HDU2813Interesting Fibonacci(斐波那契數列+迴圈節)
Interesting Fibonacci
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 694 Accepted Submission(s): 121
Problem Description
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are a sequence of numbers named after Leonardo of Pisa, known as Fibonacci (a contraction of filius Bonaccio, "son of Bonaccio"). Fibonacci's 1202 book Liber Abaci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics,
although the sequence had been previously described in Indian mathematics.
The first number of the sequence is 0, the second number is 1, and each subsequent number is equal to the sum of the previous two numbers of the sequence itself, yielding the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, etc. In mathematical terms, it is defined by the following recurrence relation:
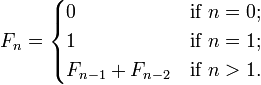
That is, after two starting values, each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The first Fibonacci numbers (sequence A000045 in OEIS), also denoted as F[n];
F[n] can be calculate exactly by the following two expressions:
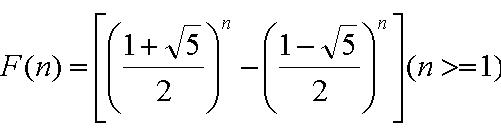
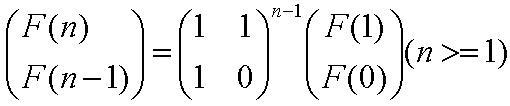
A Fibonacci spiral created by drawing arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling; this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and 34;
So you can see how interesting the Fibonacci number is.
Now AekdyCoin denote a function G(n)
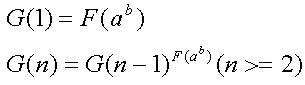
Now your task is quite easy, just help AekdyCoin to calculate the value of G (n) mod C
The first number of the sequence is 0, the second number is 1, and each subsequent number is equal to the sum of the previous two numbers of the sequence itself, yielding the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, etc. In mathematical terms, it is defined by the following recurrence relation:
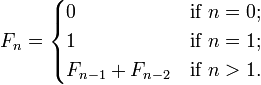
That is, after two starting values, each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The first Fibonacci numbers (sequence A000045 in OEIS), also denoted as F[n];
F[n] can be calculate exactly by the following two expressions:
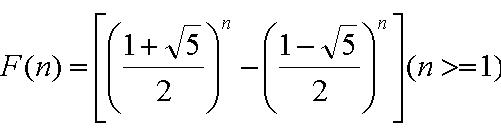
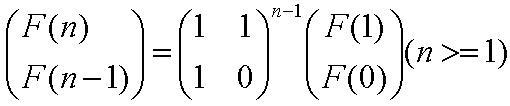
A Fibonacci spiral created by drawing arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling; this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and 34;
So you can see how interesting the Fibonacci number is.
Now AekdyCoin denote a function G(n)
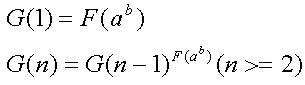
Now your task is quite easy, just help AekdyCoin to calculate the value of G (n) mod C
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case begins with a line containing A, B, N, C (10<=A, B<2^64, 2<=N<2^64, 1<=C<=300)
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the test case number( beginning with 1) followed by a integer which is the value of G(N) mod C
Sample Input
1
17 18446744073709551615 1998 139
Sample Output
Case 1: 120
根據題目給定的條件可以得到
G(n)=F(a^b)^(F(a^b)^n-1)%c;
根據公式:a^b%p=(a^(b%phi(p)+phi(p)))%p 進行降冪
由於題目中C的範圍比較小 因此我們一定可以找到它的迴圈節,進而求得F(a^b%c),F(a^b%phi(c));
然後經過一系列的快速冪取模就可以得到答案
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
LL a,b,n;
int c;
int phi(int n){
int rea=n,i;
for(i=2;i*i<=n;i++){
if(n%i==0){
rea=rea-rea/i;
while(n%i==0)
n/=i;
}
}
if(n>1)
rea=rea-rea/n;
return rea;
}
LL multi(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=0;
while(b)
{
if(b&1)
{
ans=(ans+a)%m;
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=(a+a)%m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL b,LL m){
LL ans=1;
a%=m;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=multi(ans,a,m);
b--;
}
b>>=1;
a=multi(a,a,m);
}
return ans;
}
LL f[5000];
int find_loop(int c){
f[0]=0;f[1]=1;
int loop;
for(int i=2;i<5000;i++){
f[i]=(f[i-1]%c+f[i-2]%c)%c;
if(f[i]==1&&f[i-1]==0){
loop=i;
break;
}
}
return loop-1;
}
int main()
{
int t,tt=1;
LL tmp1,tmp2;
LL t1,t2;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%I64u%I64u%I64u%d",&a,&b,&n,&c);
printf("Case %d: ",tt++);
if(c==1)
{
puts("0");
continue;
}
int p=phi(c);
int loop1=find_loop(c);
t1=quick_mod(a,b,loop1);
tmp1=f[t1]%c;
int loop2=find_loop(p);
t2=quick_mod(a,b,loop2);
tmp2=f[t2]%p;
tmp2=quick_mod(tmp2,n-1,p);
tmp2+=p;
tmp1=quick_mod(tmp1,tmp2,c);
printf("%I64u\n",tmp1);
}
return 0;
}
/*****
1
17 18446744073709551615 1998 139
Case 1: A 54
p 138
B 79
c 109
loop1 46
loop2 48
120
*****/
相關文章
- fibonacci斐波那契數列詳解 遞迴求Fn非遞迴求Fn求n最近的斐波那契數遞迴
- 斐波那契數列(Fibonacci)遞迴和非遞迴實現遞迴
- 斐波那契數列
- python for迴圈和斐波那契Python
- 斐波那契數列(Java)Java
- 斐波那契數列 (C#)C#
- PHP 與斐波那契數列PHP
- 斐波那契數列詳解
- 【演算法詳解】斐波那契數列 - Fibonacci sequence演算法
- 斐波那契數
- 【演算法】Fibonacci(斐波那契數列)相關問題演算法
- js實現斐波那契數列JS
- 斐波那契數列js 實現JS
- 斐波那契數列演算法演算法
- 斐波那契數列Ⅳ【矩陣乘法】矩陣
- 斐波那契數列的遞迴和非遞迴實現遞迴
- 演算法(1)斐波那契數列演算法
- 面試題9-斐波那契數列面試題
- [C103] 斐波那契數列
- 使用Python實現斐波那契數列Python
- JavaScript 實現:輸出斐波那契數列JavaScript
- js迭代器實現斐波那契數列JS
- 演算法一:斐波那契阿數列演算法
- 斐波那契數列的分治法計算
- 斐波那契數列的python實現Python
- 大數斐波那契數列的演算法演算法
- rust實戰系列 - 使用Iterator 迭代器實現斐波那契數列(Fibonacci )Rust
- Leedcode-斐波那契數
- 斐波那契數列三種實現函式函式
- 計算斐波那契數列的演算法演算法
- 劍指offer-9-斐波那契數列-javaJava
- 斐波那契數列演算法 JS 實現演算法JS
- hdu 3117矩陣+斐波那契數列矩陣
- 斐波那契查詢
- 斐波那契數列的通項公式及證明公式
- 每日一算 -- 斐波那契數列型別題型別
- 斐波那契數列 多語言實現 筆記筆記
- js計算斐波那契數列程式碼例項JS