ACM UVa演算法題209 Triangular Vertices的解法
有一段時間沒有做ACM演算法題目了,今天正好有空便隨便挑了209題來做做:ACM UVa演算法題#209題
這道題有幾個要點:
1. 給定座標系
座標系很容易定,我採用的是第一個點為(0, 0)點,X方向差別為2個單位,Y方向差別為1個單位,點之間的距離,也就是LEN為1個單位,這樣便於計算。注意我用的不是實際長度,而是抽象的單位,這個單位在不同方向上面意義不一樣,否則很容易通過三角形相關公理推出這樣的三角形不存在,我們關心的只是這樣的一個對應關係。這裡的人為設定確實有些Confusing,我之前也是按照一般的三角形的長度,如3,4,5來定義,但是後來發現這樣做做的乘除法太多,過於浪費CPU Cycle,如果按照我這樣的設定,大部分情況只用到加減法,另外一種情況只需用到移位操作即可。
參看下圖:
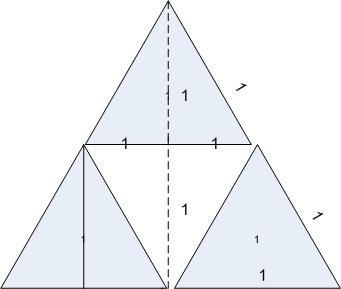
2. 判斷是否兩點連線是一條邊(Coincide)
這裡可以分兩種情況:
a. Y1 = y2, 必然是Coincide
b. 否則,X_Delta = abs(x1 – x2), Y_Delta = abs(y1 – y2), 由於之前我們人為設定X方向差別為2個單位,Y方向差別為1一個單位,因此只要X_Delta = Y_Delta即可
3. 計算距離
假定是Coincide的情況,否則直接返回出錯,因為在非Coincide的情況無需計算距離。此外,由於這裡已經知道是Coincide,並且我們並沒有統一單位,所以這裡不能也不應該用勾股定理來計算長度,而是採用比例的方法,同樣分兩種情況,參考上圖:
a. Y1 = y2, 那麼因為X方向上兩個單位對應一個長度Unit,所以長度=abs(x1 – x2) >> 1;
b. 否則,長度Unit的個數和X/Y方向(任意)的差別相等,也就是長度=abs(x1 – x2)
4. 判斷是否是目標圖形,並且每條邊相等
對於三角形,很簡單,直接對3條邊判斷即可,沒有什麼變數。對於四邊形和六邊形就不同了,需要用到遍歷來確定一個從某點開始(我們可以固定為第一個點)遍歷所有點最後回到該點的環,並且每條邊長度均相等,注意這裡由於題目的特殊性,不用判斷平行等條件。可以用一個鄰接矩陣來代表對應的邊的長度,這個應該一次性計算出來,如果非Coincide則設定為某個特殊值,比如0
剛開始提交的時候,Rank是45,之後我又做了下面的優化:
1. 當遍歷嘗試完畢從最初點出發的某條邊的時候,說明這一邊不可能成為環,將其置為0表示不可通,並且遍歷從最初點出發的其他同樣長度的邊,置為0,減少遍歷次數
2. 在初始化計算所有點的座標的時候改變了一點點演算法,用加減法代替乘法
3. 最初座標採用的是實際的長度,而不是像上面那樣用不同的抽象單位算出,修改之後減少了大量乘除法計算
4. 調整遍歷演算法,由於從初始點出發之後,後3個點必然不能是初始點,因此做了一點修改對這個情況作了優化
5. 修改對鄰接矩陣的演算法,由於adj[i][j] = adj[j][i],所以只需計算矩陣的一半即可
修改之後再提交Rank變成了33,似乎是目前個人的最好紀錄 J
|
32 |
0.170 |
792 |
C |
2002-02-04 07:02:47 |
732386 |
|
|
33 |
0.172 |
1160 |
C++ |
2007-05-02 16:05:54 |
5551868 |
|
|
34 |
0.174 |
404 |
C |
2001-08-30 08:46:54 |
539862 |
 //
//  // ACM UVa Problem #209
// ACM UVa Problem #209 // http://acm.uva.es/p/v2/209.html
// http://acm.uva.es/p/v2/209.html //
// // Author: ATField
// Author: ATField // Email: atfield_zhang@hotmail.com
// Email: atfield_zhang@hotmail.com //
//
 #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h>
#include <string.h>
 #define MAX 65535
#define MAX 65535
 struct point
struct point
 ...{
...{ public :
public : bool is_coincide(const point &pt) const
bool is_coincide(const point &pt) const
 ...{
...{ // not allow testing points with same coordinates
// not allow testing points with same coordinates if( _x == pt._x && _y == pt._y )
if( _x == pt._x && _y == pt._y ) return false;
return false;
 if( _y == pt._y )
if( _y == pt._y ) return true;
return true; else
else
 ...{
...{ int k1 = abs( _x - pt._x );
int k1 = abs( _x - pt._x ); int k2 = abs( _y - pt._y );
int k2 = abs( _y - pt._y );
 if( k1 == k2 )
if( k1 == k2 ) return true;
return true; }
}
 return false;
return false; }
}
 int get_dist(const point &pt) const
int get_dist(const point &pt) const
 ...{
...{ // not allow testing points with same coordinates
// not allow testing points with same coordinates if( _x == pt._x && _y == pt._y )
if( _x == pt._x && _y == pt._y ) return 0;
return 0;
 if( _y == pt._y )
if( _y == pt._y ) return abs(_x - pt._x) >> 1; // need to divide by 2
return abs(_x - pt._x) >> 1; // need to divide by 2 else
else
 ...{
...{ int k1 = abs( _x - pt._x );
int k1 = abs( _x - pt._x ); int k2 = abs( _y - pt._y );
int k2 = abs( _y - pt._y );
 if( k1 == k2 )
if( k1 == k2 ) return k1;
return k1; }
}
 return 0;
return 0; }
}
 public :
public : static const int X_DELTA = 2;
static const int X_DELTA = 2; static const int Y_DELTA = 3;
static const int Y_DELTA = 3; static const int LEN = 4;
static const int LEN = 4;
 public :
public : int _x;
int _x; int _y;
int _y; int _valid;
int _valid;
 private :
private : static point s_all_points[MAX];
static point s_all_points[MAX];
 public :
public : static void prepare()
static void prepare()
 ...{
...{ int level = 0;
int level = 0; int before_next_level = 1;
int before_next_level = 1; int next_x = 0;
int next_x = 0; int next_y = 0;
int next_y = 0;
 for( int i = 1; i < MAX ; ++i )
for( int i = 1; i < MAX ; ++i )
 ...{
...{ s_all_points[i]._x = next_x;
s_all_points[i]._x = next_x; s_all_points[i]._y = next_y;
s_all_points[i]._y = next_y; before_next_level--;
before_next_level--;
 if( before_next_level == 0 )
if( before_next_level == 0 )
 ...{
...{ level++;
level++; before_next_level = level + 1;
before_next_level = level + 1; next_x = -level;
next_x = -level; next_y++;
next_y++; }
} else
else next_x += 2;
next_x += 2;
 }
}

 }
}
 static point *all_points()
static point *all_points()
 ...{
...{ return s_all_points;
return s_all_points; }
} };
};
 point point::s_all_points[MAX];
point point::s_all_points[MAX];
 bool check_triangle(int *n)
bool check_triangle(int *n)
 ...{
...{ // 1. Duplicates
// 1. Duplicates // No need to check duplicate because the following checks will do
// No need to check duplicate because the following checks will do
 // 2. Coincide
// 2. Coincide // Check every edge
// Check every edge point *points = point::all_points();
point *points = point::all_points(); if( points[n[0]].is_coincide(points[n[1]]) &&
if( points[n[0]].is_coincide(points[n[1]]) && points[n[0]].is_coincide(points[n[2]]) &&
points[n[0]].is_coincide(points[n[2]]) && points[n[1]].is_coincide(points[n[2]]) )
points[n[1]].is_coincide(points[n[2]]) )
 ...{
...{ // 3. Same length
// 3. Same length // Check every edge
// Check every edge int len = points[n[0]].get_dist(points[n[1]]);
int len = points[n[0]].get_dist(points[n[1]]); if( len == points[n[0]].get_dist(points[n[2]]) &&
if( len == points[n[0]].get_dist(points[n[2]]) && len == points[n[1]].get_dist(points[n[2]]) )
len == points[n[1]].get_dist(points[n[2]]) ) return true;
return true; }
}
 return false;
return false; }
}

 bool init_adj(int *n, int num, int adj[6][6])
bool init_adj(int *n, int num, int adj[6][6])
 ...{
...{ point *points = point::all_points();
point *points = point::all_points();
 for( int i = 0; i < num; ++i )
for( int i = 0; i < num; ++i )
 ...{
...{ for( int j = i; j < num; ++j )
for( int j = i; j < num; ++j )
 ...{
...{ if( i == j )
if( i == j )
 ...{
...{ adj[i][j] = 0;
adj[i][j] = 0; adj[j][i] = 0;
adj[j][i] = 0; }
} else
else
 ...{
...{ // 1. Duplicates
// 1. Duplicates // Return false when found duplicate
// Return false when found duplicate if( n[i] == n[j] )
if( n[i] == n[j] ) return false;
return false;
 // 2. Coincide & Len (When not coincide, len = 0)
// 2. Coincide & Len (When not coincide, len = 0) adj[i][j] = points[n[i]].get_dist(points[n[j]]);
adj[i][j] = points[n[i]].get_dist(points[n[j]]); adj[j][i] = adj[i][j];
adj[j][i] = adj[i][j]; }
} }
} }
}

 return true;
return true; }
}
 int find_same_len_loop(int adj[6][6], int num)
int find_same_len_loop(int adj[6][6], int num)
 ...{
...{ int stack[6];
int stack[6]; int used[6];
int used[6]; int next[6];
int next[6];
 for( int i = 1; i < num; ++i )
for( int i = 1; i < num; ++i )
 ...{
...{  int len = adj[0][i];
int len = adj[0][i];
 // skip non-connected dots
// skip non-connected dots if( len == 0 ) continue;
if( len == 0 ) continue;
 // initialize "used" array & "next" array
// initialize "used" array & "next" array for( int j = 0; j < num; ++j )
for( int j = 0; j < num; ++j )
 ...{
...{ used[j] = 0;
used[j] = 0; }
} 
 int top = 0;
int top = 0; stack[0] = i;
stack[0] = i; used[i] = 1;
used[i] = 1; next[0] = -1;
next[0] = -1;
 top++;
top++;
 while( top > 0 )
while( top > 0 )
 ...{
...{ next[top-1]++;
next[top-1]++;
 // checked all the connected points?
// checked all the connected points? if( next[top-1] >= num )
if( next[top-1] >= num )
 ...{
...{ // yes, then pop the stack
// yes, then pop the stack top--;
top--; used[stack[top]] = 0;
used[stack[top]] = 0; }
} else
else
 ...{
...{ int next_point = next[top-1];
int next_point = next[top-1];
 // follow non-used, same-length edge
// follow non-used, same-length edge if( used[next_point] == 0 && len == adj[stack[top-1]][next_point] )
if( used[next_point] == 0 && len == adj[stack[top-1]][next_point] )
 ...{
...{ stack[top] = next_point;
stack[top] = next_point; used[next_point] = 1;
used[next_point] = 1;
 // don't allow pushing 0 into stack before the last point
// don't allow pushing 0 into stack before the last point if( top < num - 1 )
if( top < num - 1 )  next[top] = 0;
next[top] = 0; else
else next[top] = -1;
next[top] = -1;
 top++;
top++;
 // stack is full? found a loop
// stack is full? found a loop if( top == num )
if( top == num ) return len;
return len; }
} }
} }
}
 // if this doesn't work, delete all edges starting from id 0 of this len
// if this doesn't work, delete all edges starting from id 0 of this len for( int j = i; j < num; ++j )
for( int j = i; j < num; ++j ) if( adj[0][j] == len )
if( adj[0][j] == len ) adj[0][j] = 0;
adj[0][j] = 0; }
}
 return 0;
return 0; }
}
 bool check_parallelogram(int *n)
bool check_parallelogram(int *n)
 ...{
...{ int adj[6][6];
int adj[6][6]; if(!init_adj(n, 4, adj))
if(!init_adj(n, 4, adj)) return false; // found duplicate
return false; // found duplicate
 if(find_same_len_loop(adj, 4))
if(find_same_len_loop(adj, 4)) return true;
return true;
 return false;
return false; }
}
 bool check_hexagon(int *n)
bool check_hexagon(int *n)
 ...{
...{ int adj[6][6];
int adj[6][6]; if(!init_adj(n, 6, adj))
if(!init_adj(n, 6, adj)) return false; // found duplicate
return false; // found duplicate
 if(find_same_len_loop(adj, 6))
if(find_same_len_loop(adj, 6)) return true;
return true;
 return false;
return false; }
}
 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
 ...{
...{ point::prepare();
point::prepare();
 while(1)
while(1)
 ...{
...{ char input[255];
char input[255]; if( gets(input) == NULL )
if( gets(input) == NULL ) break;
break; else if( strlen(input) == 0 )
else if( strlen(input) == 0 ) break;
break;
 int n[6];
int n[6]; int fields = sscanf( input, "%d %d %d %d %d %d", &n[0], &n[1], &n[2], &n[3], &n[4], &n[5] );
int fields = sscanf( input, "%d %d %d %d %d %d", &n[0], &n[1], &n[2], &n[3], &n[4], &n[5] );
 printf("%s ", input);
printf("%s ", input); 
 switch(fields)
switch(fields)
 ...{
...{ case 3:
case 3:
 ...{
...{ bool is_triangle = check_triangle(n);
bool is_triangle = check_triangle(n);
 if( is_triangle )
if( is_triangle )
 ...{
...{ puts("are the vertices of a triangle");
puts("are the vertices of a triangle"); continue;
continue; }
}
 break;
break; }
}
 case 4:
case 4:
 ...{
...{ bool is_parallelogram = check_parallelogram(n);
bool is_parallelogram = check_parallelogram(n);
 if( is_parallelogram )
if( is_parallelogram )
 ...{
...{ puts("are the vertices of a parallelogram");
puts("are the vertices of a parallelogram"); continue;
continue; }
}
 break;
break; }
}
 case 6:
case 6:
 ...{
...{ bool is_hexagon = check_hexagon(n);
bool is_hexagon = check_hexagon(n);
 if( is_hexagon )
if( is_hexagon )
 ...{
...{ puts("are the vertices of a hexagon");
puts("are the vertices of a hexagon"); continue;
continue; }
}
 break;
break; }
} }
}
 puts("are not the vertices of an acceptable figure");
puts("are not the vertices of an acceptable figure");
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0; }
}

相關文章
- ACM演算法——數學專題ACM演算法
- 兩種解法搞定Swap Nodes in Pairs演算法題AI演算法
- 演算法(第4版)練習題1.1.27的三種解法演算法
- 演算法實踐——Twitter演算法面試題(積水問題)的線性時間解法演算法面試題
- LeetCode簡單演算法題目-JS解法LeetCode演算法JS
- acm演算法之三大揹包問題ACM演算法
- openmesh - impl - Remove Duplicated VerticesREM
- ACM演算法模版ACM演算法
- topK問題解法TopK
- UVA557 Burger 題解
- RMQ問題的各種解法MQ
- 例題 7-15 破壞正方形(Square Destyoyer,ACM/ICPC Taejon 2001,UVa1603)ACM
- acm訓練題ACM
- ACM 6174問題ACM
- JavaScript的two-sum問題解法JavaScript
- 【演算法】求眾數-js解法演算法JS
- ACM中的輸入問題ACM
- ACM中回車的問題ACM
- (UVA - 10048) Audiophobia(floyd演算法)演算法
- 【藍橋杯】試題 歷屆試題 剪格子(python解法+java解法)PythonJava
- 二分查詢(JS解法)——高頻面試演算法題(百度真題)JS面試演算法
- BFS/acm習題集ACM
- ACM 眾數問題ACM
- ACM 揹包問題ACM
- ACM 過河問題ACM
- Codeforce演算法題 | 你能想出解法,讓你的基友少氪金嗎?演算法
- 八皇后問題python解法Python
- 我竟在arm彙編除法演算法裡找到了leetcode某道題的解法演算法LeetCode
- 四人過橋問題的SQL解法SQL
- 題解:UVA124 Following Orders
- ACM 會場安排問題ACM
- ACM 荷蘭國旗問題ACM
- ACM 兄弟郊遊問題ACM
- CF 293 E Close Vertices (樹的分治+樹狀陣列)陣列
- acm/icpc入門級演算法模板ACM演算法
- (UVA - 208)Firetruck(路徑輸出問題,回溯+並查集/floyd演算法+dfs)並查集演算法
- 10元買啤酒問題Java解法Java
- 常用不等式題目解法