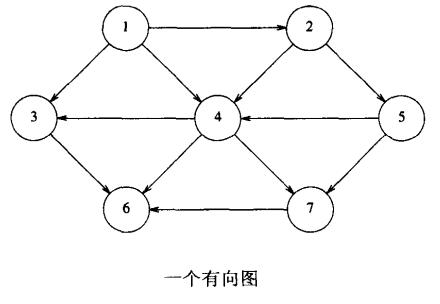
資料結構與演算法——圖的鄰接表表示法類的C++實現
圖的表示:
鄰接矩陣表示法:
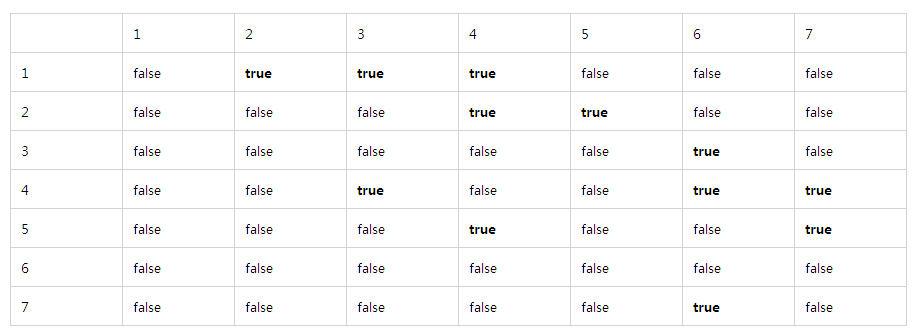
對於上面一個有向圖的一種簡單的表示方法是使用二維陣列,稱為鄰接矩陣表示法。
如果是無向圖,對於每條邊(u, v),將二維陣列元素arr[u][v]值設定為true;否則該陣列元素為false;
如果是有向圖,對於每條邊(u, v),將二維陣列元素arr[u][v]值設定為該邊的權重;否則該陣列元素設定為一個很大的數值或是一個很小的陣列(根據具體情景設定);
雖然鄰接矩陣表示法比較簡單,但是需要的空間比較大,適合於稠密型別的圖。
鄰接表表示法:
另一種表示方法是使用鄰接表表示法,該方法適合於稀疏型別的圖。

其實左邊的陣列也可以不用,如果有需要的話可以加上用來儲存各個頂點的資訊。一般實現的話根據右邊連結串列陣列的順序就可以知道每個頂點對應的連結串列。
圖中節點的資料結構:
//圖節點資訊
typedef struct Node{
int edge_num;//邊號
int src;//源點
int vertex;//自身
int weight;//邊的權重
}Node; 圖的鄰接表表示法的類介面:
/*******************************************************
* 類名稱: 鄰接表圖
********************************************************/
class Graph{
private:
int edge_num;//圖邊的個數
int vertex_num;//圖的頂點數目
list<Node> * graph_list;//鄰接表
public:
Graph(){}
Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum);
~Graph();
void print();//以鄰接表的形式列印圖資訊
private:
vector<int> get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns);//獲得每條邊的資料
void addEdge(char* graph[], int columns);
};測試函式:
1、讀取圖檔案中的資料,圖中的資料格式為下面所示:
0,0,1,1
1,0,2,2
2,0,3,1
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:read_file
* 功能描述: 讀取檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是將檔案讀取的圖資訊儲存到buff指向的二維陣列中
* spec是檔案中圖最大允許的邊的個數
* filename是要開啟的圖檔案
* 返回結果:無
*****************************************************************/
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to open file %s, %s.\n", filename, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
printf("Open file %s OK.\n", filename);
char line[MAX_LINE_LEN + 2];
unsigned int cnt = 0;
while ((cnt < spec) && !feof(fp))
{
line[0] = 0;
fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2, fp);
if (line[0] == 0) continue;
buff[cnt] = (char *)malloc(MAX_LINE_LEN + 2);
strncpy(buff[cnt], line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2 - 1);
buff[cnt][4001] = 0;
cnt++;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("There are %d lines in file %s.\n", cnt, filename);
return cnt;
}2、釋放剛才讀取的檔案中的圖的資料資訊
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:release_buff
* 功能描述: 釋放剛才讀取的檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是指向檔案讀取的圖資訊
* valid_item_num是指圖中邊的個數
* 返回結果:void
*****************************************************************/
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < valid_item_num; i++)
free(buff[i]);
}3、主測試函式
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *topo[5000];
int edge_num;
char *demand;
int demand_num;
char *topo_file = argv[1];
edge_num = read_file(topo, 5000, topo_file);
if (edge_num == 0)
{
printf("Please input valid topo file.\n");
return -1;
}
Graph G(topo, edge_num);//建立一個圖物件G
G.print();//以鄰接表的形式列印圖資訊
release_buff(topo, edge_num);
return 0;
}圖的鄰接表表示法類的原始碼:
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 600
//圖節點資訊
typedef struct Node{
int edge_num;//邊號
int src;//源點
int vertex;//自身
int weight;//邊的權重
}Node;
/*******************************************************
* 類名稱: 鄰接表圖
********************************************************/
class Graph{
private:
int edge_num;//圖邊的個數
int vertex_num;//圖的頂點數目
list<Node> * graph_list;//鄰接表
public:
Graph(){}
Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum);
~Graph();
void print();//以鄰接表的形式列印圖資訊
private:
vector<int> get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns);//獲得每條邊的資料
void addEdge(char* graph[], int columns);
};
/*************************************************
函式名稱:print
功能描述:將圖的資訊以鄰接表的形式輸出到標準輸出
引數列表:無
返回結果:無
*************************************************/
void Graph::print()
{
cout << "******************************************************************" << endl;
//for(int i = 0 ; i < MAX_VERTEX_NUM; ++i){
for(int i = 0 ; i < vertex_num; ++i){
if(graph_list[i].begin() != graph_list[i].end()){
cout << i << "-->";
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[i].begin(); it != graph_list[i].end(); ++it){
cout << (*it).vertex << "(邊號:" << (*it).edge_num << ",權重:" << (*it).weight << ")-->";
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
}
cout << "******************************************************************" << endl;
}
/*************************************************
函式名稱:get_graph_value
功能描述:將圖的每一條邊的資訊儲存到一個陣列中
引數列表: graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
columns:圖的第幾條邊
返回結果:無
*************************************************/
vector<int> Graph::get_graph_value(char* graph[], int columns)
{
vector<int> v;
char buff[20];
int i = 0, j = 0, val;
memset(buff, 0, 20);
while((graph[columns][i] != '\n') && (graph[columns][i] != '\0')){
if(graph[columns][i] != ','){
buff[j] = graph[columns][i];
j++;
}
else{
j = 0;
val = atoi(buff);
v.push_back(val);
memset(buff, 0, 20);
}
i++;
}
val = atoi(buff);
v.push_back(val);
return v;
}
/*************************************************
函式名稱:addEdge
功能描述:將圖的每一條邊的資訊加入圖的鄰接表中
引數列表:graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
columns:圖的第幾條邊
返回結果:無
*************************************************/
void Graph::addEdge(char* graph[], int columns)
{
Node node;
vector<int> v = get_graph_value(graph, columns);
node.edge_num = v[0];
node.src = v[1];
node.vertex = v[2];
node.weight = v[3];
if(node.vertex > vertex_num)
vertex_num = node.vertex;
//要考慮重複的邊,但是邊的權重不一樣
for(list<Node>::iterator it = graph_list[node.src].begin(); it != graph_list[node.src].end(); ++it){
if((*it).vertex == node.vertex){
if((*it).weight > node.weight){
(*it).weight = node.weight;
}
return;
}
}
graph_list[node.src].push_back(node);
}
/*************************************************
函式名稱:建構函式
功能描述:以鄰接表的形式儲存圖的資訊,並儲存必須經過的頂點
引數列表:graph:指向圖資訊的二維陣列
edgenum:圖的邊的個數
返回結果:無
*************************************************/
Graph::Graph(char* graph[], int edgenum)
{
edge_num = edgenum;
vertex_num = 0;
graph_list = new list<Node>[MAX_VERTEX_NUM+1];
for(int i = 0; i < edgenum; ++i){
addEdge(graph, i);
}
vertex_num++;
}
/*************************************************
函式名稱:解構函式
功能描述:釋放動態分配的記憶體
引數列表:無
返回結果:無
*************************************************/
Graph::~Graph()
{
delete[] graph_list;
}
#endif
測試函式的原始碼:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "graph.h"
#define MAX_LINE_LEN 4000
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename);
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *topo[5000];
int edge_num;
char *demand;
int demand_num;
char *topo_file = argv[1];
edge_num = read_file(topo, 5000, topo_file);
if (edge_num == 0)
{
printf("Please input valid topo file.\n");
return -1;
}
Graph G(topo, edge_num);//建立一個圖物件G
G.print();//以鄰接表的形式列印圖資訊
release_buff(topo, edge_num);
return 0;
}
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:read_file
* 功能描述: 讀取檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是將檔案讀取的圖資訊儲存到buff指向的二維陣列中
* spec是檔案中圖最大允許的邊的個數
* filename是要開啟的圖檔案
* 返回結果:無
*****************************************************************/
int read_file(char ** const buff, const unsigned int spec, const char * const filename)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to open file %s, %s.\n", filename, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
printf("Open file %s OK.\n", filename);
char line[MAX_LINE_LEN + 2];
unsigned int cnt = 0;
while ((cnt < spec) && !feof(fp))
{
line[0] = 0;
fgets(line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2, fp);
if (line[0] == 0) continue;
buff[cnt] = (char *)malloc(MAX_LINE_LEN + 2);
strncpy(buff[cnt], line, MAX_LINE_LEN + 2 - 1);
buff[cnt][4001] = 0;
cnt++;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("There are %d lines in file %s.\n", cnt, filename);
return cnt;
}
/****************************************************************
* 函式名稱:release_buff
* 功能描述: 釋放剛才讀取的檔案中的圖的資料資訊
* 引數列表: buff是指向檔案讀取的圖資訊
* valid_item_num是指圖中邊的個數
* 返回結果:void
*****************************************************************/
void release_buff(char ** const buff, const int valid_item_num)
{
for (int i = 0; i < valid_item_num; i++)
free(buff[i]);
}
測試用例0:
0,0,1,1
1,0,2,2
2,0,3,1
3,2,1,3
4,3,1,1
5,2,3,1
6,3,2,1
7,3,0,1測試用例1:
0,0,13,15
1,0,8,17
2,0,19,1
3,0,4,8
4,1,0,4
5,2,9,19
6,2,15,8
7,3,0,14
8,3,11,12
9,4,1,15
10,4,5,17
11,5,8,18
12,5,9,14
13,5,6,2
14,6,17,4
15,7,13,1
16,7,16,19
17,8,6,1
18,8,12,17
19,9,14,11
20,10,12,1
21,11,7,12
22,11,4,7
23,12,14,5
24,13,17,12
25,13,4,2
26,14,19,9
27,15,10,14
28,15,18,2
29,16,8,1
30,17,9,14
31,17,19,3
32,17,18,10
33,18,15,8
34,18,3,8
35,19,18,12
36,2,3,20
37,3,5,20
38,5,7,20
39,7,11,20
40,11,13,20
41,17,11,20
42,11,19,20
43,17,5,20
44,5,19,20執行結果:
root@linux_ever:~/linux_ever/algorithm/graph_ch9# ls
case0 case1 graph.h testGraph testGraph.cpp
root@linux_ever:~/linux_ever/algorithm/graph_ch9# ./testGraph ./case0/topo.csv
Open file ./case0/topo.csv OK.
There are 8 lines in file ./case0/topo.csv.
******************************************************************
0-->1(邊號:0,權重:1)-->2(邊號:1,權重:2)-->3(邊號:2,權重:1)-->NULL
2-->1(邊號:3,權重:3)-->3(邊號:5,權重:1)-->NULL
3-->1(邊號:4,權重:1)-->2(邊號:6,權重:1)-->0(邊號:7,權重:1)-->NULL
******************************************************************
root@linux_ever:~/linux_ever/algorithm/graph_ch9# ./testGraph ./case1/topo.csv
Open file ./case1/topo.csv OK.
There are 45 lines in file ./case1/topo.csv.
******************************************************************
0-->13(邊號:0,權重:15)-->8(邊號:1,權重:17)-->19(邊號:2,權重:1)-->4(邊號:3,權重:8)-->NULL
1-->0(邊號:4,權重:4)-->NULL
2-->9(邊號:5,權重:19)-->15(邊號:6,權重:8)-->3(邊號:36,權重:20)-->NULL
3-->0(邊號:7,權重:14)-->11(邊號:8,權重:12)-->5(邊號:37,權重:20)-->NULL
4-->1(邊號:9,權重:15)-->5(邊號:10,權重:17)-->NULL
5-->8(邊號:11,權重:18)-->9(邊號:12,權重:14)-->6(邊號:13,權重:2)-->7(邊號:38,權重:20)-->19(邊號:44,權重:20)-->NULL
6-->17(邊號:14,權重:4)-->NULL
7-->13(邊號:15,權重:1)-->16(邊號:16,權重:19)-->11(邊號:39,權重:20)-->NULL
8-->6(邊號:17,權重:1)-->12(邊號:18,權重:17)-->NULL
9-->14(邊號:19,權重:11)-->NULL
10-->12(邊號:20,權重:1)-->NULL
11-->7(邊號:21,權重:12)-->4(邊號:22,權重:7)-->13(邊號:40,權重:20)-->19(邊號:42,權重:20)-->NULL
12-->14(邊號:23,權重:5)-->NULL
13-->17(邊號:24,權重:12)-->4(邊號:25,權重:2)-->NULL
14-->19(邊號:26,權重:9)-->NULL
15-->10(邊號:27,權重:14)-->18(邊號:28,權重:2)-->NULL
16-->8(邊號:29,權重:1)-->NULL
17-->9(邊號:30,權重:14)-->19(邊號:31,權重:3)-->18(邊號:32,權重:10)-->11(邊號:41,權重:20)-->5(邊號:43,權重:20)-->NULL
18-->15(邊號:33,權重:8)-->3(邊號:34,權重:8)-->NULL
19-->18(邊號:35,權重:12)-->NULL
******************************************************************輸出結果的每一行的第一列表示各個頂點的標號。
比如:
0-->13(邊號:0,權重:15)-->8(邊號:1,權重:17)-->19(邊號:2,權重:1)-->4(邊號:3,權重:8)-->NULL
上面表示,頂點0到13的邊的邊號為0,權重為15。頂點0到頂點8的邊的邊號為1,權重為17。頂點0到頂點19的邊的邊號為2,權重為1。頂點0到頂點4的邊的邊號為3,權重為8。
相關文章
- C#實現圖的鄰接矩陣和鄰接表結構C#矩陣
- 圖的儲存結構——鄰接矩陣與鄰接表矩陣
- 資料結構與演算法——表示式樹類的C++實現(二叉樹)資料結構演算法C++二叉樹
- 資料結構與演算法——AVL樹類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——雜湊表類的C++實現(探測雜湊表)資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——雜湊表類的C++實現(分離連結雜湊表)資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——不相交集類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構作業——用鄰接表表示無向網資料結構
- 第6章 圖的學習總結(鄰接矩陣&鄰接表)矩陣
- 資料結構與演算法——B樹的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 演算法與資料結構之圖的表示與遍歷演算法資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法——二叉查詢樹類的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——普通樹的定義與C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構:圖的表示資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法——有向無環圖的拓撲排序C++實現資料結構演算法排序C++
- 資料結構與演算法——優先佇列類的C++實現(二叉堆)資料結構演算法佇列C++
- 【資料結構】實現順序表(c++)資料結構C++
- 資料結構與演算法分析-分離連結雜湊表的實現資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法——無權最短路徑演算法的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 資料結構與演算法——最短路徑Dijkstra演算法的C++實現資料結構演算法C++
- 我接觸過的前端資料結構與演算法前端資料結構演算法
- 圖的基本儲存的基本方式二—鄰接表(連結串列)
- 鄰接表
- 資料結構和演算法的圖解和實現資料結構演算法圖解
- JavaScript資料結構——圖的實現JavaScript資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法---盛最多水的容器、接雨水資料結構演算法
- 圖的深度遍歷(C語言)鄰接矩陣表示C語言矩陣
- dijkstra迪傑斯特拉演算法(鄰接表法)演算法
- 資料結構筆記(一)——C語言實現鄰接矩陣儲存的無向圖,判斷是否為連通圖,並且實現最小生成樹Prim演算法資料結構筆記C語言矩陣演算法
- 資料結構與演算法:圖形結構資料結構演算法
- 資料結構——單連結串列的C++實現資料結構C++
- 樹形結構資料儲存方案(一):鄰接列表模式模式
- 圖的鄰接表演算法---(附完整程式碼)演算法
- 小話資料結構-圖 (聚焦與於實現的理解)資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法 | 棧的實現及應用資料結構演算法
- 【資料結構】順序棧的實現(c++)資料結構C++
- 資料結構與演算法——常用高階資料結構及其Java實現資料結構演算法Java
- 坐在馬桶上看演算法(9):巧妙的鄰接表演算法