用C語言實現有限狀態自動機FSM
摘要:狀態機模式是一種行為模式,在《設計模式》這本書中對其有詳細的描述,通過多型實現不同狀態的調轉行為的確是一種很好的方法,只可惜在嵌入式環境下,有時只能寫純C程式碼,並且還需要考慮程式碼的重入和多工請求跳轉等情形,因此實現起來著實需要一番考慮。本文主要為你實現一個簡單的有限狀態機,沒有考慮程式碼的重入和多工跳轉,為以後複雜的狀態機實現,打下基礎。
本文來源:用C語言實現有限狀態自動機FSM
一、狀態機實現的要素
首先,分析一下一個普通的狀態機究竟要實現哪些內容。
狀態機儲存從開始時刻到現在的變化,並根據當前輸入,決定下一個狀態。這意味著,狀態機要儲存狀態、獲得輸入(我們把它叫做跳轉條件)、做出響應。
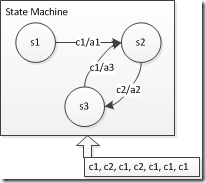
如上圖所示,{s1, s2, s3}均為狀態,箭頭c1/a1表示在s1狀態、輸入為c1時,跳轉到s2,並進行a1操作。
最下方為一組輸入,狀態機應做出如下反應:
| 當前狀態 | 輸入 | 下一個狀態 | 動作 |
| s1 | c1 | s2 | a1 |
| s2 | c2 | s3 | a2 |
| s3 | c1 | s2 | a3 |
| s2 | c2 | s3 | a2 |
| s3 | c1 | s2 | a3 |
| s2 | c1 | s_trap | a_trap |
| s_trap | c1 | s_trap | a_trap |
當某個狀態遇到不能識別的輸入時,就預設進入陷阱狀態,在陷阱狀態中,不論遇到怎樣的輸入都不能跳出。
為了表達上面這個自動機,我們定義它們的狀態和輸入型別:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef int state;typedef int condition;#define
STATES 4#define
STATE1 0#define
STATE2 1#define
STATE3 2#define
STATETRAP 3#define
CONDITIONS 2#define
CONDITION1 0#define
CONDITION2 1 |
總結一下,我們需要定義的有狀態、輸入、行為(動作+下一個狀態),其中,行為的個數是“狀態數*輸入數量”(其中有一些是重複的);其中動作一般來說可以用一個函式指標來實現。
二、具體設計
在嵌入式環境中,由於儲存空間比較小,因此把它們全部定義成巨集。此外,為了降低執行時間的不確定性,我們使用O(1)的跳轉表來模擬狀態的跳轉。
首先定義跳轉型別:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef void (*actiontype)(state
mystate, condition condition);typedef struct{ state
next; actiontype
action;}
trasition, * ptrasition; |
然後按照上圖中的跳轉關係,把三個跳轉加一個陷阱跳轉先定義出來:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
//
(s1, c1, s2, a1)trasition
t1 = { STATE2, action1};//
(s2, c2, s3, a2)trasition
t2 = { STATE3, action2};//
(s3, c1, s2, a3)trasition
t3 = { STATE2, action3};//
(s, c, trap, a1)trasition
tt = { STATETRAP, actiontrap}; |
其中的動作,由使用者自己完成,在這裡僅定義一條輸出語句。
|
1
2
3
4
|
void action1(State
state, Condition condition){ printf("Action
1 triggered.\n");} |
|
1
|
最後定義跳轉表: |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ptrasition
transition_table[STATES][CONDITIONS] = {/*
c1, c2*//*
s1 */&t1,
&tt,/*
s2 */&tt,
&t2,/*
s3 */&t3,
&tt,/*
st */&tt,
&tt,}; |
即可表達上文中的跳轉關係。
最後定義狀態機,如果不考慮多工請求,那麼狀態機僅需要儲存當前狀態便行了。例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef struct{ State
current;}
StateMachine, * pStateMachine;State
step(pStateMachine machine, Condition condition){ pTrasition
t = transition_table[machine->current][condition]; (*(t->action))(machine->current,
condition); machine->current
= t->next; return machine->current;} |
三、程式實現
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int state;
typedef int condition;
#define STATENUM 4
#define STATE1 0
#define STATE2 1
#define STATE3 2
#define STATETRAP 3
#define CONDITIONS 2
#define CONDITION1 0
#define CONDITION2 1
typedef void (* actiontype)(state mystate,condition mycondition);
typedef struct{
state next;
actiontype action;
}trasition, *ptrasition;
void action1(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void action2(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void action3(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void actiontrap(state mystate,condition myconditon);
trasition t1={
STATE2,action1
};
trasition t2={
STATE3,action2
};
trasition t3={
STATE2,action3
};
trasition tt={
STATETRAP,actiontrap
};
void action1(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action1 one triggered\n");
}
void action2(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action2 one triggered\n");
}
void action3(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action3 one triggered\n");
}
void actiontrap(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("actiontrap one triggered\n");
}
ptrasition transition_table[STATENUM][CONDITIONS] = {
/* c1, c2*/
/* s1 */&t1, &tt,
/* s2 */&tt, &t2,
/* s3 */&t3, &tt,
/* st */&tt, &tt,
};
typedef struct
{
state current;
} StateMachine, * pStateMachine;
state step(pStateMachine machine, condition mycondition)
{
ptrasition t = transition_table[machine->current][mycondition];
(*(t->action))(machine->current, mycondition);
machine->current = t->next;
printf("the current state is %d\n",t->next );
return machine->current;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
StateMachine mymachine;
mymachine.current=STATE1;
int mycon;
char ch;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&mycon);
step(&mymachine,mycon);
}
return 0;
}
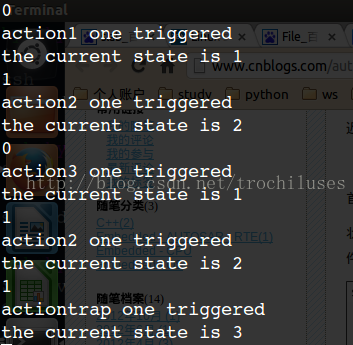
程式輸入與輸出結果示例:
相關文章
- 使用有限狀態自動機實現C語言的宣告解析器C語言
- 探索FSM (有限狀態機)應用
- [python]有限狀態機(FSM)簡單實現Python
- 用C語言實現有限狀態機--讀《C專家程式設計》C語言程式設計
- Unity——有限狀態機FSM修改Unity
- 有限狀態機(FSM)的使用
- FSM狀態機及C#反射實現邏輯C#反射
- 一個有限狀態機的C++實現C++
- Go中的有限狀態機FSM的詳細介紹Go
- Unity/C# 有限狀態機UnityC#
- 從Promise的實現來看有限狀態機Promise
- 使用有限狀態機原理實現英文分詞分詞
- Unity 中用有限狀態機來實現一個 AIUnityAI
- 前端狀態管理與有限狀態機前端
- JavaScript與有限狀態機JavaScript
- 發現C語言遞迴深度有限制C語言遞迴
- C 語言實現使用動態陣列實現迴圈佇列陣列佇列
- 作業系統:程式狀態轉換模擬,C語言實現作業系統C語言
- 23種設計模式 之 State模式(狀態模式)[C語言實現]設計模式C語言
- 在 .NET 中使用有限狀態機實現工作流建模 - Lloyd
- PHP 有限狀態機使用說明PHP
- 「譯」有限狀態機在 CSS 動畫中的應用CSS動畫
- 狀態模式(c++實現)模式C++
- C語言動態呼叫庫(轉)C語言
- C語言動態走迷宮C語言
- 試試用有限狀態機的思路來定義javascript元件JavaScript元件
- FSM自動售貨機 verilog 實現及 code 細節講解
- Spring狀態機(FSM),讓訂單狀態流轉如絲般順滑Spring
- 實戰併發-使用分散式快取和有限狀態機分散式快取
- C 語言實現使用靜態陣列實現迴圈佇列陣列佇列
- 用C語言實現八數碼問題C語言
- C語言(動態記憶體分配)C語言記憶體
- 從React Redux的實際業務場景來看有限狀態機ReactRedux
- c語言實用小程式C語言
- 掃雷--C語言實現C語言
- C語言實現DES加密C語言加密
- c語言實現階乘C語言
- C++容器巢狀實現動態二維陣列C++巢狀陣列