D3 selections選擇DOM元素以便可以對這些dom元素做相應的操作,比如:更改其style,修改其屬性,執行data-join操作,或者插入、刪除相應elements
比如,如果給定5個circles:
我們可以使用d3.selectAll來選中所有的circles,並且通過.style和.attr來修改其樣式或者屬性
d3.selectAll('circle')
.style('fill', 'orange')
.attr('r', function() {
return 10 + Math.random() * 40;
});

Making selections
D3有兩個函式來執行選擇操作:d3.select和d3.selectAll
d3.select進選中第一個匹配的元素。而d3.selectAll則選中所有匹配的元素。這兩個函式都接收一個引數來指定選擇器字串:和css選擇器相同語法 selector string.
比如我們使用css class類名來選擇
d3.selectAll('.item').
Modifying elements
一旦我們完成了選擇得到了selection,則我們可以使用selection的以下函式:
| Name | Behaviour | Example |
|---|---|---|
| .style | Update the style | d3.selectAll('circle').style('fill', 'red') |
| .attr | Update an attribute | d3.selectAll('rect').attr('width', 10) |
| .classed | Add/remove a class attribute | d3.select('.item').classed('selected', true) |
| .property | Update an element's property | d3.selectAll('.checkbox').property('checked', false) |
| .text | Update the text content | d3.select('div.title').text('My new book') |
| .html | Change the html content | d3.select('.legend').html('<div class="block"></div><div>0 - 10</div>') |
需要注意的是,無論是select還是selectAll返回的selection,執行上面的操作都將對所有選中的元素產生影響。
Updating selections with functions
除了傳入常量值到對應attr,style函式外,我們也可以傳入一個函式,,該函式輸出值作為attr, style最終設定的值:
d3.selectAll('circle')
.attr('cx', function(d, i) {
return i * 100;
});
該函式將自動接收(d,i). d 是joined在該元素上的資料 (參考 data joins section) 而 i 則是該元素在selection中對應的index
如果我們希望根據其在selection中的index來更改selection中的元素對應的x軸位置,比如我們希望水平佈置rect元素在不同的位置(而不是堆砌在一起):
d3.selectAll('rect')
.attr('x', function(d, i) {
return i * 40;
});
大多數情況下,傳入一個匿名函式就好,但是我們也可以使用命名的
function positionRects(d, i) { return i * 40; } d3.selectAll('rect') .attr('x',
Handling events
我們可以通過selection.on()來為selection中的elements新增事件處理函式,而這個事件處理函式,同樣地會傳入d和i兩個引數以方便處理。同樣地,d是本元素joined data,i則是本元素在selection中的index值,下面是列出的主要event時間
| Event name | Description |
|---|---|
| click | Element has been clicked |
| mouseenter | Mouse pointer has moved onto the element |
| mouseover | Mouse pointer has moved onto the element or its children |
| mouseleave | Mouse pointer has moved off the element |
| mouseout | Mouse pointer has moved off the element or its children |
| mousemove | Mouse pointer has moved over the element |
比如下面我們寫一個小的程式碼,實現當點選後就修改其text指明是第幾個元素被點選
d3.selectAll('circle')
.on('click', function(d, i) {
d3.select('.status')
.text('You clicked on circle ' + i);
});
需要注意的是,在事件回撥函式中,this的值是DOM 元素本身,和selection無關!如果要使用d3對該dom操作,必須先做select操作:
d3.selectAll('circle')
.on('click', function(d, i) {
d3.select(this) // this指被點選的dom元素,而不是d3 selection!
.style('fill', 'orange');
});
Inserting and removing elements
我們看一個例子:3個g元素,每個g都包含了一個circle:
<g class="item" transform="translate(0, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
</g>
<g class="item" transform="translate(120, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
</g>
<g class="item" transform="translate(240, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
</g>我們可以插入一個 text element到每個g元素中:
d3.selectAll('g.item')
.append('text')
.text(function(d, i) {
return i + 1;
});最終的結果是在每個g.item元素中追加了一個text元素,其text值為對應i的值:
<g class="item" transform="translate(0, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
<text>1</text>
</g>
<g class="item" transform="translate(120, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
<text>2</text>
</g>
<g class="item" transform="translate(240, 0)">
<circle r="40" />
<text>3</text>
</g>.remove 刪除selection中的元素:
d3.selectAll('circle')
.remove();Chaining
絕大部分selection的方法都仍然返回selection本身,因此這意味著我們可以鏈式方法繼續呼叫其他的方法:
d3.selectAll('circle')
.style('fill', 'orange')
.attr('r', 20)
.on('click', function(d, i) {
d3.select('.status')
.text('You clicked on circle ' + i);
});Each and call
.each 允許對每個selection中的每個元素執行一段函式功能(同樣傳入d,i, this引數可以使用), .call 則允許對 selection itself. 執行相應的函式功能
看下面的例子:
function addNumberedCircle(d, i) { d3.select(this) .append('circle') .attr('r', 40); d3.select(this) .append('text') .text(i + 1) .attr('y', 50) .attr('x', 30); } d3.selectAll('g.item') .each(addNumberedCircle);
再看一個.each 呼叫的例子
d3.selectAll('circle')
.each(function(d, i) {
var odd = i % 2 === 1;
d3.select(this)
.style('fill', odd ? 'orange' : '#ddd') // 對奇偶元素使用不用的顏色和半徑大小
.attr('r', odd ? 40 : 20);
});
而.call則傳入selection本身,這實際上是javascript本身的特性!
function addNumberedCircle(selection) { selection .append('circle') .attr('r', 40); selection .append('text') .text(function(d, i) { return i + 1; }) .attr('y', 50) .attr('x', 30); } d3.selectAll('g.item') .call(addNumberedCircle);
Filtering and sorting selections
We can filter a selection using .filter. A function is usually passed into .filter which returns true if the element should be included. .filter returns the filtered selection.
我們也可以使用selection的.filter方法來過濾對應selection中的元素。通常我們通過傳入一個函式(該函式同樣具有d,i,this可以訪問)給到.filter方法來告訴d3,如果該函式返回true則該i元素將被包含住,如果返回false,則不被包含在filter的返回selection中,而.filter則返回filtered selection.
比如下面的例子中我們對偶數的元素來著色為orange色,奇數元素作色為藍色:
d3.selectAll('circle')
.filter(function(d, i) { // filter返回偶數的元素
return i % 2 === 0;
})
.style('fill', 'orange');// 偶數元素作色為橘色
d3.selectAll('circle')
.filter(function(d, i) { // filter返回奇數的元素
return i % 2 === 1;
})
.style('fill', 'blue'); // 奇數元素作色為藍色
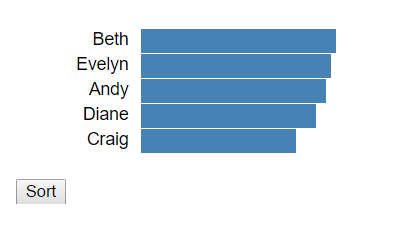
.sort()排序只有在有joined資料時才有意義。我們可以傳入一個比較函式來呼叫.sort對selection中的元素執行排序操作。比較函式本身有兩個引數,通常為a,b分別代表了被比較的兩個元素上繫結的datam.如果比較函式返回負值,那麼a將在b之前,如果是正,則a放在b之後。
下面假定selection上有以下繫結的資料:
[ {"name":"Andy","score":37}, {"name":"Beth","score":39}, {"name":"Craig","score":31}, {"name":"Diane","score":35}, {"name":"Evelyn","score":38} ]
d3.selectAll('.person')
.sort(function(a, b) {
return b.score - a.score;
});
myData = [ { "name": "Andy", "score": 37 }, { "name": "Beth", "score": 39 }, { "name": "Craig", "score": 31 }, { "name": "Diane", "score": 35 }, { "name": "Evelyn", "score": 38 } ]; var barWidth = 400; var barScale = d3.scaleLinear().domain([0, 100]).range([0, barWidth]); var u = d3.select('#wrapper') .selectAll('.person') .data(myData); var entering = u.enter() .append('div') .classed('person', true); entering.append('div') .classed('label', true) .text(function(d) { return d.name; }); entering.append('div') .classed('bar', true) .style('width', function(d) { return barScale(d.score) + 'px'; }); function sort() { d3.selectAll('.person') .sort(function(a, b) { return b.score - a.score; }); }