一、ELK日誌分析工具介紹
1) Elasticsearch
1.1) Elasticsearch介紹
ElasticSearch是一個基於Lucene的搜尋伺服器。它提供了一個分散式多使用者能力的全文搜尋引擎,基於RESTful web介面。Elasticsearch是用Java開發的,並作為Apache許可條款下的開放原始碼釋出,是第二流行的企業搜尋引擎。設計用於雲端計算中,能夠達到實時搜尋,穩定,可靠,快速,安裝使用方便。
1.2) Elasticsearch幾個重要術語
- NRT
elasticsearch是一個近似實時的搜尋平臺,從索引文件到可搜尋有些延遲,通常為1秒。
- 叢集
叢集就是一個或多個節點儲存資料,其中一個節點為主節點,這個主節點是可以通過選舉產生的,並提供跨節點的聯合索引和搜尋的功能。叢集有一個唯一性標示的名字,預設是elasticsearch,叢集名字很重要,每個節點是基於叢集名字加入到其叢集中的。因此,確保在不同環境中使用不同的叢集名字。一個叢集可以只有一個節點。強烈建議在配置elasticsearch時,配置成叢集模式。
- 節點
節點就是一臺單一的伺服器,是叢集的一部分,儲存資料並參與叢集的索引和搜尋功能。像叢集一樣,節點也是通過名字來標識,預設是在節點啟動時隨機分配的字元名。當然啦,你可以自己定義。該名字也蠻重要的,在叢集中用於識別伺服器對應的節點。
節點可以通過指定叢集名字來加入到叢集中。預設情況下,每個節點被設定成加入到elasticsearch叢集。如果啟動了多個節點,假設能自動發現對方,他們將會自動組建一個名為elasticsearch的叢集。
- 索引
索引是有幾分相似屬性的一系列文件的集合。如nginx日誌索引、syslog索引等等。索引是由名字標識,名字必須全部小寫。這個名字用來進行索引、搜尋、更新和刪除文件的操作。
索引相對於關係型資料庫的庫。
- 型別
在一個索引中,可以定義一個或多個型別。型別是一個邏輯類別還是分割槽完全取決於你。通常情況下,一個型別被定於成具有一組共同欄位的文件。如ttlsa運維生成時間所有的資料存入在一個單一的名為logstash-ttlsa的索引中,同時,定義了使用者資料型別,帖子資料型別和評論型別。
型別相對於關係型資料庫的表。
- 文件
文件是資訊的基本單元,可以被索引的。文件是以JSON格式表現的。
在型別中,可以根據需求儲存多個文件。
雖然一個文件在物理上位於一個索引,實際上一個文件必須在一個索引內被索引和分配一個型別。
文件相對於關係型資料庫的列。
- 分片和副本
在實際情況下,索引儲存的資料可能超過單個節點的硬體限制。如一個十億文件需1TB空間可能不適合儲存在單個節點的磁碟上,或者從單個節點搜尋請求太慢了。為了解決這個問題,elasticsearch提供將索引分成多個分片的功能。當在建立索引時,可以定義想要分片的數量。每一個分片就是一個全功能的獨立的索引,可以位於叢集中任何節點上。
分片的兩個最主要原因:
a) 水平分割擴充套件,增大儲存量;
b) 分散式並行跨分片操作,提高效能和吞吐量;
分散式分片的機制和搜尋請求的文件如何彙總完全是有elasticsearch控制的,這些對使用者而言是透明的。
網路問題等等其它問題可以在任何時候不期而至,為了健壯性,強烈建議要有一個故障切換機制,無論何種故障以防止分片或者節點不可用。
為此,elasticsearch讓我們將索引分片複製一份或多份,稱之為分片副本或副本。
副本也有兩個最主要原因:
a) 高可用性,以應對分片或者節點故障。出於這個原因,分片副本要在不同的節點上。
b) 提供效能,增大吞吐量,搜尋可以並行在所有副本上執行。
總之,每一個索引可以被分成多個分片。索引也可以有0個或多個副本。複製後,每個索引都有主分片(母分片)和複製分片(複製於母分片)。分片和副本數量可以在每個索引被建立時定義。索引建立後,可以在任何時候動態的更改副本數量,但是,不能改變分片數。
預設情況下,elasticsearch為每個索引分片5個主分片和1個副本,這就意味著叢集至少需要2個節點。索引將會有5個主分片和5個副本(1個完整副本),每個索引總共有10個分片。 每個elasticsearch分片是一個Lucene索引。一個單個Lucene索引有最大的文件數LUCENE-5843, 文件數限制為2147483519(MAX_VALUE – 128)。 可通過_cat/shards來監控分片大小。
2) Logstash
2.1) Logstash 介紹
LogStash由JRuby語言編寫,基於訊息(message-based)的簡單架構,並執行在Java虛擬機器(JVM)上。不同於分離的代理端(agent)或主機端(server),LogStash可配置單一的代理端(agent)與其它開源軟體結合,以實現不同的功能。
2.2) LogStash的四大元件
Shipper:傳送事件(events)至LogStash;通常,遠端代理端(agent)只需要執行這個元件即可;
Broker and Indexer:接收並索引化事件;
Search and Storage:允許對事件進行搜尋和儲存;
Web Interface:基於Web的展示介面
正是由於以上元件在LogStash架構中可獨立部署,才提供了更好的叢集擴充套件性。
2.3) LogStash主機分類
代理主機(agent host):作為事件的傳遞者(shipper),將各種日誌資料傳送至中心主機;只需執行Logstash 代理(agent)程式;
中心主機(central host):可執行包括中間轉發器(Broker)、索引器(Indexer)、搜尋和儲存器(Search and Storage)、Web介面端(Web Interface)在內的各個元件,以實現對日誌資料的接收、處理和儲存。
3) Kibana
Logstash是一個完全開源的工具,他可以對你的日誌進行收集、分析,並將其儲存供以後使用(如,搜尋),您可以使用它。說到搜尋,logstash帶有一個web介面,搜尋和展示所有日誌。
二、使用ELK日誌分析工具的必要性(解決運維痛點)
- 開發人員不能登入線上伺服器檢視詳細日誌;
- 各個系統都有日誌,日誌資料分散難以查詢;
- 日誌資料量大,查詢速度慢,或者資料不夠實時;
三、ELK日誌分析環境部署
1) 準備機器
兩臺虛擬機器: hostname:linux-node1 和 linux-node2 ip地址:192.168.56.11 和 192.168.56.22
2) 系統環境(兩臺完全一致)
[root@linux-node2 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 (Core) [root@linux-node2 ~]# uname -a Linux linux-node2 3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Mar 6 11:36:42 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux [root@linux-node2 ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.56.11 linux-node1.oldboyedu.com linux-node1 192.168.56.12 linux-node2.oldboyedu.com linux-node2
3) elk準備環境(兩臺完全一致)
1) elasticsearch安裝 下載並安裝GPG key [root@linux-node2 ~]# rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch 新增yum倉庫 [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo [elasticsearch-2.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 2.x packages baseurl=http://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/2.x/centos gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 安裝elasticsearch [root@hadoop-node2 ~]# yum install -y elasticsearch 2) logstash安裝 下載並安裝GPG key [root@linux-node2 ~]# rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch 新增yum倉庫 [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/logstash.repo [logstash-2.1] name=Logstash repository for 2.1.x packages baseurl=http://packages.elastic.co/logstash/2.1/centos gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 安裝logstash [root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install -y logstash 3) kibana安裝 [root@linux-node2 ~]# cd /usr/local/src [root@linux-node1 src]# wget https://download.elastic.co/kibana/kibana/kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64.tar.gz [root@linux-node1 src]# tar -zvxf kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64.tar.gz [root@linux-node1 src]# mv kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64 /usr/local/ [root@linux-node2 src]# ln -s /usr/local/kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64/ /usr/local/kibana 安裝Redis,nginx和java [root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install -y redis nginx java
4) 管理配置elasticsearch
4.1) 管理linux-node1的elasticsearch
修改elasticsearch配置檔案,並授權
[root@linux-node1 src]# grep -n '^[a-Z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
17:cluster.name: chuck-cluster #判別節點是否是統一叢集
23:node.name: linux-node1 #節點的hostname
33:path.data: /data/es-data #資料存放路徑
37:path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/ #日誌路徑
43:bootstrap.mlockall: true #鎖住記憶體,使記憶體不會再swap中使用
54:network.host: 0.0.0.0 #允許訪問的ip
58:http.port: 9200 #埠
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /data/es-data
[root@linux-node1 src]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data/es-data/
啟動elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl start elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl enable elasticsearch
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/elasticsearch.service'
[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl status elasticsearch
elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2016-01-14 09:30:25 CST; 14s ago
Docs: http://www.elastic.co
Main PID: 37954 (java)
CGroup: /system.slice/elasticsearch.service
└─37954 /bin/java -Xms256m -Xmx1g -Djava.awt.headless=true -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConc...
Jan 14 09:30:25 linux-node1 systemd[1]: Starting Elasticsearch...
Jan 14 09:30:25 linux-node1 systemd[1]: Started Elasticsearch.
[root@linux-node1 src]# netstat -lntup|grep 9200
tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 37954/java
訪問9200埠,會把資訊顯示出來

elasticsearch進行互動
1) 互動的兩種方法
a) Java API :
node client
Transport client
b) RESTful API
Javascript
.NET
php
Perl
Python
Ruby
2) 使用RESTful API進行互動
檢視當前索引和分片情況,稍後會有外掛展示
[root@linux-node1 src]# curl -i -XGET 'http://192.168.56.11:9200/_count?pretty' -d '{
"query" {
"match_all": {}
}
}'
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 95
{
"count" : 0, 索引0個
"_shards" : { 分割槽0個
"total" : 0,
"successful" : 0, 成功0個
"failed" : 0 失敗0個
}
}
使用head外掛顯示索引和分片情況
[root@linux-node1 src]# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head
在外掛中新增一個index-demo/test的索引,提交請求

傳送一個GET(當然可以使用其他型別請求)請求,查詢上述索引id
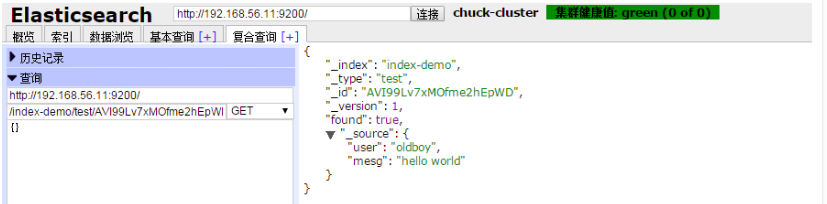
在基本查詢中檢視所建索引
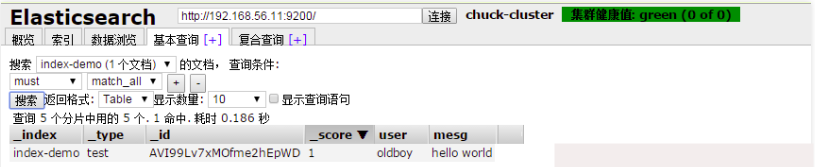
4.2) 管理linux-node2的elasticsearch
將linux-node1的配置檔案拷貝到linux-node2中,並修改配置檔案並授權配置檔案中cluster.name的名字一定要一致,當叢集內節點啟動的時候,預設使用組播(多播),尋找叢集中的節點:
[root@linux-node1 src]# scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 192.168.56.12:/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# sed -i '23s#node.name: linux-node1#node.name: linux-node2#g' elasticsearch.yml
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# mkdir -p /data/es-data
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data/es-data/
啟動elasticsearch
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/elasticsearch.service'
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl status elasticsearch.service
elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2016-01-14 02:56:35 CST; 4s ago
Docs: http://www.elastic.co
Process: 38519 ExecStartPre=/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-systemd-pre-exec (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 38520 (java)
CGroup: /system.slice/elasticsearch.service
└─38520 /bin/java -Xms256m -Xmx1g -Djava.awt.headless=true -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConc...
Jan 14 02:56:35 linux-node2 systemd[1]: Starting Elasticsearch...
Jan 14 02:56:35 linux-node2 systemd[1]: Started Elasticsearch.
在linux-node2配置中新增如下內容,使用單播模式(嘗試了使用組播,但是不生效)
[root@linux-node1 ~]# grep -n "^discovery" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
79:discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["linux-node1", "linux-node2"]
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
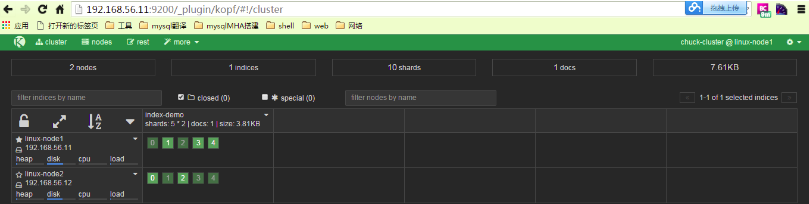
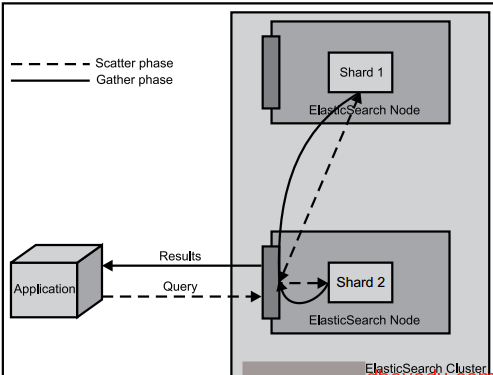
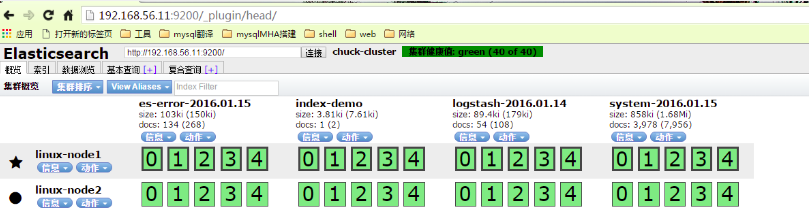
在瀏覽器中檢視分片資訊,一個索引預設被分成了5個分片,每份資料被分成了五個分片(可以調節分片數量),下圖中外圍帶綠色框的為主分片,不帶框的為副本分片,主分片丟失,副本分片會複製一份成為主分片,起到了高可用的作用,主副分片也可以使用負載均衡加快查詢速度,但是如果主副本分片都丟失,則索引就是徹底丟失。

4.3) 使用kopf外掛監控elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install lmenezes/elasticsearch-kopf
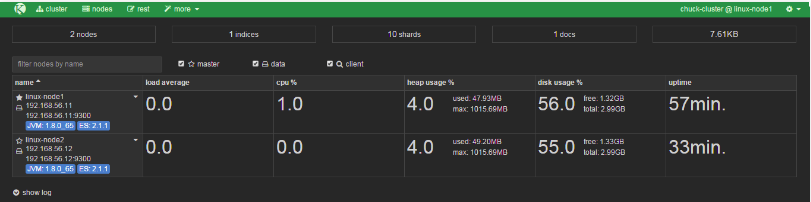
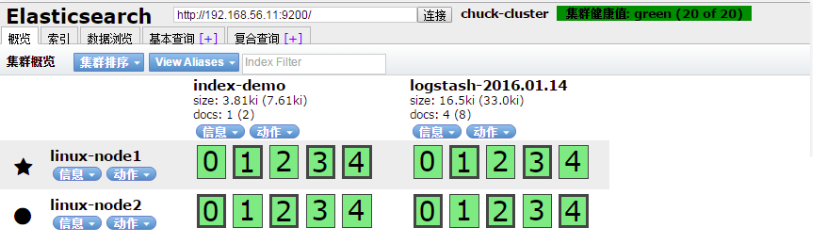
從下圖可以看出節點的負載,cpu適應情況,java對記憶體的使用(heap usage),磁碟使用,啟動時間
除此之外,kopf外掛還提供了REST API 等,類似kopf外掛的還有bigdesk,但是bigdesk目前還不支援2.1!!安裝bigdesk的方法如下:
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install lukas-vlcek/bigdesk
4.4) node間組播通訊和分片
當第一個節點啟動,它會組播發現其他節點,發現叢集名字一樣的時候,就會自動加入叢集。隨便一個節點都是可以連線的,並不是主節點才可以連線,連線的節點起到的作用只是彙總資訊展示:

最初可以自定義設定分片的個數,分片一旦設定好,就不可以改變。主分片和副本分片都丟失,資料即丟失,無法恢復,可以將無用索引刪除。有些老索引或者不常用的索引需要定期刪除,否則會導致es資源剩餘有限,佔用磁碟大,搜尋慢等。如果暫時不想刪除有些索引,可以在外掛中關閉索引,就不會佔用記憶體了。
5) 配置Logstash
5.1) 循序漸進學習Logstash
啟動一個logstash, 其中-e:在命令列執行;input輸入,stdin標準輸入,是一個外掛;output輸出,stdout:標準輸出
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }' Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
chuck ==>輸入
2016-01-14T06:01:07.184Z linux-node1 chuck ==>輸出
www.chuck-blog.com ==>輸入
2016-01-14T06:01:18.581Z linux-node1 www.chuck-blog.com ==>輸出
使用rubudebug顯示詳細輸出,codec為一種編解碼器
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec => rubydebug} }'
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
chuck ==>輸入
{
"message" => "chuck",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:07:50.117Z",
"host" => "linux-node1"
} ==>使用rubydebug輸出
上述每一條輸出的內容稱為一個事件,多個相同的輸出的內容合併到一起稱為一個事件(舉例:日誌中連續相同的日誌輸出稱為一個事件)! 使用logstash將資訊寫入到elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] } }'
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
maliang
chuck
chuck-blog.com
www.chuck-blog.com
在elasticsearch中檢視logstash新加的索引

在elasticsearch中寫一份,同時在本地輸出一份,也就是在本地保留一份文字檔案,也就不用在elasticsearch中再定時備份到遠端一份了。此處使用的保留文字檔案三大優勢:1)文字最簡單; 2) 文字可以二次加工; 3) 文字的壓縮比最高;
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { huihuisearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] } stdout{ codec => rubydebug } }'
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
www.shibo.com
{
"message" => "www.shibo.com",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:27:49.014Z",
"host" => "linux-node1"
}
www.huihui.co
{
"message" => "www.huihui.co",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:27:58.058Z",
"host" => "linux-node1"
}
使用logstash啟動一個配置檔案,會在elasticsearch中寫一份
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat normal.conf
input { stdin { } }
output {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"] }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f normal.conf
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
123
{
"message" => "123",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:51:13.411Z",
"host" => "linux-node1
5.2) 學習編寫conf格式
- 輸入外掛配置,此處以file為例,可以設定多個
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "syslog"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/apache/access.log"
type => "apache"
}
}
- 介紹幾種收集檔案的方式,可以使用陣列方式或者用*匹配,也可以寫多個path
path => ["/var/log/messages","/var/log/*.log"] path => ["/data/mysql/mysql.log"]
- 設定boolean值
ssl_enable => true
- 檔案大小單位
my_bytes => "1113" # 1113 bytes my_bytes => "10MiB"# 10485760 bytes my_bytes => "100kib" # 102400 bytes my_bytes => "180 mb" # 180000000 bytes
- jason收集
codec => “json”
- hash收集
match => {
"field1" => "value1"
"field2" => "value2"
...
}
- 埠
port => 33
- 密碼
my_password => "password"
5.3) 學習編寫input的file外掛
input外掛之input
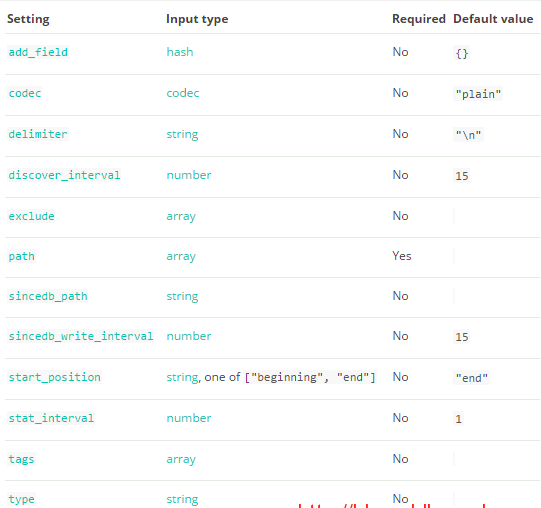
sincedb_path:記錄logstash讀取位置的路徑
start_postion :包括beginning和end,指定收集的位置,預設是end,從尾部開始
add_field: 加一個域
discover_internal: 發現間隔,每隔多久收集一次,預設15秒
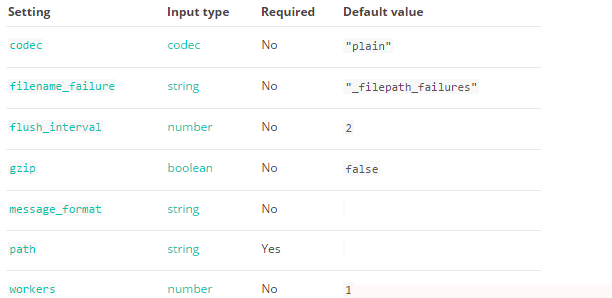
5.4) 學習編寫output的file外掛
5.5) 通過input和output外掛編寫conf檔案
- 收集系統日誌的conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat system.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f system.conf


- 收集elasticsearch的error日誌
此處把上個system日誌和這個error(java程式日誌)日誌,放在一起。使用if判斷,兩種日誌分別寫到不同索引中.此處的type(固定的就是type,不可更改)不可以和日誌格式的任何一個域(可以理解為欄位)的名稱重複,也就是說日誌的域不可以有type這個名稱。
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat all.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-cluster.log"
type => "es-error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "es-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f all.conf
5.6) 把多行整個報錯收集到一個事件中
舉例說明

以at.org開頭的內容都屬於同一個事件,但是顯示在不同行,這樣的日誌格式看起來很不方便,所以需要把他們合併到一個事件中.
- 引入codec的multiline外掛
input {
stdin {
codec => multiline {
`pattern => "pattern, a regexp"
negate => "true" or "false"
what => "previous" or "next"`
}
}
}
regrxp:使用正則,什麼情況下把多行合併起來
negate: 正向匹配和反向匹配
what: 合併到當前行還是下一行
在標準輸入和標準輸出中測試以證明多行收集到一個日誌成功
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat muliline.conf
input {
stdin {
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^\["
negate => true
what => "previous"
}
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f muliline.conf
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
[1
[2
{
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-15T06:46:10.712Z",
"message" => "[1",
"@version" => "1",
"host" => "linux-node1"
}
chuck
chuck-blog.com
123456
[3
{
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-15T06:46:16.306Z",
"message" => "[2\nchuck\nchuck-blog\nchuck-blog.com\n123456",
"@version" => "1",
"tags" => [
[0] "multiline"
],
"host" => "linux-node1"
繼續將上述實驗結果放到all.conf的es-error索引中
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat all.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-clueser.log"
type => "es-error"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^\["
negate => true
what => "previous"
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "es-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
6) 瞭解 Kibana
6.1) 編輯kinaba配置檔案使之生效
[root@linux-node1 ~]# grep '^[a-Z]' /usr/local/kibana/config/kibana.yml server.port: 5601 #kibana埠 server.host: "0.0.0.0" #對外服務的主機 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.56.11:9200" #訪問elasticsearch的地址 kibana.index: ".kibana #在elasticsearch中新增.kibana索引
開啟一個screen,並啟動kibana
[root@linux-node1 ~]# screen [root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/local/kibana/bin/kibana 注意: 使用crtl +a+d退出screen
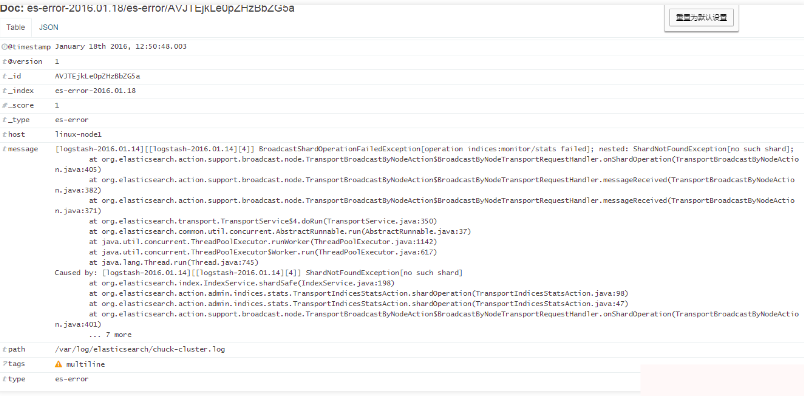
6.2) 驗證error的muliline外掛生效
在kibana中新增一個es-error索引
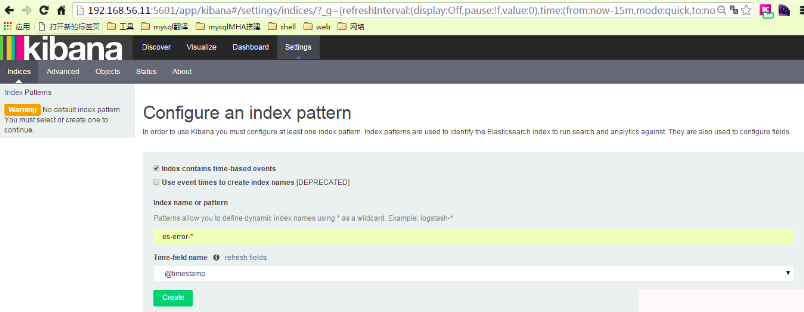
可以看到預設的欄位
選擇discover檢視
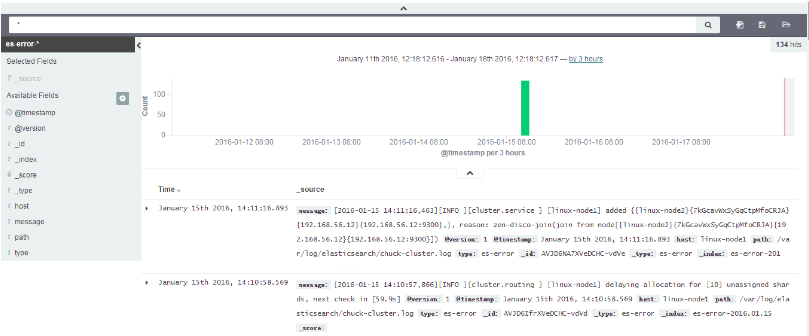
驗證error的muliline外掛生效
7) Logstash收集nginx、syslog和tcp日誌
7.1) 收集nginx的訪問日誌
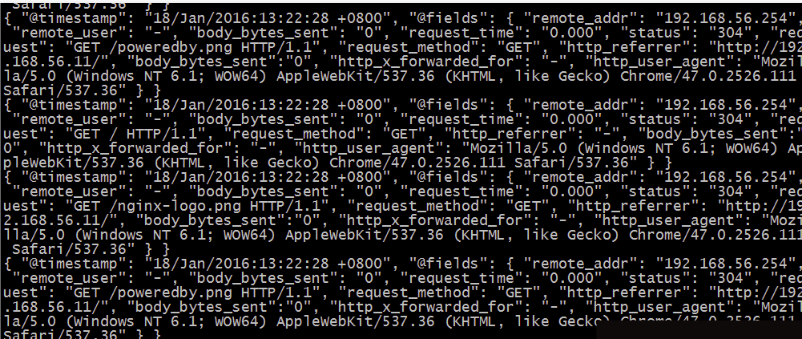
在這裡使用codec的json外掛將日誌的域進行分段,使用key-value的方式,使日誌格式更清晰,易於搜尋,還可以降低cpu的負載
更改nginx的配置檔案的日誌格式,使用json
[root@linux-node1 ~]# sed -n '15,33p' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
log_format json '{ "@timestamp": "$time_local", '
'"@fields": { '
'"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
'"remote_user": "$remote_user", '
'"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", '
'"request_time": "$request_time", '
'"status": "$status", '
'"request": "$request", '
'"request_method": "$request_method", '
'"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent", '
'"http_x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", '
'"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent" } }';
# access_log /var/log/nginx/access_json.log main;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log json;
啟動nginx
[root@linux-node1 ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful [root@linux-node1 ~]# nginx [root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -lntup|grep 80 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 43738/nginx: master tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 43738/nginx: master
日誌格式顯示如下
使用logstash將nginx訪問日誌收集起來,繼續寫到all.conf中
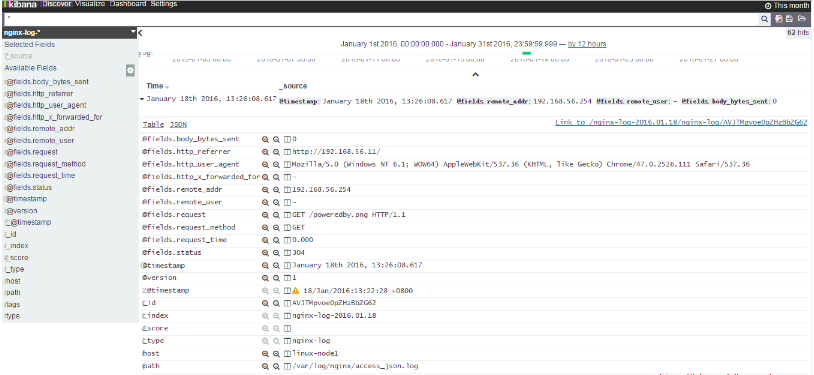
將nginx-log加入kibana中並顯示
7.2) 收集系統syslog日誌
前文中已經使用檔案file的形式收集了系統日誌/var/log/messages,但是實際生產環境是需要使用syslog外掛直接收集
修改syslog的配置檔案,把日誌資訊傳送到514埠上
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/rsyslog.conf 90 *.* @@192.168.56.11:514
將system-syslog放到all.conf中,啟動all.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat all.conf
input {
syslog {
type => "system-syslog"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "514"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/access_json.log"
codec => json
start_position => "beginning"
type => "nginx-log"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-cluster.log"
type => "es-error"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^\["
negate => true
what => "previous"
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "es-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "nginx-log" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "nginx-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "system-syslog" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-syslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f all.conf
在elasticsearch外掛中就可見到增加的system-syslog索引
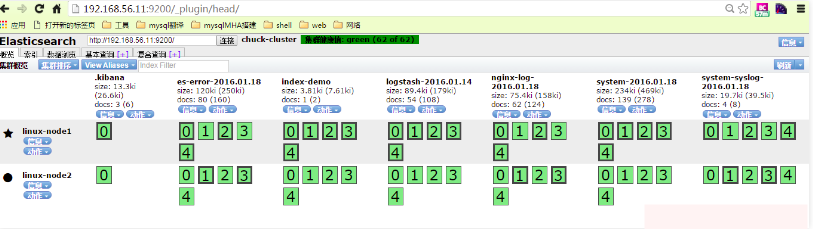
7.3) 收集tcp日誌

編寫tcp.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat tcp.conf
input {
tcp {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6666"
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
使用nc對6666埠寫入資料
[root@linux-node1 ~]# nc 192.168.56.11 6666 </var/log/yum.log
將資訊輸入到tcp的偽裝置中
[root@linux-node1 ~]# echo "chuck" >/dev/tcp/192.168.56.11/6666
8) Logstash解耦之訊息佇列
8.1) 圖解使用訊息佇列架構
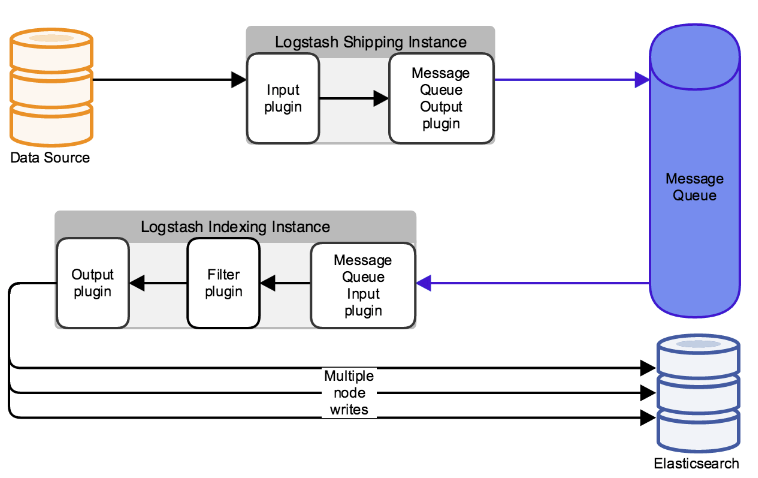
上圖中,資料流向:
- 資料來源Datasource把資料寫到input外掛中;
- output外掛使用訊息佇列把訊息寫入到訊息佇列Message Queue中
- Logstash indexing Instance啟動logstash使用input外掛讀取訊息佇列中的資訊
- Fliter外掛過濾後在使用output寫入到elasticsearch中。如果生產環境中不適用正則grok匹配,可以寫Python指令碼從訊息佇列中讀取資訊,輸出到elasticsearch中.
8.2 )上圖架構的優點
- 解耦,鬆耦合
- 解除了由於網路原因不能直接連elasticsearch的情況
- 方便架構演變,增加新內容
- 訊息佇列可以使用rabbitmq,zeromq等,也可以使用redis,kafka(訊息不刪除,但是比較重量級)等.
9) 引入redis到架構中
9.1) 使用redis收集logstash的資訊
修改redis的配置檔案並啟動redis
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/redis.conf 37 daemonize yes 65 bind 192.168.56.11 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start redis [root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -lntup|grep 6379 tcp 0 0 192.168.56.11:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 45270/redis-server
編寫redis.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat redis-out.conf
input{
stdin{
}
}
output{
redis{
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list" #資料型別為list
key => "demo"
}
啟動配置檔案輸入資訊
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f redis-out.conf Settings: Default filter workers: 1 Logstash startup completed chuck chuck-blog
使用redis-cli連線到redis並檢視輸入的資訊
[root@linux-node1 ~]# redis-cli -h 192.168.56.11
192.168.56.11:6379> info #輸入info檢視資訊
# Server
redis_version:2.8.19
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:c0359e7aa3798aa2
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64 x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll
gcc_version:4.8.3
process_id:45270
run_id:83f428b96e87b7354249fe42bd19ee8a8643c94e
tcp_port:6379
uptime_in_seconds:1111
uptime_in_days:0
hz:10
lru_clock:10271973
config_file:/etc/redis.conf
# Clients
connected_clients:2
client_longest_output_list:0
client_biggest_input_buf:0
blocked_clients:0
# Memory
used_memory:832048
used_memory_human:812.55K
used_memory_rss:5193728
used_memory_peak:832048
used_memory_peak_human:812.55K
used_memory_lua:35840
mem_fragmentation_ratio:6.24
mem_allocator:jemalloc-3.6.0
# Persistence
loading:0
rdb_changes_since_last_save:0
rdb_bgsave_in_progress:0
rdb_last_save_time:1453112484
rdb_last_bgsave_status:ok
rdb_last_bgsave_time_sec:0
rdb_current_bgsave_time_sec:-1
aof_enabled:0
aof_rewrite_in_progress:0
aof_rewrite_scheduled:0
aof_last_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_current_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_last_bgrewrite_status:ok
aof_last_write_status:ok
# Stats
total_connections_received:2
total_commands_processed:2
instantaneous_ops_per_sec:0
total_net_input_bytes:164
total_net_output_bytes:9
instantaneous_input_kbps:0.00
instantaneous_output_kbps:0.00
rejected_connections:0
sync_full:0
sync_partial_ok:0
sync_partial_err:0
expired_keys:0
evicted_keys:0
keyspace_hits:0
keyspace_misses:0
pubsub_channels:0
pubsub_patterns:0
latest_fork_usec:9722
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:0
master_repl_offset:0
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0
# CPU
used_cpu_sys:1.95
used_cpu_user:0.40
used_cpu_sys_children:0.00
used_cpu_user_children:0.00
# Keyspace
db6:keys=1,expires=0,avg_ttl=0
192.168.56.11:6379> select 6 #選擇db6
OK
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> keys * #選擇demo這個key
1) "demo"
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> LINDEX demo -2 #檢視訊息
"{\"message\":\"chuck\",\"@version\":\"1\",\"@timestamp\":\"2016-01-18T10:21:23.583Z\",\"host\":\"linux-node1\"}"
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> LINDEX demo -1 #檢視訊息
"{\"message\":\"chuck-blog\",\"@version\":\"1\",\"@timestamp\":\"2016-01-18T10:25:54.523Z\",\"host\":\"linux-node1\"}"
為了下一步寫input外掛到把訊息傳送到elasticsearch中,多在redis中寫入寫資料
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f redis-out.conf Settings: Default filter workers: 1 Logstash startup completed chuck chuck-blog a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
檢視redis中名字為demo的key長度
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 28
9.2) 使用redis傳送訊息到elasticsearch中
編寫redis-in.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat redis-in.conf
input{
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "demo"
}
}
output{
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "redis-demo-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
啟動配置檔案
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f redis-in.conf Settings: Default filter workers: 1 Logstash startup completed
不斷重新整理demo這個key的長度(讀取很快,重新整理一定要速度)
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 28 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 28 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 19 #可以看到redis的訊息正在寫入到elasticsearch中 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 7 #可以看到redis的訊息正在寫入到elasticsearch中 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen demo (integer) 0
在elasticsearch中檢視增加了redis-demo
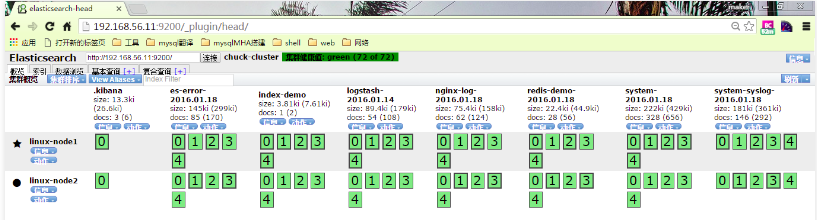
9.3) 將all.conf的內容改為經由redis
編寫shipper.conf作為redis收集logstash配置檔案
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cp all.conf shipper.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim shipper.conf
input {
syslog {
type => "system-syslog"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "514"
}
tcp {
type => "tcp-6666"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6666"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/access_json.log"
codec => json
start_position => "beginning"
type => "nginx-log"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-cluster.log"
type => "es-error"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^\["
negate => true
what => "previous"
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "system"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "es-error"
}
}
if [type] == "nginx-log" {
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "nginx-log"
}
}
if [type] == "system-syslog" {
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "system-syslog"
}
}
if [type] == "tcp-6666" {
redis {
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "tcp-6666"
}
}
}
在redis中檢視keys
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> select 6 OK 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> keys * 1) "system" 2) "nginx-log" 3) "tcp-6666"
編寫indexer.conf作為redis傳送elasticsearch配置檔案
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat indexer.conf
input {
redis {
type => "system-syslog"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "system-syslog"
}
redis {
type => "tcp-6666"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "tcp-6666"
}
redis {
type => "system"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "system"
}
redis {
type => "nginx-log"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "nginx-log"
}
redis {
type => "es-error"
host => "192.168.56.11"
port => "6379"
db => "6"
data_type => "list"
key => "es-error"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.56.11"
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.56.11"
index => "es-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "nginx-log" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.56.11"
index => "nginx-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "system-syslog" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.56.11"
index => "system-syslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "tcp-6666" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.56.11"
index => "tcp-6666-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
啟動shipper.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f shipper.conf Settings: Default filter workers: 1
由於日誌量小,很快就會全部被髮送到elasticsearch,key也就沒了,所以多寫寫資料到日誌中
[root@linux-node1 ~]# for n in `seq 10000` ;do echo $n >>/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-cluster.log;done [root@linux-node1 ~]# for n in `seq 10000` ;do echo $n >>/var/log/nginx/access_json.log;done [root@linux-node1 ~]# for n in `seq 10000` ;do echo $n >>/var/log/messages;done
檢視key的長度看到key在增長
(integer) 2481 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 2613 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 2795 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 2960
啟動indexer.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f indexer.conf Settings: Default filter workers: 1 Logstash startup completed
檢視key的長度看到key在減小
192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen nginx-log (integer) 9680 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen nginx-log (integer) 9661 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen nginx-log (integer) 9661 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 9591 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 9572 192.168.56.11:6379[6]> llen system (integer) 9562
kibana檢視nginx-log索引
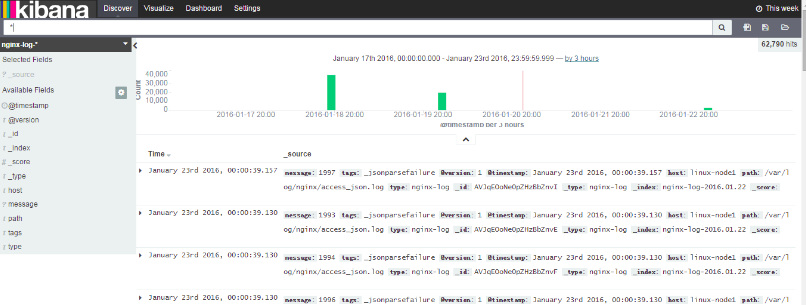
10) 學習logstash的fliter外掛
10.1) 熟悉grok
前面介紹了input和output外掛,在這裡學習fliter外掛
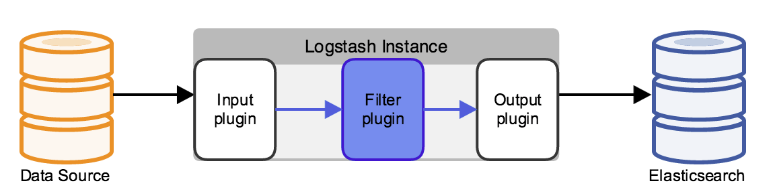
filter外掛有很多,在這裡就學習grok外掛,使用正則匹配日誌裡的域來拆分。在實際生產中,apache日誌不支援jason,就只能使用grok外掛匹配;mysql慢查詢日誌也是無法拆分,只能石油grok正規表示式匹配拆分。
在如下連結,github上有很多寫好的grok模板,可以直接引用https://github.com/logstash-plugins/logstash-patterns-core/blob/master/patterns/grok-patterns 在裝好的logstash中也會有grok匹配規則,直接可以引用,路徑如下:
[root@linux-node1 patterns]# pwd /opt/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/1.9/gems/logstash-patterns-core-2.0.2/patterns
10.2) 根據官方文件提供而編寫的grok.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat grok.conf
input {
stdin {}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{IP:client} %{WORD:method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{NUMBER:duration}" }
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
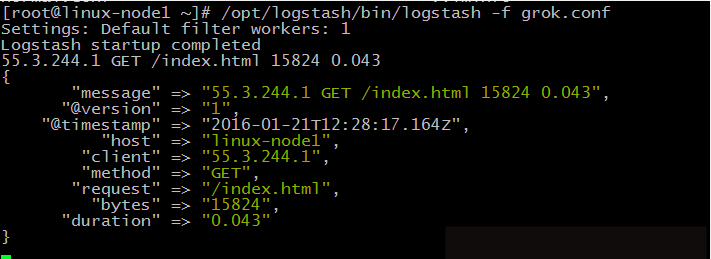
啟動logstash,並根據官方文件提供輸入,可得到拆分結果如下顯示
10.3) 使用logstash收集mysql慢查詢日誌
倒入生產中mysql的slow日誌,示例格式如下:
# Time: 160108 15:46:14
# User@Host: dev_select_user[dev_select_user] @ [192.168.97.86] Id: 714519
# Query_time: 1.638396 Lock_time: 0.000163 Rows_sent: 40 Rows_examined: 939155
SET timestamp=1452239174;
SELECT DATE(create_time) as day,HOUR(create_time) as h,round(avg(low_price),2) as low_price
FROM t_actual_ad_num_log WHERE create_time>='2016-01-07' and ad_num<=10
GROUP BY DATE(create_time),HOUR(create_time);
使用multiline處理,並編寫slow.conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat mysql-slow.conf
input{
file {
path => "/root/slow.log"
type => "mysql-slow-log"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^# User@Host:"
negate => true
what => "previous"
}
}
}
filter {
# drop sleep events
grok {
match => { "message" =>"SELECT SLEEP" }
add_tag => [ "sleep_drop" ]
tag_on_failure => [] # prevent default _grokparsefailure tag on real records
}
if "sleep_drop" in [tags] {
drop {}
}
grok {
match => [ "message", "(?m)^# User@Host: %{USER:user}\[[^\]]+\] @ (?:(?<clienthost>\S*) )?\[(?:%{IP:clientip})?\]\s+Id: %{NUMBER:row_id:int}\s*# Query_time: %{NUMBER:query_time:float}\s+Lock_time: %{NUMBER:lock_time:float}\s+Rows_sent: %{NUMBER:rows_sent:int}\s+Rows_examined: %{NUMBER:rows_examined:int}\s*(?:use %{DATA:database};\s*)?SET timestamp=%{NUMBER:timestamp};\s*(?<query>(?<action>\w+)\s+.*)\n#\s*" ]
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp", "UNIX" ]
remove_field => [ "timestamp" ]
}
}
output {
stdout{
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
執行該配置檔案,檢視grok正則匹配結果

11) 生產如何上線ELK
11.1) 日誌分類
系統日誌 rsyslog logstash syslog外掛 訪問日誌 nginx logstash codec json 錯誤日誌 file logstash file+ mulitline 執行日誌 file logstash codec json 裝置日誌 syslog logstash syslog外掛 debug日誌 file logstash json or mulitline
10.2) 日誌標準化
- 路徑固定標準化 - 格式儘量使用json