資料結構與演算法——有向無環圖的拓撲排序C++實現
拓撲排序簡介:
拓撲排序是對有向無環圖的頂點的一種排序,它使得如果存在一條從Vi到Vj的路徑,那麼在排序中Vi在Vj的前面。
如果圖中含有迴路,那麼拓撲排序是不可能的。此外,拓撲排序不必是唯一的,任何合理的排序都可以。
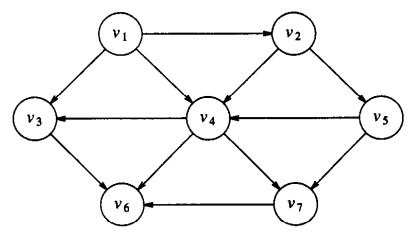
對於上面的無環圖:v1,v2,v5,v4,v3,v7,v6和v1,v2,v5,v4,v7,v3,v6都是合理的拓撲排序。
一個簡單的求拓撲排序的思路:
1、先找出任意一個沒有入邊的頂點
2、然後顯出該點,並將它和它鄰接的所有的邊全部刪除。
3、然後,對圖中其它部分做同樣的處理。
圖用鄰接表表示法來儲存:
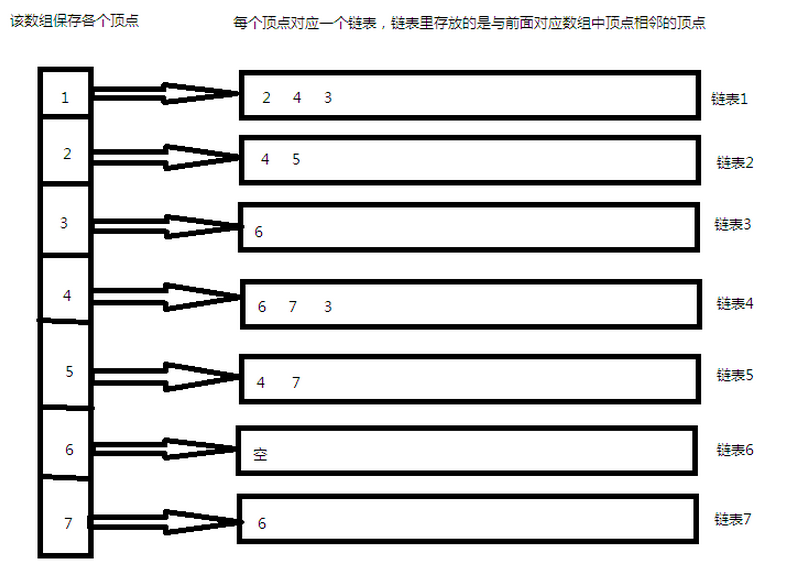
左邊的陣列此時就有用了,用來儲存每個頂點的資訊,該陣列中每個元素的資料結構為:
//儲存每個頂點資訊的資料結構
struct GraphNode{
int vertex;//當前頂點的標號
int inDegree;//當前頂點的入度
int topNum;//當前頂點的拓撲排序的順序標號
};圖的鄰接表示法的類的介面:
/*******************************************************
* 類名稱: 鄰接表圖
********************************************************/
class Graph{
private:
int edge_num;//圖邊的個數
int vertex_num;//圖的頂點數目
list<Node> * graph_list;//鄰接表
vector<GraphNode> nodeArr;//儲存每個頂點資訊的陣列
public:
Graph(){}
Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum);
~Graph();
void print();
vector<int> topoSort();//拓撲排序
private:
vector<int> get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns);
void addEdge(char* graph[], int columns);
};拓撲排序成員函式:
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:topoSort()
* 功能描述:對圖中的頂點進行拓撲排序
* 引數列表:無
* 返回結果:返回頂點拓撲排序之後的結果
*************************************************/
vector<int> Graph::topoSort()
{
vector<int> topoSortArr;
for(int count = 0; count < vertex_num; ++count){
//找到一個入度為0的頂點
int i;
for(i = 0; i < vertex_num; ++i){
if((nodeArr[i].inDegree == 0)&&(nodeArr[i].vertex != -1))
break;
}
if(i == vertex_num)
break;
//此時頂點i的入度為0
//刪除該點和刪除與該點相鄰的邊
//並將與頂點i相連的頂點的入度減1
nodeArr[i].inDegree = -1;
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[i].begin(); it != graph_list[i].end(); ++it){
nodeArr[(*it).vertex].inDegree--;
}
topoSortArr.push_back(i);
}
return topoSortArr;
}測試函式:
1、讀取圖檔案中的資料,圖中的資料格式為下面所示:
0,0,1,1
1,0,2,2
2,0,3,1
第1列是邊號,第2列是邊的起點,第3列是邊的終點,第4列是邊的權重。
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:read_file
* 功能描述: 讀取檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是將檔案讀取的圖資訊儲存到buff指向的二維陣列中
* spec是檔案中圖最大允許的邊的個數
* filename是要開啟的圖檔案
* 返回結果:無
*****************************************************************/
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to open file %s, %s.\n", filename, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
printf("Open file %s OK.\n", filename);
char line[MAX_LINE_LEN + 2];
unsigned int cnt = 0;
while ((cnt < spec) && !feof(fp))
{
line[0] = 0;
fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2, fp);
if (line[0] == 0) continue;
buff[cnt] = (char *)malloc(MAX_LINE_LEN + 2);
strncpy(buff[cnt], line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2 - 1);
buff[cnt][4001] = 0;
cnt++;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("There are %d lines in file %s.\n", cnt, filename);
return cnt;
}2、釋放剛才讀取的圖的資訊
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:release_buff
* 功能描述: 釋放剛才讀取的檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是指向檔案讀取的圖資訊
* valid_item_num是指圖中邊的個數
* 返回結果:void
*****************************************************************/
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < valid_item_num; i++)
free(buff[i]);
}3、主測試函式
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *topo[5000];
int edge_num;
char *demand;
int demand_num;
char *topo_file = argv[1];
edge_num = read_file(topo, 5000, topo_file);
if (edge_num == 0)
{
printf("Please input valid topo file.\n");
return -1;
}
Graph G(topo, edge_num);
G.print();
vector<int> topoSortArr = G.topoSort();
cout << "拓撲排序的結果: ";
for(unsigned i = 0; i < topoSortArr.size(); ++i)
cout << topoSortArr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
release_buff(topo, edge_num);
return 0;
}圖類的原始碼:
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 600
//儲存每個頂點資訊的資料結構
struct GraphNode{
int vertex;//當前頂點的標號
int inDegree;//當前頂點的入度
int topNum;//當前頂點的拓撲排序的順序標號
};
//圖節點資訊
typedef struct Node{
int edge_num;//邊號
int src;//源點
int vertex;//自身
int weight;//邊的權重
}Node;
/*******************************************************
* 類名稱: 鄰接表圖
********************************************************/
class Graph{
private:
int edge_num;//圖邊的個數
int vertex_num;//圖的頂點數目
list<Node> * graph_list;//鄰接表
vector<GraphNode> nodeArr;//儲存每個頂點資訊的陣列
public:
Graph(){}
Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum);
~Graph();
void print();
vector<int> topoSort();//拓撲排序
private:
vector<int> get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns);
void addEdge(char* graph[], int columns);
};
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:topoSort()
* 功能描述:對圖中的頂點進行拓撲排序
* 引數列表:無
* 返回結果:返回頂點拓撲排序之後的結果
*************************************************/
vector<int> Graph::topoSort()
{
vector<int> topoSortArr;
for(int count = 0; count < vertex_num; ++count){
//找到一個入度為0的頂點
int i;
for(i = 0; i < vertex_num; ++i){
if((nodeArr[i].inDegree == 0)&&(nodeArr[i].vertex != -1))
break;
}
if(i == vertex_num)
break;
//此時頂點i的入度為0
//刪除該點和刪除與該點相鄰的邊
//並將與頂點i相連的頂點的入度減1
nodeArr[i].inDegree = -1;
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[i].begin(); it != graph_list[i].end(); ++it){
nodeArr[(*it).vertex].inDegree--;
}
topoSortArr.push_back(i);
}
return topoSortArr;
}
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:print
* 功能描述:將圖的資訊以鄰接表的形式輸出到標準輸出
* 引數列表:無
* 返回結果:無
*************************************************/
void Graph::print()
{
cout << "******************************************************************" << endl;
//for(int i = 0 ; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; ++i){
for(int i = 0 ; i < vertex_num; ++i){
if(graph_list[i].begin() != graph_list[i].end()){
cout << i << "-->";
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[i].begin(); it != graph_list[i].end(); ++it){
cout << (*it).vertex << "(邊號:" << (*it).edge_num << ",權重:" << (*it).weight << ")-->";
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
}
cout << "******************************************************************" << endl;
}
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:get_graph_value
* 功能描述:將圖的每一條邊的資訊儲存到一個陣列中
* 引數列表: graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
columns:圖的第幾條邊
* 返回結果:無
*************************************************/
vector<int> Graph::get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns)
{
vector<int> v;
char buff[20];
int i = 0, j = 0, val;
memset(buff, 0, 20);
while((graph[columns][i] != '\n') && (graph[columns][i] != '\0')){
if(graph[columns][i] != ','){
buff[j] = graph[columns][i];
j++;
}
else{
j = 0;
val = atoi(buff);
v.push_back(val);
memset(buff, 0, 20);
}
i++;
}
val = atoi(buff);
v.push_back(val);
return v;
}
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:addEdge
* 功能描述:將圖的每一條邊的資訊加入圖的鄰接表中
* 引數列表:graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
columns:圖的第幾條邊
* 返回結果:無
*************************************************/
void Graph::addEdge(char* graph[], int columns)
{
Node node;
vector<int> v = get_graph_value(graph, columns);
node.edge_num = v[0];
node.src = v[1];
node.vertex = v[2];
node.weight = v[3];
//根據頂點的標號,求的總的頂點數目
if(node.vertex > vertex_num)
vertex_num = node.vertex;
//要考慮重複的邊,但是邊的權重不一樣
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[node.src].begin(); it != graph_list[node.src].end(); ++it){
if((*it).vertex == node.vertex){
if((*it).weight > node.weight){
(*it).weight = node.weight;
}
return;
}
}
//將資訊寫入到儲存每個頂點的陣列中
nodeArr[node.src].vertex = node.src;
nodeArr[node.vertex].vertex = node.vertex;
nodeArr[node.vertex].inDegree++;//入度加1
graph_list[node.src].push_back(node);
}
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:建構函式
* 功能描述:以鄰接表的形式儲存圖的資訊,並儲存必須經過的頂點
* 引數列表:graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
edgenum:圖的邊的個數
* 返回結果:無
*************************************************/
Graph::Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum):nodeArr(MAX_VERTEX_NUM)
{
edge_num = edgenum;
vertex_num = 0;
graph_list = new list<Node>[MAX_VERTEX_NUM+1];
//對儲存頂點資訊的陣列進行初始化,如果vertext=-1表示沒有該頂點
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; ++i){
nodeArr[i].vertex = -1;
nodeArr[i].inDegree = 0;
nodeArr[i].topNum = -1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < edgenum; ++i){
addEdge(graph, i);
}
vertex_num++;
}
/*************************************************
* 函式名稱:解構函式
* 功能描述:釋放動態分配的記憶體
* 引數列表:無
* 返回結果:無
*************************************************/
Graph::~Graph()
{
delete[] graph_list;
}
#endif
測試函式的原始碼:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "graphTopoSort.h"
#define MAX_LINE_LEN 4000
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename);
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *topo[5000];
int edge_num;
char *demand;
int demand_num;
char *topo_file = argv[1];
edge_num = read_file(topo, 5000, topo_file);
if (edge_num == 0)
{
printf("Please input valid topo file.\n");
return -1;
}
Graph G(topo, edge_num);
G.print();
vector<int> topoSortArr = G.topoSort();
cout << "拓撲排序的結果: ";
for(unsigned i = 0; i < topoSortArr.size(); ++i)
cout << topoSortArr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
release_buff(topo, edge_num);
return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:read_file
* 功能描述: 讀取檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是將檔案讀取的圖資訊儲存到buff指向的二維陣列中
* spec是檔案中圖最大允許的邊的個數
* filename是要開啟的圖檔案
* 返回結果:無
*****************************************************************/
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to open file %s, %s.\n", filename, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
printf("Open file %s OK.\n", filename);
char line[MAX_LINE_LEN + 2];
unsigned int cnt = 0;
while ((cnt < spec) && !feof(fp))
{
line[0] = 0;
fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2, fp);
if (line[0] == 0) continue;
buff[cnt] = (char *)malloc(MAX_LINE_LEN + 2);
strncpy(buff[cnt], line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2 - 1);
buff[cnt][4001] = 0;
cnt++;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("There are %d lines in file %s.\n", cnt, filename);
return cnt;
}
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:release_buff
* 功能描述: 釋放剛才讀取的檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是指向檔案讀取的圖資訊
* valid_item_num是指圖中邊的個數
* 返回結果:void
*****************************************************************/
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < valid_item_num; i++)
free(buff[i]);
}
測試用例:
0,1,2,1
1,1,3,1
2,1,4,1
3,2,4,1
4,2,5,1
5,3,6,1
6,4,3,1
7,4,6,1
8,4,7,1
9,5,4,1
10,5,7,1
11,7,6,1執行結果:

相關文章
- C語言實現有向無環圖的拓撲排序演算法C語言排序演算法
- 拓撲排序 (BFS )DAG (有向無環圖)排序
- 有向圖的拓撲排序——DFS排序
- C++輸出有向無環圖的所有拓撲序列C++
- 演算法資料結構 | 圖論基礎演算法——拓撲排序演算法資料結構圖論排序
- 圖的拓撲排序詳解與實現排序
- POJ1094[有向環 拓撲排序]排序
- 圖解拓撲排序+程式碼實現圖解排序
- 演算法-圖論-拓撲排序演算法圖論排序
- DFS實現拓撲排序排序
- 圖論——拓撲排序圖論排序
- 拓撲排序小結排序
- Reward (圖論+拓撲排序)圖論排序
- 資料結構與演算法——無權最短路徑演算法的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——插入排序以及C++函式模板實現資料結構演算法排序C++函式
- AOV網與拓撲排序排序
- 演算法與資料結構——選擇排序(c++)演算法資料結構排序C++
- 圖(3)--拓撲排序與關鍵路徑排序
- 資料結構學習(C++)——圖【3】(無向圖)(上) (轉)資料結構C++
- 資料結構學習(C++)——圖【3】(無向圖)(下) (轉)資料結構C++
- 拓撲排序排序
- 資料結構與演算法——B樹的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 【資料結構】 各種排序演算法的實現資料結構排序演算法
- 資料結構與演算法——AVL樹類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- vue 實現動態拓撲圖Vue
- 資料結構與演算法——排序資料結構演算法排序
- 資料結構與演算法——圖的鄰接表表示法類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 拓撲排序,YYDS排序
- 拓撲排序模板排序
- 資料結構與演算法——普通樹的定義與C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 網路拓撲結構
- 資料結構與演算法——基數排序簡單Java實現資料結構演算法排序Java
- 資料結構與演算法——不相交集類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構和演算法(Golang實現)(25)排序演算法-快速排序資料結構演算法Golang排序
- 資料結構與演算法(八):排序資料結構演算法排序
- 資料結構與演算法——堆排序資料結構演算法排序
- 【資料結構與演算法】堆排序資料結構演算法排序
- 資料結構與演算法之排序資料結構演算法排序