安卓開發之服務Service
一、Service是什麼?
- Service是一個應用元件,它用來在後臺完成一個時間跨度比較大的工作,且沒有關聯任何介面。(生命週期在應用程式程式的主執行緒執行)
- 一個Service可以完成的工作:訪問網路(在Service中啟動分執行緒)、播放音樂、檔案IO操作、大資料量的資料庫操作等。如果需要在Service中處理一些網路連線等耗時的操作,那麼應該將這些任務放在分執行緒中處理,避免在主執行緒中阻塞使用者介面。
- 特點:Service在後臺執行,不用與使用者進行互動。即使應用退出,服務也不會停止。當應用程式被殺死時(例如一鍵清理),服務便會停止。
二、Service的分類
- Local Service (本地服務)
Service物件與Service的啟動者在同個程式中進行,兩者的通訊是程式內的通訊。 - Remote Service (遠端服務)
Service物件與Service的啟動者不在同個程式中進行,這時存在一個程式間的通訊問題,Android專門為此設計了AIDL來實現程式間的通訊。
三、Service的定義
定義一個類繼承於Service類,重寫方法。
public class MusicService extends Service { public MusicService(){ Log.i("TAG","MusicService"); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.i("TAG","onBind"); return new Binder(); //return 到ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected中 } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Log.i("TAG","onCreate"); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.i("TAG","onStartCommand"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); //返回值不同,Service被殺掉的情況也不同 } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.i("TAG","onDestroy"); } @Override public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) { Log.i("TAG","onUnbind"); return super.onUnbind(intent); } }在AndroidManifest.xml中配置Service
<service android:name="com.cxmscb.cxm.moodmusic.MusicService" /> <!--本地Service不需要intent-filter--> <!--可以使用process標籤讓服務執行在另一個程式--> <service android:name="com.cxmscb.cxm.moodmusic.MusicService" android:process=":remote" />注意:onStartCommand()方法必須返回一個整數,這個整數是一個描述了在系統的殺死事件中,系統應該如何繼續這個服務的值。從onStartCommand()方法中返回的值必須是以下常量:
START_NOT_STICKY 如果系統在onStartCommand()方法返回之後殺死這個服務,那麼直到接受到新的Intent物件,這個服務才會被重新建立。 START_STICKY 如果系統在onStartCommand()返回後殺死了這個服務,系統就會重新建立這個服務並且呼叫onStartCommand()方法,但是它不會重新傳遞最後的Intent物件,系統會用一個null的Intent物件來呼叫onStartCommand()方法。 在這個情況下,除非有一些被髮送的Intent物件在等待啟動服務。這適用於不執行命令的媒體播放器(或類似的服務),它只是無限期的執行著並等待工作的到來。 START_REDELIVER_INTENT 如果系統在onStartCommand()方法返回後,系統就會重新建立了這個服務,並且用傳送給這個服務的最後的Intent物件呼叫了onStartCommand()方法。任意等待中的Intent物件會依次被髮送。這適用於那些應該立即恢復正在執行的工作的服務,如下載檔案。
四、啟動/停止服務Service
Service分為兩種工作狀態,一種是啟動狀態,主要用於執行後臺計算;另一種是繫結狀態,主要用於其他元件和Service的互動。
Service的這兩種狀態是可以共存的,即Service既可以處於啟動狀態也可以同時處於繫結狀態。
啟動服務:(不繫結)
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MusicService.class); this.startService(intent); //通過intent信使來啟動停止服務:
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MusicService.class); this.stopService(intent); //通過intent信使來停止 // 也可以在Service中呼叫 stopSelf() 來停止服務繫結服務:
ServiceConnection serviceConnection; // 與Activity繫結服務來啟動服務 Intent intent = new Intent(this,MusicService.class); if(serviceConnection==null){ serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) { //當Activity與服務連線上時回撥。 //onBind() --> onServiceConnected() //iBinder為Service中的onBind返回的iBinder } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) { //當Activity與服務斷開後回撥。 } }; this.bindService(intent,serviceConnection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);解綁服務:
//當Activity銷燬時,要與繫結的服務Sercive解綁,否則會報錯 if(serviceConnection!=null){ Intent intent = new Intent(this,MusicService.class); this.unbindService(intent,serviceConnection); serviceConnection = null; }
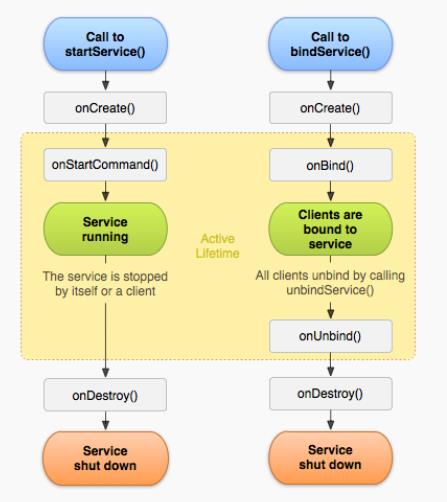
五、Service的生命週期
因啟動服務的方式不同,Service的生命週期也不同。
startService
第一次啟動服務: —>構造方法—>onCreate—>onStartCommand
再次啟動該服務:—>onStartCommandstopService( )
呼叫:—>onDestorybindService
呼叫:—>構造方法—>onCreate—>onBind—->onServiceConnetedunbindService
呼叫:(當前Activity與該Service連線)—>onUnbind—>onDestory
六、Activity與Service的資料交流
Activity傳資料給Service:在啟動服務時通過Intent傳遞資料。(注意第一次啟動服務時和再次啟動服務時的方法呼叫區別。)
Service傳即時資料給Activity:Service可以通過特定廣播來傳遞即時資料給接收特定廣播的Activity,傳送廣播時也會帶有Intent物件,可通過Intent攜帶資料。
當Activity和Service繫結時,可以通過Binder來連結Service和Activity,通過Binder來返回繫結的Service來獲取Service物件內部的資料。
a。使用Binder擴充套件類物件進行交流:返回Service物件(非跨程式)
@Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.i("TAG","onBind"); return new LocalBinder(); //return 到ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected中 } ------------------------------------------------------------ // MyService的內部類LocalBinder public class LocalBinder extends Binder{ public MyService getService(){ return MyService.this; } } ---------------------------------------------------------------------- MyService service = null; // 在Activity繫結服務時需要的ServiceConnection中的onServiceConnected方法 @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) { //當Activity與服務連線上時回撥。 //onBind() --> onServiceConnected() //iBinder為Service中的onBind返回的iBinder MyService.LocalBinder localBinder = (MyService.LocalBinder)iBinder; service = localBinder.getService(); }b. 使用AIDL / Messenger 進行跨程式交流
使用Messenger進行交流:
服務端實現一個 Handler,由其處理來自客戶端的訊息Message
class ServiceHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case 0: Log.i(TAG, "thanks,Service had receiver message from client!"); break; default: super.handleMessage(msg); } } }在服務端將 Handler例項 封裝為 Messenger 物件
Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new ServiceHandler());獲取Messenger的IBinder例項,在 onBind() 中將其返回客戶端
@Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return mMessenger.getBinder(); }客戶端獲取 IBinder 物件後將其 再封裝 Messenger 物件,然後使用Messenger將 Message 物件傳送給服務端
/** * 與服務端互動的Messenger */ Messenger mMessenger = null; private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) { /** * 通過服務端傳遞的IBinder物件,封裝為相應的Messenger */ mMessenger = new Messenger(service); } public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) { mMessenger = null; } }; // 使用mMessenger傳送訊息 : .... // 建立Messager物件msg // 傳送msg物件,由服務端的Handler來處理訊息 mMessenger..send(msg) ;(同理可以在客戶端建立客戶端的Handler和Messenger,將Messenger物件通過訊息msg傳遞給服務端,服務端再使用客戶端的Messenger物件來傳送訊息)
使用AIDL進行交流:
七、前臺服務
將服務置為前臺狀態,可對服務的程式進行提權,即在記憶體不足時,系統也不會考慮將其程式終止。不過將服務置為前臺時,需要在狀態列中顯示一個通知Notification來告知使用者。
startForeground(int id, Notification notification)
把當前服務設定為前臺服務,其中id引數代表唯一標識通知的整型數(不可以為 0),notification是一個狀態列的通知例項。stopForeground(boolean removeNotification)
將處於前臺狀態的服務降權,恢復原來的狀態。方法傳入一個布林值,表示是否刪除狀態列通知,true為刪除。 (該方法並不會停止服務)
八、IntentService
- IntentService是Service類的子類,為非同步服務。可以通過startService(Intent)方法傳遞請求給IntentService。
- 可以在IntentService實現虛擬函式onHandleIntent,在裡面根據Intent的不同進行不同的處理,按佇列來一一處理。當執行完一個Intent請求物件所對應的工作之後,如果沒有新的Intent請求達到,則自動停止Service;否則執行下一個Intent請求所對應的任務。
- 使用場景:需要將任務按佇列來排列處理時,可以用IntentService。
- IntentService預設實現了Onbind()方法,返回值為null。
相關文章
- 安卓開發之呼叫攝像頭安卓
- 服務網格service mesh 之 Linkerd
- 安卓微信小程式開發之“藍芽”安卓微信小程式藍芽
- 安卓開發--AIDL研究安卓AI
- 安卓開發框架系列開篇安卓框架
- 安卓開發日記4安卓
- 安卓開發日記26安卓
- 安卓開發日記25安卓
- 安卓開發日記24安卓
- 安卓開發日記19安卓
- 安卓開發日記18安卓
- go語言安卓開發Go安卓
- 安卓開發日記28安卓
- 安卓開發日記27安卓
- 安卓開發日記17安卓
- 安卓開發日記16安卓
- 安卓開發日記14安卓
- 安卓開發日記13安卓
- 安卓開發日記12安卓
- 安卓開發日記15安卓
- 安卓開發日記46安卓
- 安卓開發日記45安卓
- 安卓開發日記47安卓
- 安卓開發日記57安卓
- 安卓開發日記56安卓
- 安卓開發日記55安卓
- 阿里雲Kubernetes容器服務Istio實踐之整合日誌服務Log Service阿里
- 【2021/12/31】uniapp之安卓原生外掛開發教程APP安卓
- QT之安卓開發——生成APK以及真機測試QT安卓APK
- 安卓中高階開發工程師之——未來的路安卓工程師
- WindowsService服務程式開發 安裝和解除安裝Windows
- 安卓開發第一步:安卓面試題安卓面試題
- 服務網格 Service Mesh
- 【Azure 應用服務】App Service服務無法啟動,開啟Kudu站點,App Service Editor 頁面均丟擲:The service is unavailableAPPAI
- 服務發現與負載均衡機制-Service負載
- 安卓中高階開發面試知識點之——快取安卓面試快取
- 【應用服務 App Service】 App Service Rewrite 例項 - 反向代理轉發功能APP
- 安卓開發小組的反思安卓
- 5.11安卓開發日記32安卓