試想一下,如果你的JSP頁面中包含一句程式碼“System.exit(1);”,你的web應用訪問到該JSP時,會發生什麼?
一般使用tomcat可能都沒有注意到這個問題,本篇主要講述tomcat 6中SecurityManager的管理機制,儘量使用簡單明瞭的圖片表示其中關係。
其他知識參考tomcat文件翻譯。如有錯誤,請予指正。
理解java.policy
Java是一門安全性很高的語言,因此也會考慮到使用者程式碼對整個系統的侵入性。試想一下,如果你引用了一個jar包,裡面包含了依據system.exit(),每次執行到這裡都直接退出,會不會很蛋疼!
Java開發者肯定想過如此的問題,所以引入了java安全策略機制,利用一個配置檔案來管理所有的程式碼許可權。
JDK中就有這樣的檔案,就是 jre/lib/security/java.policy ,參考下該檔案,就能理解其中的關係:

// default permissions granted to all domains
grant {
// Allows any thread to stop itself using the java.lang.Thread.stop()
// method that takes no argument.
// Note that this permission is granted by default only to remain
// backwards compatible.
// It is strongly recommended that you either remove this permission
// from this policy file or further restrict it to code sources
// that you specify, because Thread.stop() is potentially unsafe.
// See the API specification of java.lang.Thread.stop() for more
// information.
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "stopThread";
// allows anyone to listen on dynamic ports
permission java.net.SocketPermission "localhost:0", "listen";
// "standard" properies that can be read by anyone
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vendor.url", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.class.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.arch", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.separator", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "path.separator", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "line.separator", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.name", "read";
};
上面給出了基本的許可權,例如任何人都可以監聽動態埠,以及一些讀操作。
基本過程如下面的圖所示:
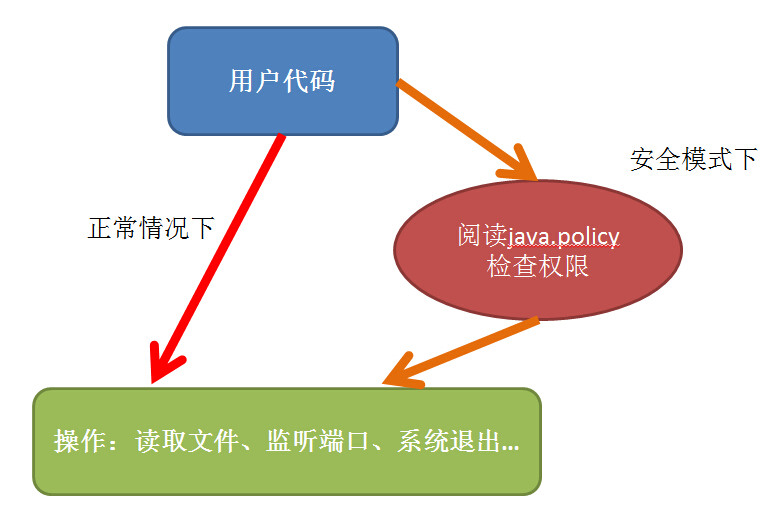
使用者如果啟用了安全管理,即在執行時新增了-Djava.security.manager, 就會在執行某些操作前 先讀取 許可權檔案java.policy,檢查是否具體相應許可權。
當然也可以自己定義安全檔案,一般有兩種方式:
一種是自己建立SecuirtyManager類,建立一些checkXXX的方法,進行驗證;
另一種就是建立my.policy檔案(名字隨意),按照規定的語法配置許可權,然後啟動時新增-Djava.security.manager-Djava.security.policy=xxxx/my.policy引數。
關於java本身的安全管理不是本篇的重點,下面介紹下tomcat中的安全策略。
理解tomcat中的Security
Tomcat中的安全管理原理基本與前面JDK中的security類似,只是啟動時需要在start後面新增-security引數,tomcat會自動讀取 conf/catalina.policy 檔案中的許可權配置。啟動命令如下:
F:apache-tomcat-xxx/bin/startup.bat -security
catalina.policy中預設已經配置了很多的安全策略,這裡就不多說明了,下個部分會針對某一特定檔案進行說明:

// Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
// contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
// this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
// The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
// (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
// the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
// ============================================================================
// catalina.policy - Security Policy Permissions for Tomcat 6
//
// This file contains a default set of security policies to be enforced (by the
// JVM) when Catalina is executed with the "-security" option. In addition
// to the permissions granted here, the following additional permissions are
// granted to the codebase specific to each web application:
//
// * Read access to its document root directory
// * Read, write and delete access to its working directory
// ============================================================================
// ========== SYSTEM CODE PERMISSIONS =========================================
// These permissions apply to javac
grant codeBase "file:${java.home}/lib/-" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// These permissions apply to all shared system extensions
grant codeBase "file:${java.home}/jre/lib/ext/-" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// These permissions apply to javac when ${java.home] points at $JAVA_HOME/jre
grant codeBase "file:${java.home}/../lib/-" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// These permissions apply to all shared system extensions when
// ${java.home} points at $JAVA_HOME/jre
grant codeBase "file:${java.home}/lib/ext/-" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// ========== CATALINA CODE PERMISSIONS =======================================
// These permissions apply to the daemon code
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.home}/bin/commons-daemon.jar" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// These permissions apply to the logging API
// Note: If tomcat-juli.jar is in ${catalina.base} and not in ${catalina.home},
// update this section accordingly.
// grant codeBase "file:${catalina.base}/bin/tomcat-juli.jar" {..}
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.home}/bin/tomcat-juli.jar" {
permission java.io.FilePermission
"${java.home}${file.separator}lib${file.separator}logging.properties", "read";
permission java.io.FilePermission
"${catalina.base}${file.separator}conf${file.separator}logging.properties", "read";
permission java.io.FilePermission
"${catalina.base}${file.separator}logs", "read, write";
permission java.io.FilePermission
"${catalina.base}${file.separator}logs${file.separator}*", "read, write";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "shutdownHooks";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "getClassLoader";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "setContextClassLoader";
permission java.util.logging.LoggingPermission "control";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.util.logging.config.class", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.util.logging.config.file", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "catalina.base", "read";
// Note: To enable per context logging configuration, permit read access to
// the appropriate file. Be sure that the logging configuration is
// secure before enabling such access.
// E.g. for the examples web application (uncomment and unwrap
// the following to be on a single line):
// permission java.io.FilePermission "${catalina.base}${file.separator}
// webapps${file.separator}examples${file.separator}WEB-INF
// ${file.separator}classes${file.separator}logging.properties", "read";
};
// These permissions apply to the server startup code
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.home}/bin/bootstrap.jar" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// These permissions apply to the servlet API classes
// and those that are shared across all class loaders
// located in the "lib" directory
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.home}/lib/-" {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
// If using a per instance lib directory, i.e. ${catalina.base}/lib,
// then the following permission will need to be uncommented
// grant codeBase "file:${catalina.base}/lib/-" {
// permission java.security.AllPermission;
// };
// ========== WEB APPLICATION PERMISSIONS =====================================
// These permissions are granted by default to all web applications
// In addition, a web application will be given a read FilePermission
// and JndiPermission for all files and directories in its document root.
grant {
// Required for JNDI lookup of named JDBC DataSource's and
// javamail named MimePart DataSource used to send mail
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.home", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.naming.*", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "javax.sql.*", "read";
// OS Specific properties to allow read access
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "os.arch", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.separator", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "path.separator", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "line.separator", "read";
// JVM properties to allow read access
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vendor.url", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.class.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.specification.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.specification.name", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.version", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.vendor", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "java.vm.name", "read";
// Required for OpenJMX
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "getAttribute";
// Allow read of JAXP compliant XML parser debug
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "jaxp.debug", "read";
// Precompiled JSPs need access to these packages.
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.jasper.el";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.jasper.runtime";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.jasper.runtime.*";
// Precompiled JSPs need access to these system properties.
permission java.util.PropertyPermission
"org.apache.jasper.runtime.BodyContentImpl.LIMIT_BUFFER", "read";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "org.apache.el.parser.COERCE_TO_ZERO", "read";
};
// The Manager application needs access to the following packages to support the
// session display functionality. These settings support the following
// configurations:
// - default CATALINA_HOME == CATALINA_BASE
// - CATALINA_HOME != CATALINA_BASE, per instance Manager in CATALINA_BASE
// - CATALINA_HOME != CATALINA_BASE, shared Manager in CATALINA_HOME
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.base}/webapps/manager/-" {
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina.manager";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina.manager.util";
};
grant codeBase "file:${catalina.home}/webapps/manager/-" {
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina.manager";
permission java.lang.RuntimePermission "accessClassInPackage.org.apache.catalina.manager.util";
};
// You can assign additional permissions to particular web applications by
// adding additional "grant" entries here, based on the code base for that
// application, /WEB-INF/classes/, or /WEB-INF/lib/ jar files.
//
// Different permissions can be granted to JSP pages, classes loaded from
// the /WEB-INF/classes/ directory, all jar files in the /WEB-INF/lib/
// directory, or even to individual jar files in the /WEB-INF/lib/ directory.
//
// For instance, assume that the standard "examples" application
// included a JDBC driver that needed to establish a network connection to the
// corresponding database and used the scrape taglib to get the weather from
// the NOAA web server. You might create a "grant" entries like this:
//
// The permissions granted to the context root directory apply to JSP pages.
// grant codeBase "file:${catalina.base}/webapps/examples/-" {
// permission java.net.SocketPermission "dbhost.mycompany.com:5432", "connect";
// permission java.net.SocketPermission "*.noaa.gov:80", "connect";
// };
//
// The permissions granted to the context WEB-INF/classes directory
// grant codeBase "file:${catalina.base}/webapps/examples/WEB-INF/classes/-" {
// };
//
// The permission granted to your JDBC driver
// grant codeBase "jar:file:${catalina.base}/webapps/examples/WEB-INF/lib/driver.jar!/-" {
// permission java.net.SocketPermission "dbhost.mycompany.com:5432", "connect";
// };
// The permission granted to the scrape taglib
// grant codeBase "jar:file:${catalina.base}/webapps/examples/WEB-INF/lib/scrape.jar!/-" {
// permission java.net.SocketPermission "*.noaa.gov:80", "connect";
// };
這裡需要注意的是其配置語法:
grant [signedBy <signer>,] [codeBase <code source>] { permission <class> [<name> [, <action list>]]; };
都要按照上面的格式進行配置。其中:
codeBase 是通過URL的方式指定檔案,可以使用變數${java.home}或者${catalina.home}來表示JDK和tomcat的根目錄。
class 指定了相應的操作
[name,[,action]] name指定具體的操作或者檔案,action指定可選的動作(比如read write等等)。
具體的配置樣例,可以參考上面的預設檔案。
另外要說明的就是都可以配置哪些操作,也就是permission後面都可以跟哪些類,他們的作用都是什麼?
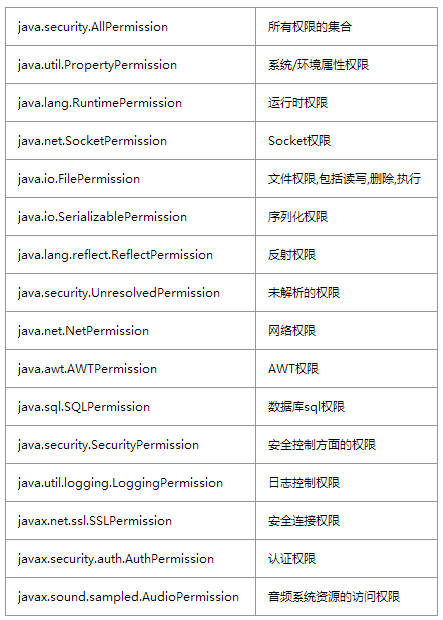
上面列表中,最常用的java.io.FilePermission用於檔案的操作、java.lang.RuntimePermission(可以通過禁用該許可權達到防止system.exit(1)的目的)等等。
Security配置實戰
在tomcat中配置security,可以按照下面幾個步驟:
1 在樣例程式碼中執行特殊許可權操作:

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
import="java.net.*,java.io.*"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>security Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>security Test</h1>
<hr>
<%!
String txt2String(File file){
String result = "";
try{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));//構造一個BufferedReader類來讀取檔案
String s = null;
while((s = br.readLine())!=null){//使用readLine方法,一次讀一行
result = result + "\n" +s;
}
br.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
%>
<%
//是否啟用了security,如果沒有啟用會輸入null。
System.out.println("SecurityManager: " + System.getSecurityManager());
File file = new File("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.txt");
//執行檔案讀操作,即java.io.FilePermission
System.out.println(txt2String(file));
//執行獲取檔案屬性操作,即java.util.PropertyPermission
System.out.println(System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
%>
</body>
</html>
當訪問該頁面時,會自動執行下面的程式碼,如果不具有相應的許可權,會直接報錯:
//執行檔案讀操作,即java.io.FilePermission System.out.println(txt2String(file)); //執行獲取檔案屬性操作,即java.util.PropertyPermission System.out.println(System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
2 配置安全策略檔案catalina.policy:
只需要在catalina.policy末尾新增如下的配置即可:
grant { permission java.io.FilePermission "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.txt", "read"; permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.encoding", "read"; };
3 在命令列中新增-security啟動

訪問JSP執行程式碼,樣例中訪問 http://localhost:8080/JSPTest/securityTest.jsp
可以看到控制檯正常輸出:
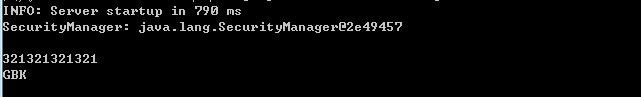
對比下正常啟動的輸出,SecurityManager會輸出null(此時,如果JSP中有system.exit(1);程式就會直接退出):

如果沒有配置讀寫檔案的許可權,會報錯(註釋掉安全配置的第一句):
grant { //permission java.io.FilePermission "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.txt", "read"; permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.encoding", "read"; };
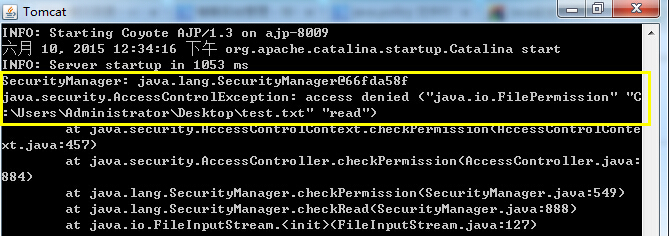
如果沒有配置獲取檔案屬性許可權,則會報錯:
grant { permission java.io.FilePermission "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test.txt", "read"; //permission java.util.PropertyPermission "file.encoding", "read"; };

因此,如果在安全管理模式下,進行了越權的操作,就會報錯有的甚至直接導致程式退出。
通過報錯資訊,可以快速的知道缺乏什麼許可權,根絕該報錯就可以方便的配置安全策略。
參考
【1】Java.security.policy檔案:http://www.tmser.com/post-187.html
【2】Java安全管理器:http://bubuko.com/infodetail-306759.html
【3】tomcat 6.0 security manager:http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-6.0-doc/security-manager-howto.html
