entry>::iterator it = expired.begin();
it != expired.end(); ++it)
{
ActiveTimer timer(it->second, it->second->sequence());
size_t n = activeTimers_.erase(timer);
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
return expired;
}
void TimerQueue::reset(const std::vector<Entry>& expired, Timestamp now)
{
Timestamp nextExpire;
for (std::vector<Entry>::const_iterator it = expired.begin();
it != expired.end(); ++it)
{
ActiveTimer timer(it->second, it->second->sequence());
// 如果是重複的定時器並且不在cancelingTimers_集合中,則重啟該定時器
if (it->second->repeat()
&& cancelingTimers_.find(timer) == cancelingTimers_.end())
{
it->second->restart(now);
insert(it->second);
}
else
{
// 一次性定時器或者已被取消的定時器是不能重置的,因此刪除該定時器
// FIXME move to a free list
delete it->second; //FIXME: no delete please
}
}
if (!timers_.empty())
{
// 獲取最早到期的定時器超時時間
nextExpire = timers_.begin()->second->expiration();
}
if (nextExpire.valid())
{
// 重置定時器的超時時刻(timerfd_settime)
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, nextExpire);
}
}
// 插入一個timer
bool TimerQueue::insert(Timer* timer)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
bool earliestChanged = false;
Timestamp when = timer->expiration();
TimerList::iterator it = timers_.begin();
// 如果timers_為空或者when小於timers_中的最早到期時間
if (it == timers_.end() || when < it->first)
{
earliestChanged = true;
}
{
// 插入到timers_中
std::pair<TimerList::iterator, bool> result
= timers_.insert(Entry(when, timer));
assert(result.second); (void)result;
}
{
// 插入到activeTimers_中
std::pair<ActiveTimerSet::iterator, bool> result
= activeTimers_.insert(ActiveTimer(timer, timer->sequence()));
assert(result.second); (void)result;
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
return earliestChanged;
}相關文章
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(5):執行緒池的實現筆記執行緒
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(1):Timestamp類筆記
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(2):原子性操作筆記
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(3):Thread類筆記thread
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(11):有用的runInLoop()函式筆記OOP函式
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(14):chargen服務示例筆記
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(13):TcpConnection生命期的管理筆記TCP
- muduo網路庫學習之EventLoop(一):事件迴圈類圖簡介和muduo 定時器TimeQueueOOP事件定時器
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(9):Reactor模式的關鍵結構筆記React模式
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(8):高效日誌類的封裝筆記封裝
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(12):TcpServer和TcpConnection類筆記TCPServer
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(7):執行緒特定資料筆記執行緒
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(6):單例類(執行緒安全的)筆記單例執行緒
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(4):互斥量和條件變數筆記變數
- muduo網路庫學習之muduo_http 庫涉及到的類HTTP
- muduo網路庫學習之muduo_inspect 庫涉及到的類
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(15):關於使用stdio和iostream的討論筆記iOS
- MySQL定時器EVENT學習筆記MySql定時器筆記
- muduo網路庫學習之EventLoop(七):TcpClient、ConnectorOOPTCPclient
- JMeter學習筆記--詳解JMeter定時器JMeter筆記定時器
- 【D3D11遊戲程式設計】學習筆記六:定時器的實現3D遊戲程式設計筆記定時器
- 【學習筆記】網路流筆記
- [網路]NIO學習筆記筆記
- 網路流學習筆記筆記
- muduo網路庫學習之EventLoop(四):EventLoopThread 類、EventLoopThreadPool 類OOPthread
- muduo網路庫Timestamp類
- muduo網路庫使用心得
- JS學習筆記之由定時器引發的深入思考JS筆記定時器
- [筆記]laravel定時任務的實現筆記Laravel
- muduo網路庫學習之EventLoop(六):TcpConnection::send()、shutdown()、handleRead()、handleWrite()OOPTCP
- muduo網路庫Exception異常類Exception
- muduo網路庫編譯安裝編譯
- muduo網路庫學習筆記(0):物件導向程式設計風格和基於物件程式設計風格的比較筆記物件程式設計
- swoft 學習筆記之資料庫配置與實體定筆記資料庫
- 學習筆記16:殘差網路筆記
- Mudo C++網路庫第五章學習筆記C++筆記
- Mudo C++網路庫第七章學習筆記C++筆記
- Mudo C++網路庫第十一章學習筆記C++筆記