【Codeforces Round 362 (Div 2)C】【STL-map 最近公共祖先思想】Lorenzo Von Matterhorn 數域二叉樹的路徑權值變更查詢
Barney lives in NYC. NYC has infinite number of intersections numbered with positive integers starting from 1. There exists a bidirectional road between intersections i and 2i and another road between i and 2i + 1 for every positive integer i. You can clearly see that there exists a unique shortest path between any two intersections.

Initially anyone can pass any road for free. But since SlapsGiving is ahead of us, there will qconsecutive events happen soon. There are two types of events:
1. Government makes a new rule. A rule can be denoted by integers v, u and w. As the result of this action, the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v increases by w dollars.
2. Barney starts moving from some intersection v and goes to intersection u where there's a girl he wants to cuddle (using his fake name Lorenzo Von Matterhorn). He always uses the shortest path (visiting minimum number of intersections or roads) between two intersections.
Government needs your calculations. For each time Barney goes to cuddle a girl, you need to tell the government how much money he should pay (sum of passing fee of all roads he passes).
The first line of input contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1 000).
The next q lines contain the information about the events in chronological order. Each event is described in form 1 v u w if it's an event when government makes a new rule about increasing the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v by w dollars, or in form 2 v u if it's an event when Barnie goes to cuddle from the intersection v to the intersection u.
1 ≤ v, u ≤ 1018, v ≠ u, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109 states for every description line.
For each event of second type print the sum of passing fee of all roads Barney passes in this event, in one line. Print the answers in chronological order of corresponding events.
7 1 3 4 30 1 4 1 2 1 3 6 8 2 4 3 1 6 1 40 2 3 7 2 2 4
94 0 32
In the example testcase:
Here are the intersections used:
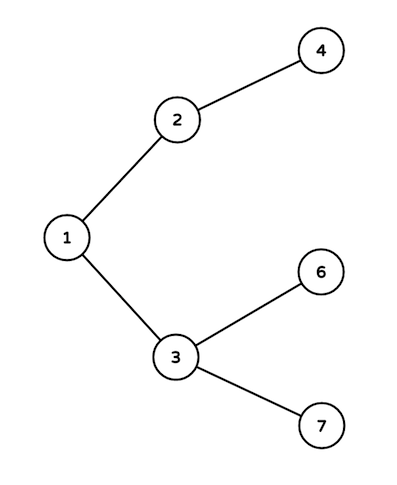
- Intersections on the path are 3, 1, 2 and 4.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are only 3 and 6.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2, 1 and 3. Passing fee of roads on the path are 32, 32and 30 in order. So answer equals to 32 + 32 + 30 = 94.
- Intersections on the path are 6, 3 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are 3 and 7. Passing fee of the road between them is 0.
- Intersections on the path are 2 and 4. Passing fee of the road between them is 32(increased by 30 in the first event and by 2 in the second).
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre() { freopen("c://test//input.in", "r", stdin); freopen("c://test//output.out", "w", stdout); }
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T1, class T2>inline void gmax(T1 &a, T2 b) { if (b>a)a = b; }
template <class T1, class T2>inline void gmin(T1 &a, T2 b) { if (b<a)a = b; }
const int N = 0, M = 0, Z = 1e9 + 7, ms63 = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n;
map<LL, LL>mop;
void add(LL x, LL y, LL z)
{
while (x != y)
{
if (y > x)swap(x, y);
mop[x] += z;
x >>= 1;
}
}
LL check(LL x, LL y)
{
LL sum = 0;
while (x != y)
{
if (y > x)swap(x, y);
if (mop.count(x))sum += mop[x];
x >>= 1;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
while (~scanf("%d", &n))
{
mop.clear();
int op;
LL x, y, z;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &x, &y, &z);
add(x, y, z);
}
else
{
scanf("%lld%lld", &x, &y);
printf("%lld\n", check(x, y));
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
【題意】
對於正整數域上的二叉樹,x的左兒子為2x,右兒子為2x+1
有q(1000)次操作。
對於每次操作,有兩種型別:
1 x,y,z 我們增加從x到y路徑上每條邊的權值為z
2 x y 詢問從x到y的路徑邊權
【型別】
STL - map 最近公共祖先思想
【分析】
雖然數域範圍很大,但是運算元很小,我們可以用一個map
mop[x]表示x到其父節點的路徑上的權值累計量。
然後我們就可以O(lognlogn)的複雜度維護每次詢問啊
【時間複雜度&&優化】
O(qlognlogn)
*/相關文章
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) C 模擬二叉樹二叉樹
- 二叉樹的最近公共祖先二叉樹
- 二叉搜尋樹和二叉樹的最近公共祖先二叉樹
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) B 模擬
- # 劍指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉樹的最近公共祖先二叉樹
- 二叉樹路徑查詢二叉樹
- 最近公共祖先
- leetcode 235. 二叉搜尋樹的最近公共祖先LeetCode
- Codeforces Round #470 div2 C
- Codeforces Round #453 (Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round #452 (Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round 973 (Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round 972 (Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round 982 (Div. 2)(A~C)
- 二叉樹:距離最近的共同祖先二叉樹
- lc235.二叉搜尋樹的最近公共祖先【①分別得到祖先序列,然後比較;②***同時查詢,找出分岔結點】
- Google S2 中的四叉樹求 LCA 最近公共祖先Go
- 【Codeforces Round 362 (Div 2)B】【模擬】Barnicle 科學計數法轉普通表示法
- Codeforces Round #321 (Div. 2) C DFS
- 【Codeforces Round 362 (Div 2)D】【樹的遍歷 概率均分思想】Puzzles 兄弟節點的等概率遍歷下 樹的遍歷每點期望時間戳時間戳
- (117)235. 二叉搜尋樹的最近公共祖先(leetcode)LeetCode
- Codeforces Round #320 (Div. 2) [Bayan Thanks-Round] C 數學
- LeetCode——最近公共祖先LeetCode
- Educational Codeforces Round 33 (Rated for Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round #323 (Div. 2) C gcdGC
- Codeforces Round #325 (Div. 2) C 模擬
- Codeforces Round #359 (Div. 2) C DFS
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D
- codeforces Round #252 (Div. 2) C - Valera and Tubes
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 2) C、The Child and Toy
- Codeforces Round 977 (Div. 2)(B-C2)
- 二叉樹中兩個節點的最低公共祖先二叉樹
- 【leetcode 簡單】 第六十八題 二叉搜尋樹的最近公共祖先LeetCode
- Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2)A-C題解
- Codeforces Round #401 (Div. 2)(C,D,E)
- Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) A-C題解
- Codeforces Round #Pi (Div. 2) —— C-Geometric Progression
- Codeforces Round #446 (Div. 2) C. PrideIDE