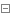
1 public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
2 if (str == null)
3 return appendNull();
4 int len = str.length();
5 //檢查char[]陣列是否需要擴容,擴容,並將原來的資料copy進去新擴容的陣列中
6 ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
7 //將新新增的資料新增到StringBuilder中的char[]陣列中,實現字串的新增
8 str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
9 count += len;
10 return this;
11 }
12
13
14 /**
15 *元陣列char[]的擴容過程
16 */
17 void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
18 int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
19 if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
20 newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
21 if (newCapacity < 0) {
22 if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
23 throw new OutOfMemoryError();
24 newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
25 }
26 value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
27 }
28
29
30 /**
31 *擴容實現
32 */
33 public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) {
34 char[] copy = new char[newLength];
35 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
36 Math.min(original.length, newLength));
37 return copy;
38 }