第二章——用Python實現感知器模型(MNIST資料集)
感知器模型
適用問題:二類分類
模型特點:分離超平面
模型型別:判別模型
感知機學習策略
學習策略:極小化誤分點到超平面距離
學習的損失函式:誤分點超平面距離
感知機學習演算法
學習演算法:隨機梯度下降
演算法中感知器模型是一個sigmoid函式,於是上述模型是一個二分類的線性分類器。
資料集介紹
我們選擇MNIST資料集進行實驗
MNIST是一個入門級的計算機視覺資料集,它包含各種手寫數字圖片: 
它也包含每一張圖片對應的標籤,告訴我們這個是數字幾。比如,上面這四張圖片的標籤分別是5,0,4,1。
其官方下載地址:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
但是原始資料太麻煩了,我們選擇kaggle提供的已處理好的資料
地址:https://www.kaggle.com/c/digit-recognizer/data
由於我們是二分類器,所以需要對train.csv中的label列進行一些微調,label等於0的繼續等於0,label大於0改為1。
這樣就將十分類的資料改為二分類的資料。
也可以從我的github上下載:https://github.com/WenDesi/lihang_book_algorithm/blob/master/data/train_binary.csv
HOG特徵提取
MNIST資料都是28*28的圖片,可選擇的特徵有很多,包括:
1. 自己提取特徵
2. 將整個圖片作為特徵向量
3. HOG特徵
我們選擇HOG特徵,HOG特徵相關內容大家可以參考zouxy09 的相關博文
我們的目標是實用!因此只展示如何用Python提取HOG特徵。
Python提取特徵需要呼叫opencv2,程式碼如下所示
hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor('../hog.xml')
img = np.reshape(img,(28,28))
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
hog_feature = hog.compute(cv_img)其中hog.xml儲存hog的配置資訊,如下所示
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<opencv_storage>
<hog type_id="opencv-object-detector-hog">
<winSize>
28 28</winSize>
<blockSize>
14 14</blockSize>
<blockStride>
7 7</blockStride>
<cellSize>
7 7</cellSize>
<nbins>9</nbins>
<derivAperture>1</derivAperture>
<winSigma>4.</winSigma>
<histogramNormType>0</histogramNormType>
<L2HysThreshold>2.0000000000000001e-001</L2HysThreshold>
<gammaCorrection>1</gammaCorrection>
<nlevels>64</nlevels></hog>
</opencv_storage>關於更多hog特徵配置資訊,大家可以參考這篇文章
程式碼
程式碼我已經放到Github上了,大家可以參考我的Github:https://github.com/WenDesi/lihang_book_algorithm
感知器程式碼位於perceptron/binary_perceptron.py
這裡也貼一下程式碼
#encoding=utf-8
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random
import time
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 利用opencv獲取影象hog特徵
def get_hog_features(trainset):
features = []
hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor('../hog.xml')
for img in trainset:
img = np.reshape(img,(28,28))
cv_img = img.astype(np.uint8)
hog_feature = hog.compute(cv_img)
# hog_feature = np.transpose(hog_feature)
features.append(hog_feature)
features = np.array(features)
features = np.reshape(features,(-1,324))
return features
def Train(trainset,train_labels):
# 獲取引數
trainset_size = len(train_labels)
# 初始化 w,b
w = np.zeros((feature_length,1))
b = 0
study_count = 0 # 學習次數記錄,只有當分類錯誤時才會增加
nochange_count = 0 # 統計連續分類正確數,當分類錯誤時歸為0
nochange_upper_limit = 100000 # 連續分類正確上界,當連續分類超過上界時,認為已訓練好,退出訓練
while True:
nochange_count += 1
if nochange_count > nochange_upper_limit:
break
# 隨機選的資料
index = random.randint(0,trainset_size-1)
img = trainset[index]
label = train_labels[index]
# 計算yi(w*xi+b)
yi = int(label != object_num) * 2 - 1 # 如果等於object_num, yi= 1, 否則yi=1
result = yi * (np.dot(img,w) + b)
# 如果yi(w*xi+b) <= 0 則更新 w 與 b 的值
if result <= 0:
img = np.reshape(trainset[index],(feature_length,1)) # 為了維數統一,需重新設定一下維度
w += img*yi*study_step # 按演算法步驟3更新引數
b += yi*study_step
study_count += 1
if study_count > study_total:
break
nochange_count = 0
return w,b
def Predict(testset,w,b ):
predict = []
for img in testset:
result = np.dot(img,w) + b
result = result > 0
predict.append(result)
return np.array(predict)
study_step = 0.0001 # 學習步長
study_total = 10000 # 學習次數
feature_length = 324 # hog特徵維度
object_num = 0 # 分類的數字
if __name__ == '__main__':
print 'Start read data'
time_1 = time.time()
raw_data = pd.read_csv('../data/train_binary.csv',header=0)
data = raw_data.values
imgs = data[0::,1::]
labels = data[::,0]
features = get_hog_features(imgs)
# 選取 2/3 資料作為訓練集, 1/3 資料作為測試集
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.33, random_state=23323)
# print train_features.shape
# print train_features.shape
time_2 = time.time()
print 'read data cost ',time_2 - time_1,' second','\n'
print 'Start training'
w,b = Train(train_features,train_labels)
time_3 = time.time()
print 'training cost ',time_3 - time_2,' second','\n'
print 'Start predicting'
test_predict = Predict(test_features,w,b)
time_4 = time.time()
print 'predicting cost ',time_4 - time_3,' second','\n'
score = accuracy_score(test_labels,test_predict)
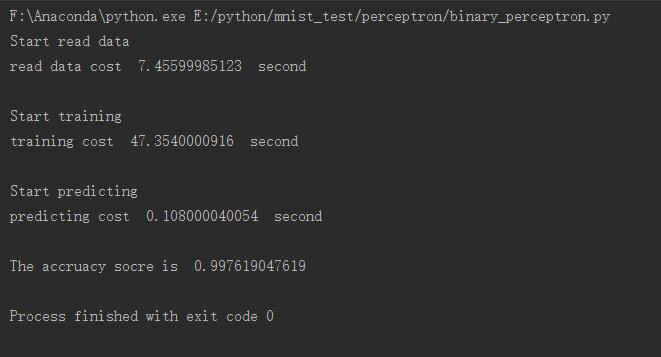
print "The accruacy socre is ", score執行結果如下所示,可以看到準確度還不錯
演算法的收斂性
證明:Novikoff定理
演算法的對偶形式
為了求解更簡單,所以用對偶形式
相關文章
- 【原創】python實現BP神經網路識別Mnist資料集Python神經網路
- MNIST資料集介紹
- TensorFlow 入門(MNIST資料集)
- Pytorch筆記之 多層感知機實現MNIST資料集分類PyTorch筆記
- Python後臺開發(第二章: 模型類實現)Python模型
- python 將Mnist資料集轉為jpg,並按比例/標籤拆分為多個子資料集Python
- 深度學習(一)之MNIST資料集分類深度學習
- 感知器演算法及其python 實現 V2.0演算法Python
- keras 手動搭建alexnet並訓練mnist資料集Keras
- 首次!用合成人臉資料集訓練的識別模型,效能高於真實資料集模型
- TensorFlow系列專題(六):實戰專案Mnist手寫資料集識別
- MNIST資料集詳解及視覺化處理(pytorch)視覺化PyTorch
- 目標檢測(2):LeNet-5 的 PyTorch 復現(MNIST 手寫資料集篇)PyTorch
- Python資料模型Python模型
- 前饋神經網路進行MNIST資料集分類神經網路
- 目標檢測(2):我用 PyTorch 復現了 LeNet-5 神經網路(MNIST 手寫資料集篇)!PyTorch神經網路
- 使用tensorflow操作MNIST資料
- 基於Python和TensorFlow實現BERT模型應用Python模型
- 用tensorflow2實現mnist手寫數字識別
- Tensorflow實現的深度NLP模型集錦(附資源)模型
- 用Python實現一個大資料搜尋引擎Python大資料
- PLC實時資料採集如何實現?
- FCM聚類演算法詳解(Python實現iris資料集)聚類演算法Python
- 教你如何運用python實現不同資料庫間資料同步功能Python資料庫
- [譯] 使用 PyTorch 在 MNIST 資料集上進行邏輯迴歸PyTorch邏輯迴歸
- Kafka 叢集如何實現資料同步?Kafka
- ImageAI實現完整的流程:資料集構建、模型訓練、識別預測AI模型
- Python深度學習入門之mnist-inception(Tensorflow2.0實現)Python深度學習
- matlab練習程式(神經網路識別mnist手寫資料集)Matlab神經網路
- Spring AI中使用嵌入模型和向量資料庫實現RAG應用SpringAI模型資料庫
- 用DolphinScheduler輕鬆實現Flume資料採集任務自動化!
- 《資料安全能力成熟度模型》實踐指南02:資料採集管理模型
- PowerDesigner實現Oracle資料庫連線生成模型Oracle資料庫模型
- 手把手教你在Python中實現文字分類(附程式碼、資料集)Python文字分類
- 基於Python的Xgboost模型實現Python模型
- 尋找手寫資料集MNIST程式的最佳引數(learning_rate、nodes、epoch)
- DeepLab 使用 Cityscapes 資料集訓練模型模型
- ML.NET呼叫Tensorflow模型示例——MNIST模型
- 資料重整:用Java實現精準Excel資料排序的實用策略JavaExcel排序