STL案例程式碼
//1.指標迭代器
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 100
int iarray[SIZE];
int main()
{
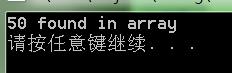
iarray[20] = 50;
int* ip = find(iarray, iarray + SIZE, 50);
if (ip == iarray + SIZE)//如果指標指向陣列的尾部,就表示沒有找到
cout << "50 not found in array" << endl;
else
cout << *ip << " found in array" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
===========================================
//2.容器迭代器1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
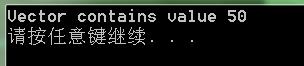
vector<int> intVector(100);
intVector[20] = 50;
vector<int>::iterator intIter = find(intVector.begin(), intVector.end(), 50);
if (intIter != intVector.end())
cout << "Vector contains value" << *intIter << endl;
else
cout << "Vector does not contain 50" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
================================================
//3.輸出迭代器
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double darray[10] = { 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9 };
vector<double> vdouble(10);
vector<double>::iterator outputInterator = vdouble.begin();//定義容器迭代器,
copy(darray, darray + 10, outputInterator);
while (outputInterator != vdouble.end())
{
cout << *outputInterator << endl;
outputInterator++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
提示:小夥伴們不要驚訝,這個1.0輸出後變成了1,這在DEV和VS2013下輸出都是一樣的。
=========================================================
//4.流迭代器
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
void Display(vector<int>& v, const char* s)
{
cout << endl << s << endl;
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, "\t"));//使用流迭代器,使用“\t”隔開
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));// 用時間初始化隨機發生器
vector<int> collection(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
collection[i] = rand() % 1000; // 產生的隨機數用1000 模運算
Display(collection, "Before sorting");//排序前輸出
sort(collection.begin(), collection.end());//對容器進行排序
Display(collection, "After sorting");//排序後輸出
system("pause");
return 0;
}
===========================================================
//5.插入代器
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
void Display(list<int>& a, const char* s)
{
cout << s << endl;
copy(a.begin(), a.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
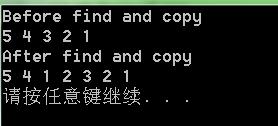
int iArray[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> iList;
//使用copy函式把陣列中值複製到STL容器,複製的時候利用前端插入,插入後,再在前面插入
// 若插入 1,再插入2,就變成了2,1
copy(iArray, iArray + 5, front_inserter(iList));
Display(iList, "Before find and copy ");
// 定義list容器迭代器,找到3的位置初始化迭代器,當前list容器的迭代器是(5,4,3,2,1)
list<int>::iterator p = find(iList.begin(), iList.end(), 3);
// 將陣列的前兩個元素插入到容器,插入位置為之前找到3的位置之前
copy(iArray, iArray + 2, inserter(iList, p));
Display(iList, "After find and copy");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
=======================================================
// 6. 函式和斷言
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define VSIZE 10
vector<long> v(VSIZE);
void initialize(long &ri);
void show(const long &ri);
bool isMinus(const long &ri);
int main()
{
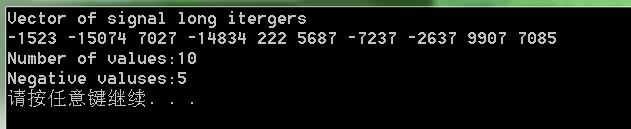
srand(time(NULL));// 初始化隨機發生器種子
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), initialize); //遍歷容器,呼叫普通函式賦值操作
cout << "Vector of signal long itergers" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), show); // 編譯容器,並顯示
cout << endl;
int count = 0;
vector<long>::iterator p;
// 呼叫斷言函式,如果容器中存在小於0的數,則返回第一個小於0 的迭代器
p = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), isMinus);
//cout << *p << endl;
// 統計小於0 的數的個數
while (p != v.end())
{
count++;
p = find_if(p + 1, v.end(), isMinus);
}
cout << "Number of values:" << VSIZE << endl;
cout << "Negative valuses:" << count << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 利用隨機數獲得值
void initialize(long &ri)
{
ri = (rand() - (RAND_MAX / 2));
}
// 顯示
void show(const long &ri)
{
cout << ri << " ";
}
// 判斷小於0的數,返回為真
bool isMinus(const long &ri)
{
return (ri < 0);
}
==========================================================
// 7. 函式物件
#include <iostream>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
vector<long> v(MAX);
int main()
{
//初始化容器容器中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v[i] = i + 1;
// accumulate函式對容器內元素求和,標頭檔案numeric
long sum = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
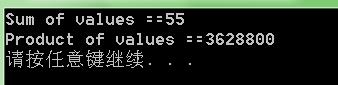
cout << "Sum of values ==" << sum << endl;
// 函式模板acumulate利用multiplies仿函式(標頭檔案functional)對容器內元素進行連續相乘操作
long product = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(),1, multiplies<long>());
cout << "Product of values ==" << product << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
===================================================
// 8.發生器函式物件
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
void Display(vector<int>& vr, const char* s);
unsigned int RandInt(const unsigned int n);
int main()
{
int iarray[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
vector<int> v(iarray, iarray + 10);
srand(time(NULL));
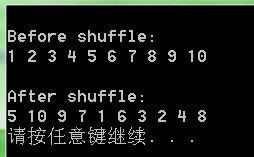
Display(v, "Before shuffle:");
//Converts a unary function pointer into an adaptable unary function.
pointer_to_unary_function<unsigned int, unsigned int> ptr_RandInt =
ptr_fun(RandInt);
//對一個元素序列進行重新排序(隨機的),包含在標頭檔案 algorithm.h中
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end(), ptr_RandInt);
Display(v,"After shuffle:");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/// 顯示
void Display(vector<int>& vr, const char* s)
{
cout << endl << s << endl;
copy(vr.begin(), vr.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
}
//返回隨機值
unsigned int RandInt(const unsigned int n)
{
return rand() % n;
}
=============================================
//9. 發生器函式物件
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
/*
FiboRand模板函式物件類,繼承自unary_function<Arg,Arg>
該類定義了兩個成員函式,一個是建構函式,另一是operator()()函式,
該操作符允許random_shuffle()演算法像一個函式一樣“呼叫"一個FiboRand物件。
*/
template <typename Arg>
class FiboRand :public unary_function<Arg, Arg>
{
int i, j;
Arg sequence[18];
public:
FiboRand();
Arg operator()(const Arg& arg);
};
template<typename Arg>
FiboRand<Arg>::FiboRand()
{
sequence[17] = 1;
sequence[16] = 2;
for (int n = 15; n >= 0; n--)
sequence[n] = sequence[n + 1] + sequence[n + 2];
i = 17;
j = 5;
/*
for (i = 0; i < 18; ++i)
cout << sequence[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
*/
}
template<typename Arg>
Arg FiboRand<Arg>::operator()(const Arg& arg)
{
Arg k = sequence[i] + sequence[j];
sequence[i] = k;
i--;
j--;
if (i == 0) i = 17;
if (j == 0) j = 17;
return k%arg;
}
void Display(vector<int>& vr, const char* s)
{
cout << endl << s << endl;
copy(vr.begin(), vr.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int iarray[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
vector<int> v(iarray, iarray + 10);
FiboRand<int> fibogen; //construct generator object
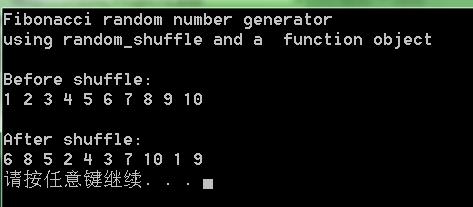
cout << "Fibonacci random number generator" << endl;
cout << "using random_shuffle and a function object" << endl;
Display(v, "Before shuffle:");
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end(), fibogen);
Display(v, "After shuffle:");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
===============================================
//10.繫結器函式物件
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
/*
bind1st() 建立一個函式物件,函式物件將值V作為第一個引數A
bind2nd() 建立一個函式物件,函式物件將值V作為第二個引數B
*/
int main()
{
int iarray[10] = { 1, 2, 11, 4, 34, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
list<int> aList(iarray, iarray + 10);
int k = 0;
/*
typename iterator_traits<_InIt>::difference_type
count_if(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{// count elements satisfying _Pred
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
_DEBUG_POINTER(_Pred);
return (_Count_if(_Unchecked(_First), _Unchecked(_Last), _Pred));
}
*/
// count_if() 計算滿足特定條件的元素的數目
k = count_if(aList.begin(), aList.end(), bind1st(greater<int>(), 8));
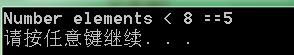
cout << "Number elements < 8 ==" << k << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
==============================================
// 11.混合迭代器函式
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
/*
advance() 按指定的數目增減迭代器
distance() 返回到達一個迭代器所需(遞增)操作的數目
*/
void Display(list<int>& v, const char* s)
{
cout << endl;
cout << s << endl;
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
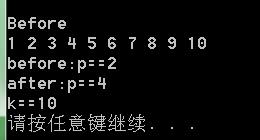
int iArray[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
list<int> iList;
list<int>::iterator p = iList.begin(); //定義迭代器並指向容器開始
copy(iArray, iArray + 10, inserter(iList, p));//從p開始插入
//copy(iArray, iArray + 10, front_inserter(iList));//前端插入
Display(iList, "Before");
p = find(iList.begin(), iList.end(), 2);
cout << "before:p==" << *p << endl;
advance(p, 2);//p+=2
cout << "after:p==" << *p << endl;
int k = 0;
p = iList.begin();
k = distance(p, iList.end());//等價於iList.end()-p,
cout << "k==" << k << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
除錯平臺: VS2013
參考自《三十分鐘掌握STL》
相關文章
- 《STL原始碼剖析》 -- stl_algo.h原始碼Go
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_algobase.h原始碼Go
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_hashtable.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_multimap.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_map.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_multiset.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_set.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_tree.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_heap.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_slist.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_queue.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_stack.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_deque.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_list.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_pair.h原始碼AI
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_vector.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_iterator.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_uninitialized.h原始碼Zed
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_alloc.h原始碼
- 【STL 原始碼剖析】淺談 STL 迭代器與 traits 程式設計技法原始碼AI程式設計
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_relops.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_hash_map.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_hash_set.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_construct.h原始碼Struct
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- stl_config.h原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- memory原始碼
- stl原始碼分析——map/multimap原始碼
- STL原始碼剖析——vector容器原始碼
- 業務程式碼程式設計陷阱案例 - jaxenter程式設計
- 機器學習去除馬賽克案例(程式碼)機器學習
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- defalloc.h原始碼
- 案例分析之JavaScript程式碼優化JavaScript優化
- 一個濫用程式碼的案例
- 二維陣列程式碼案例分析陣列
- 《STL原始碼剖析》 -- 寫在最後原始碼
- 《STL原始碼剖析》-- 特別說明原始碼
- STL
- 搶紅包案例分析以及程式碼實現