opencv中svm原始碼
線性SVM
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/ml.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ml;
int main(int, char**)
{
// Data for visual representation
int width = 512, height = 512;
Mat image = Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC3);
// Set up training data
//! [setup1]
int labels[5] = {1, 1, -1, -1,-1};
float trainingData[5][2] = { {501, 10}, {255, 10}, {501, 255}, {10, 501},{10,10} }; //建立訓練資料,必須是線性可分的。
//! [setup1]
//! [setup2]
Mat trainingDataMat(5, 2, CV_32FC1, trainingData); //32位float型
Mat labelsMat(5, 1, CV_32SC1, labels); //32位int型
//! [setup2]
// Train the SVM
//! [init]
Ptr<SVM> svm = SVM::create(); //採用智慧指標調研SVM
svm->setType(SVM::C_SVC);
svm->setKernel(SVM::LINEAR); //線性可分因此採用線性核
svm->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 100, 1e-6)); 終止準則函式:當迭代次數達到最大值時終止
//! [init]
//! [train]
svm->train(trainingDataMat, ROW_SAMPLE, labelsMat);
//! [train]
// Show the decision regions given by the SVM
//! [show]
Vec3b green(0,255,0), blue (255,0,0);
for (int i = 0; i < image.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < image.cols; ++j)
{
Mat sampleMat = (Mat_<float>(1,2) << j,i);
float response = svm->predict(sampleMat);//predict是用來預測的,引數為:樣本、返回值型別(如果值為ture而且是一個2類問題則返回判決函式值,否則返回類標籤)
if (response == 1)
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j) = green;
else if (response == -1)
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j) = blue;
}
//! [show]
// Show the training data
//! [show_data]
int thickness = -1;
int lineType = 8; //線形
circle( image, Point(501, 10), 5, Scalar( 0, 0, 0), thickness, lineType );
circle( image, Point(255, 10), 5, Scalar(0, 0, 0), thickness, lineType );
circle( image, Point(501, 255), 5, Scalar(255, 255, 255), thickness, lineType );
circle( image, Point( 10, 501), 5, Scalar(255, 255, 255), thickness, lineType );
circle(image, Point(10, 10), 5, Scalar(255, 255, 255), thickness, lineType);
//! [show_data]
// Show support vectors
//! [show_vectors]
thickness = 2;
lineType = 8;
Mat sv = svm->getUncompressedSupportVectors();
for (int i = 0; i < sv.rows; ++i)
{
const float* v = sv.ptr<float>(i);
circle( image, Point( (int) v[0], (int) v[1]), 6, Scalar(128, 128, 128), thickness, lineType);
}
//! [show_vectors]
imwrite("result.png", image); // save the image
imshow("SVM Simple Example", image); // show it to the user
waitKey(0);
}非線性SVM
opencv 原始碼中SVM核型別還是LINEAR ,要改成非線性型比如POLY 多項式型
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/ml.hpp>
#define NTRAINING_SAMPLES 100 // Number of training samples per class
#define FRAC_LINEAR_SEP 0.9f // Fraction of samples which compose the linear separable part
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ml;
using namespace std;
static void help()
{
cout<< "\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< "This program shows Support Vector Machines for Non-Linearly Separable Data. " << endl
<< "Usage:" << endl
<< "./non_linear_svms" << endl
<< "--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< endl;
}
int main()
{
help();
// Data for visual representation
const int WIDTH = 512, HEIGHT = 512;
Mat I = Mat::zeros(HEIGHT, WIDTH, CV_8UC3); //建立畫布
//--------------------- 1. Set up training data randomly ---------------------------------------
Mat trainData(2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES, 2, CV_32FC1);
Mat labels (2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES, 1, CV_32SC1);
RNG rng(100); // Random value generation class
// Set up the linearly separable part of the training data
int nLinearSamples = (int) (FRAC_LINEAR_SEP * NTRAINING_SAMPLES); //float型強制轉換為int
//! [setup1]
// Generate random points for the class 1
Mat trainClass = trainData.rowRange(0, nLinearSamples);
// The x coordinate of the points is in [0, 0.4)
Mat c = trainClass.colRange(0, 1);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(1), Scalar(0.4 * WIDTH));
// The y coordinate of the points is in [0, 1)
c = trainClass.colRange(1,2);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(1), Scalar(HEIGHT));
// Generate random points for the class 2
trainClass = trainData.rowRange(2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES-nLinearSamples, 2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES);
// The x coordinate of the points is in [0.6, 1]
c = trainClass.colRange(0 , 1);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(0.6*WIDTH), Scalar(WIDTH));
// The y coordinate of the points is in [0, 1)
c = trainClass.colRange(1,2);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(1), Scalar(HEIGHT));
//! [setup1]
//------------------ Set up the non-linearly separable part of the training data ---------------
//! [setup2]
// Generate random points for the classes 1 and 2
trainClass = trainData.rowRange( nLinearSamples, 2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES-nLinearSamples);
// The x coordinate of the points is in [0.4, 0.6)
c = trainClass.colRange(0,1);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(0.4*WIDTH), Scalar(0.6*WIDTH));
// The y coordinate of the points is in [0, 1)
c = trainClass.colRange(1,2);
rng.fill(c, RNG::UNIFORM, Scalar(1), Scalar(HEIGHT));
//! [setup2]
//------------------------- Set up the labels for the classes ---------------------------------
labels.rowRange( 0, NTRAINING_SAMPLES).setTo(1); // Class 1
labels.rowRange(NTRAINING_SAMPLES, 2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES).setTo(2); // Class 2
//------------------------ 2. Set up the support vector machines parameters --------------------
//------------------------ 3. Train the svm ----------------------------------------------------
cout << "Starting training process" << endl;
//! [init]
Ptr<SVM> svm = SVM::create();
svm->setType(SVM::C_SVC);
/*svm->setC(0.1);
svm->setKernel(SVM::LINEAR);//不應該用線性核*/
svm->setKernel(SVM::POLY); //採用多項式核
svm->setGamma(3);
svm->setDegree(1);
//svm->setKernel(SVM::RBF);
//svm->setKernel(SVM::SIGMOID);
svm->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, (int)1e7, 1e-6));//個最大迭代次數和容許誤差,
//! [init]
//! [train]
svm->train(trainData, ROW_SAMPLE, labels);
//! [train]
cout << "Finished training process" << endl;
//------------------------ 4. Show the decision regions ----------------------------------------
//! [show]
Vec3b green(0,100,0), blue (100,0,0);
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)
{
Mat sampleMat = (Mat_<float>(1,2) << i, j);
float response = svm->predict(sampleMat);
if (response == 1) I.at<Vec3b>(j, i) = green;
else if (response == 2) I.at<Vec3b>(j, i) = blue;
}
//! [show]
//----------------------- 5. Show the training data --------------------------------------------
//! [show_data]
int thick = -1;
int lineType = 8;
float px, py;
// Class 1
for (int i = 0; i < NTRAINING_SAMPLES; ++i)
{
px = trainData.at<float>(i,0);
py = trainData.at<float>(i,1);
circle(I, Point( (int) px, (int) py ), 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), thick, lineType);
}
// Class 2
for (int i = NTRAINING_SAMPLES; i <2*NTRAINING_SAMPLES; ++i)
{
px = trainData.at<float>(i,0);
py = trainData.at<float>(i,1);
circle(I, Point( (int) px, (int) py ), 3, Scalar(255, 0, 0), thick, lineType);
}
//! [show_data]
//------------------------- 6. Show support vectors --------------------------------------------
//! [show_vectors]
thick = 2;
lineType = 8;
Mat sv = svm->getSupportVectors();
for (int i = 0; i < sv.rows; ++i)
{
const float* v = sv.ptr<float>(i);
circle( I, Point( (int) v[0], (int) v[1]), 6, Scalar(128, 128, 128), thick, lineType);
}
//! [show_vectors]
imwrite("result.png", I); // save the Image
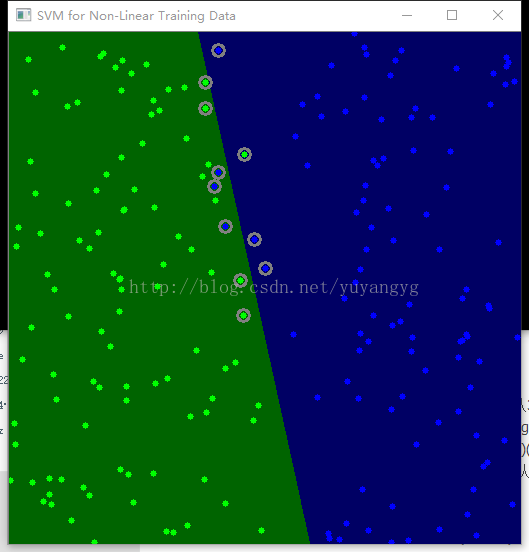
imshow("SVM for Non-Linear Training Data", I); // show it to the user
waitKey(0);
}

在二維顯示分錯的情況。原因是在在高維空間是可分的,低維空間只是這樣表示表示? 還是用了軟間隔的原因?
degree設為2情況
SVM的引數意義
SVM經常選用的核函式
高斯核
多項式核
sigmoid
相關文章
- opencv中SVMOpenCV
- opencv + SVM 程式碼OpenCV
- opencv SVM的使用OpenCV
- opencv SVM分類DemoOpenCV
- OpenCV中使用SVM簡介OpenCV
- OpenCV進階---介紹SVMOpenCV
- OpenCV筆記(3)實現支援向量機(SVM)OpenCV筆記
- opencv python 基於SVM的手寫體識別OpenCVPython
- 機器學習(3),opencv4.0中SVM各個引數的意義,設定機器學習OpenCV
- 【opencv3】 svm實現手寫體與人臉識別OpenCV
- 學習SVM(四) 理解SVM中的支援向量(Support Vector)
- OpenCL中的SVM使用案例
- SVM
- 【OpenCV教程】OpenCV中的資料型別OpenCV資料型別
- SVM大解密(附程式碼和公式)解密公式
- 【OpenCV教程】OpenCV中對矩陣的常用操作OpenCV矩陣
- 「從原始碼中學習」Vue原始碼中的JS騷操作原始碼VueJS
- SVM原理
- 手把手教你使用LabVIEW OpenCV dnn實現影像分類(含原始碼)ViewOpenCVDNN原始碼
- 【Python】【OpenCV】定位二維碼PythonOpenCV
- 支援向量機(Support Vector Machine,SVM)—— 線性SVMMac
- Android中IntentService原始碼分析AndroidIntent原始碼
- koa原始碼中的promise原始碼Promise
- Cglib中LoadingCache原始碼分析CGLibGC原始碼
- LinkedBlockingQueue中put原始碼分析BloC原始碼
- SVM家族(一)
- 原始碼原始碼原始碼樹品原始碼原始碼
- Python機器學習筆記:SVM(1)——SVM概述Python機器學習筆記
- 支援向量機(SVM)從原理到python程式碼實現Python
- DepartmentService介面中queryIndexPatternByDepartmentId的原始碼Index原始碼
- go 中 select 原始碼閱讀Go原始碼
- python中doctest如何嵌入原始碼?Python原始碼
- etcd中watch原始碼解讀原始碼
- Trap (陷入/中斷) 原始碼解析原始碼
- go中waitGroup原始碼解讀GoAI原始碼
- go中errgroup原始碼解讀Go原始碼
- go中panic原始碼解讀Go原始碼
- Tomcat 中的 NIO 原始碼分析Tomcat原始碼
- Python機器學習筆記:SVM(3)——證明SVMPython機器學習筆記





