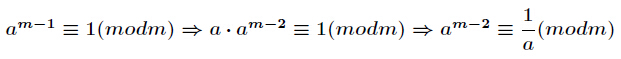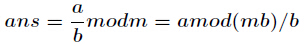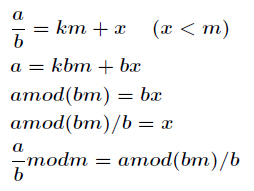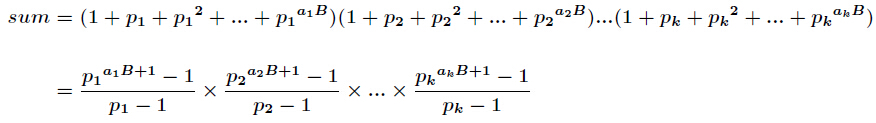逆元學習
定義:對於正整數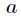
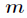
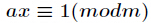
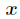
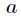
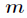
逆元一般用擴充套件歐幾里得演算法來求得,如果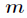
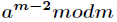
推導過程如下
求現在來看一個逆元最常見問題,求如下表示式的值(已知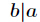
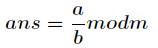
當然這個經典的問題有很多方法,最常見的就是擴充套件歐幾里得,如果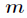
但是你會發現費馬小定理和擴充套件歐幾里得演算法求逆元是有侷限性的,它們都會要求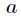
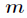
種通用的求逆元方法,適合所有情況。公式如下
現在我們來證明它,已知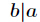
題意:給定兩個正整數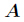
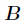

分析:很容易知道,先把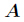
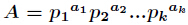
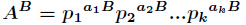
的所有因子和的表示式如下
方法一:二分求等比數列和:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
//#define debug
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MOD = 9901;
const int maxn = 10005;
int p[maxn],cnt;
int num[maxn];
bool prime[maxn];
void isprime()
{
cnt = 0;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(int i=2; i<maxn; i++)
{
if(prime[i])
{
p[cnt++] = i;
for(int j=i+i; j<maxn; j+=i)
prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
/*void fenjie(int n)
{
cnt=0;
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
for(int i=2;i*i<=n;i++){
if(n%i==0) p[cnt]=i;
while(n%i==0)
num[cnt]++;
cnt++;
}
if(n!=1){
p[cnt]=n;
num[cnt++]=1;
}
}*/
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL b)
{
LL ans=1;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=ans*a%MOD;
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=a*a%MOD;
}
return ans;
}
LL sum(LL a,LL n)
{
if(n==0) return 1;
LL t=sum(a,(n-1)/2);
if(n&1){
LL tmp=quick_mod(a,(n+1)/2);
t=(t+t%MOD*tmp%MOD)%MOD;
}
else{
LL tmp=quick_mod(a,(n+1)/2);
t = (t + t % MOD * tmp % MOD) % MOD;
t = (t + quick_mod(a,n)) % MOD;
}
return t;
}
void solve(LL a,LL b)
{
//fenjie(a);
isprime();
LL ans=1;
#ifdef debug
cout<<"*****************"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
cout<<p[i]<<" "<<num[i]<<endl;
cout<<"*****************"<<endl;
#endif // debug
for(int i=0;p[i]*p[i]<=a;i++){
if(a%p[i]==0){
int num=0;
while(a%p[i]==0)
num++,a/=p[i];
ans*=sum(p[i],num*b)%MOD;
ans%=MOD;
}
}
if(a>1)
ans*=sum(a,b)%MOD;
printf("%lld\n",ans%MOD);
}
int main()
{
LL a,b;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b)){
solve(a,b);
}
return 0;
}
方法二:求逆元+等比數列求和公式
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
//#define debug
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MOD = 9901;
const int maxn = 10005;
int p[maxn],cnt;
int num[maxn];
bool prime[maxn];
void isprime()
{
cnt = 0;
memset(prime,true,sizeof(prime));
for(int i=2; i<maxn; i++)
{
if(prime[i])
{
p[cnt++] = i;
for(int j=i+i; j<maxn; j+=i)
prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
LL multi(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=0;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=(ans+a)%m;
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=(a+a)%m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=1;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=multi(ans,a,m);
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=multi(a,a,m);
}
return ans;
}
void solve(LL a,LL b)
{
isprime();
LL ans=1;
for(int i=0;p[i]*p[i]<=a;i++){
if(a%p[i]==0){
int num=0;
while(a%p[i]==0)
num++,a/=p[i];
LL M = (p[i]-1)*MOD;
ans*=(quick_mod(p[i],num*b+1,M)+M-1)/(p[i]-1);
ans%=MOD;
}
}
if(a>1){
LL M=(a-1)*MOD;
ans*=(quick_mod(a,b+1,M)+M-1)/(a-1);
ans%=MOD;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
LL a,b;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b)){
solve(a,b);
}
return 0;
}
相關文章
- 數論學習筆記 (5):同餘與逆元筆記
- 演算法學習筆記(2): 逆元及其應用演算法筆記
- [學習筆記] 丟番圖方程 & 同餘 & 逆元 - 數論筆記
- 模運算與逆元
- Python如何用歐幾里得求逆元Python
- 初等數論——素數,逆元,EXGCD有關GC
- ACdream1139 Sum(推公式+逆元求解)公式
- 求 1~n 在模意義下的乘法逆元
- 學習學習再學習
- BZOJ 3456: 城市規劃 [多項式求逆元 組合數學 | 生成函式 多項式求ln]函式
- HDU4675 GCD of Sequence(預處理階乘逆元+推公式)GC公式
- 深度學習——學習目錄——學習中……深度學習
- 深度學習(一)深度學習學習資料深度學習
- 深度學習學習框架深度學習框架
- 強化學習-學習筆記3 | 策略學習強化學習筆記
- 學習產品快報09 | “CSDN學習”:增加學習提醒,提示學習不忘記
- 【強化學習】強化學習/增強學習/再勵學習介紹強化學習
- 學習ThinkPHP,學習OneThinkPHP
- 前端學習之Bootstrap學習前端boot
- 學而習之,成就學習
- 前端週刊第62期:學習學習再學習前端
- 深度學習+深度強化學習+遷移學習【研修】深度學習強化學習遷移學習
- 強化學習-學習筆記2 | 價值學習強化學習筆記
- Golang 學習——interface 介面學習(一)Golang
- Golang 學習——interface 介面學習(二)Golang
- 深度學習學習7步驟深度學習
- 《JAVA學習指南》學習筆記Java筆記
- Go學習【二】學習資料Go
- java學習之道 --- 如何學習java?Java
- 免殺學習-基礎學習
- 強化學習10——迭代學習強化學習
- 程式設計學習MarkDown學習程式設計
- this學習
- 學習
- 【區塊鏈學習】《區塊鏈學習指南》學習筆記區塊鏈筆記
- Flutter學習記錄(一)Dart學習FlutterDart
- 從學習語文聊聊如何學習
- kitten 學習教程(一) 學習筆記筆記