1、狀態模式簡介
1.1>、定義
狀態模式的核心思想是允許一個物件在它的內部狀態改變時改變它的行為,即不同的狀態對應不同的行為。
狀態模式的針對性很強,當有狀態變化的時候可以選擇狀態模式。
1.2>、使用頻率
 中等
中等
2、狀態模式結構
2.1>、結構圖

2.2>、參與者
狀態模式參與者:
◊ Context:狀態管理器
° 定義對Client感興趣的介面
° 維持一個ConcreteState子類的例項,這個例項定義當前狀態
◊ State:狀態,定義一個介面以封裝與Context的一個特定狀態相關的行為。
◊ ConcreteState:具體狀態子類,每一子類實現的一個與Context的一個狀態相關的行為。
3、狀態模式結構實現
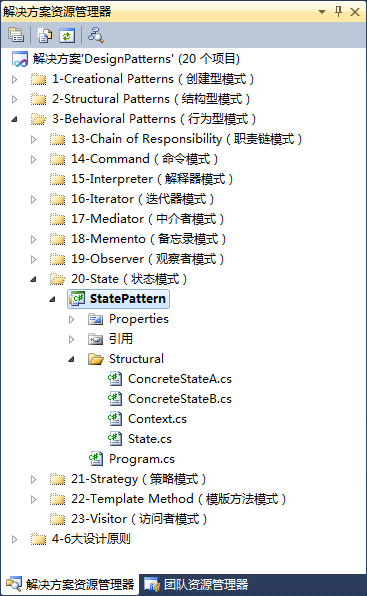
State.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Structural
{
public abstract class State
{
public abstract void Handle(Context context);
}
}
Context.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Structural
{
public class Context
{
private State _state;
public Context(State state)
{
this.State = state;
}
public State State
{
get
{
return _state;
}
set
{
_state = value;
Console.WriteLine("State: " + _state.GetType().Name);
}
}
public void Request()
{
_state.Handle(this);
}
}
}
ConcreteStateA.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Structural
{
public class ConcreteStateA : State
{
public override void Handle(Context context)
{
context.State = new ConcreteStateB();
}
}
}
ConcreteStateB.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Structural
{
public class ConcreteStateB : State
{
public override void Handle(Context context)
{
context.State = new ConcreteStateA();
}
}
}
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Structural;
namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Setup context in a state
Context c = new Context(new ConcreteStateA());
// Issue requests, which toggles state
c.Request();
c.Request();
c.Request();
c.Request();
}
}
}
執行輸出:
State: ConcreteStateA State: ConcreteStateB State: ConcreteStateA State: ConcreteStateB State: ConcreteStateA 請按任意鍵繼續. . .
4、狀態模式的實踐應用
假設有一個Task,其狀態有4種:Pending、Running、Cancelled和Finished。
根據業務需求描述,建立狀態圖。

狀態模式實現:

State.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical { public abstract class State { public abstract void Start(Task task); public abstract void Cancel(Task task); } }
PendingState.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical { public class PendingState : State { public override void Start(Task task) { task.State = new RunningState(); } public override void Cancel(Task task) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
RunningState.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical { public class RunningState:State { public override void Start(Task task) { // RunningState執行Start方法轉為FinishedState task.State = new FinishedState(); } public override void Cancel(Task task) { // RunningState執行Cancel方法轉為CancelledState task.State = new CancelledState(); } } }
CancelledState.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical { public class CancelledState : State { public override void Start(Task task) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void Cancel(Task task) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
FinishedState.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical { public class FinishedState : State { public override void Start(Task task) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void Cancel(Task task) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
Program.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using DesignPatterns.StatePattern.Practical; namespace DesignPatterns.StatePattern { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Task task = new Task(); task.State = new PendingState(); //Task task = new Task(new PendingState()); task.Start(); //task.Start(); task.Cancel(); } } }
執行結果:
State : Pending
State : Running
State : Cancelled
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
5、狀態模式應用分析
狀態模式效果:
1>、狀態模式的本質是將條件語句的各個分支封裝起來,從而實現了狀態邏輯與動作的分離。當分支很多時,狀態模式可以給程式碼的維護帶來很大的便利。
2>、多型性的實現。
3>、狀態轉換的顯示化。狀態模式將狀態的切換邏輯存放到狀態物件中,可以實現狀態的自動切換,使各個狀態界限分明,相互獨立。
4>、採用分支結構時,Context物件需要關心所有狀態的切換邏輯,當分支越來越多時,複雜度也會越來越大。而狀態模式中Context無需關心狀態的切換邏輯,每個狀態物件也只需關心狀態的下一個可能狀態的切換邏輯。
狀態模式主要解決的是當控制一個物件狀態的條件表示式過於複雜時的情況。把狀態的判斷邏輯表示不同狀態的一系列類中,可以把複雜的判斷邏輯簡化。狀態模式的目的是為了將狀態與不同狀態下的行為進行分離,從而簡化複雜的條件判斷。
狀態模式主要適用場景:
◊ 一個物件的行為取決於它的狀態,並且必須在執行時刻根據狀態改變其行為;
◊ 一個操作中包含龐大的分支結構,並且這些分支決定於物件的狀態。