http協議、HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse
http協議
什麼是http協議
對瀏覽器客戶端和伺服器端之間資料傳輸的格式規範
檢視http資料的工具
1)使用火狐的firebug外掛(右鍵->firebug->網路)
2)使用谷歌的“審查元素”
3)使用系統自帶的telnet工具(遠端訪問工具)
- a)telnet localhost 8080 訪問tomcat伺服器
- b)ctrl+] 回車 可以看到回顯
- c)輸入請求內容
如:輸入請求的http可以是這樣(不一定要完整)
GET /day08_01/hello HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
http資料內容
請求資料
GET /day09/hello HTTP/1.1 --請求行
Host: localhost:8080 --請求頭(多個key-value物件)
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:35.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/35.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: zh-cn,en-us;q=0.8,zh;q=0.5,en;q=0.3
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
--一個空行
name=eric&password=123456 --(可選)實體內容
1、請求行
GET /day09/hello HTTP/1.1請求方式+URI+http版本號
請求方式:
GET vs POST 區別
1)GET方式提交
a)位址列(URI)會跟上引數資料。以?開頭,多個引數之間以&分割。
GET /day09/testMethod.html?name=eric&password=123456 HTTP/1.1b)GET提交引數資料有限制,不超過1KB。
c)GET方式不適合提交敏感密碼。
d)注意: 瀏覽器直接訪問的請求,預設提交方式是GET方式
2)POST方式提交
a)引數不會跟著URI後面。引數而是跟在請求的實體內容中。沒有?開頭,多個引數之間以&分割。
POST /day09/testMethod.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:35.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/35.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: zh-cn,en-us;q=0.8,zh;q=0.5,en;q=0.3
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Referer: http://localhost:8080/day09/testMethod.html
Connection: keep-alive
name=eric&password=123456
b)POST提交的引數資料沒有限制。
c)POST方式提交敏感資料。
URI:
URI: 統一資源標記符。/day09/hello。用於標記任何資源。是一種路徑表示
URL: 統一資源定位符。如:http://localhost:8080/day09/testImg.html。只能定位網際網路資源。是URI 的子集。
http版本號
http1.0:當前瀏覽器客戶端與伺服器端建立連線之後,只能傳送一次請求,一次請求之後連線關閉。
http1.1:當前瀏覽器客戶端與伺服器端建立連線之後,可以在一次連線中傳送多次請求。(基本都使用1.1)
2、請求頭
會出現的請求頭及其含義如下:
Accept: text/html,image/* -- 瀏覽器接受的資料型別
Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1 -- 瀏覽器接受的編碼格式
Accept-Encoding: gzip,compress --瀏覽器接受的資料壓縮格式
Accept-Language: en-us,zh- --瀏覽器接受的語言
Host: www.it315.org:80 --(必須的)當前請求訪問的目標地址(主機:埠)
If-Modified-Since: Tue, 11 Jul 2000 18:23:51 GMT --瀏覽器最後的快取時間
Referer: http://www.it315.org/index.jsp -- 當前請求來自於哪裡
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT 5.0) --瀏覽器型別
Cookie:name=eric -- 瀏覽器儲存的cookie資訊
Connection: close/Keep-Alive -- 瀏覽器跟伺服器連線狀態。close: 連線關閉 keep-alive:儲存連線。
Date: Tue, 11 Jul 2000 18:23:51 GMT -- 請求發出的時間
3、請求實體
只有POST提交的引數會放到實體內容中
返回資料
HTTP/1.1 200 OK --響應行
Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 --響應頭(key-vaule)
Content-Length: 24
Date: Fri, 30 Jan 2015 01:54:57 GMT
--一個空行
this is hello servlet!!! --實體內容
1、響應行
http協議+狀態碼+狀態標識
狀態碼:
常見的狀態:
200 : 表示請求處理完成並完美返回
302: 表示請求需要進一步細化。
404: 表示客戶訪問的資源找不到。
500: 表示伺服器的資源傳送錯誤。(伺服器內部錯誤)
2、響應頭
常見的響應頭如下:
Location: http://www.it315.org/index.jsp -表示重定向的地址,該頭和302的狀態碼一起使用。
Server:apache tomcat ---表示伺服器的型別
Content-Encoding: gzip -- 表示伺服器傳送給瀏覽器的資料壓縮型別
Content-Length: 80 --表示伺服器傳送給瀏覽器的資料長度
Content-Language: zh-cn --表示伺服器支援的語言
Content-Type: text/html; charset=GB2312 --表示伺服器傳送給瀏覽器的資料型別及內容編碼
Last-Modified: Tue, 11 Jul 2000 18:23:51 GMT --表示伺服器資源的最後修改時間
Refresh: 1;url=http://www.it315.org --表示定時重新整理
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=aaa.zip --表示告訴瀏覽器以下載方式開啟資源(下載檔案時用到)
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Set-Cookie:SS=Q0=5Lb_nQ; path=/search --表示伺服器傳送給瀏覽器的cookie資訊(會話管理用到)
Expires: -1 --表示通知瀏覽器不進行快取
Cache-Control: no-cache
Pragma: no-cache
Connection: close/Keep-Alive --表示伺服器和瀏覽器的連線狀態。close:關閉連線 keep-alive:儲存連線
3、實體內容
可以是html,也可以是image影象,也可以是文字資訊等…
HttpServletRequest
什麼是HttpServletRequest
伺服器將客戶端(瀏覽器)傳過來的http請求封裝成HttpServletRequest物件,供開發者呼叫,方便拿到請求的相關資訊
核心API
請求行:
request.getMethod(); 請求方式
request.getRequetURI() / request.getRequetURL() 請求資源
request.getProtocol() 請求http協議版本
請求頭:
request.getHeader("名稱") 根據請求頭獲取請求值
request.getHeaderNames() 獲取所有的請求頭名稱拿請求實體內容
request.getParameter(“引數名”); 根據引數名獲取引數值(注意,只能獲取一個值的引數)
request.getParameterValue(“引數名“);根據引數名獲取引數值(可以獲取多個同名值的引數)
request.getParameterNames(); 獲取所有引數名稱列表
請求引數中文編碼問題
瀏覽器將請求資料編碼成utf-8,而HttpServletRequest在解碼時採用的是iso-8859-1方式(因為是老外寫的,沒考慮中文),因而在瀏覽器返回時會出現亂碼現象。
如圖:
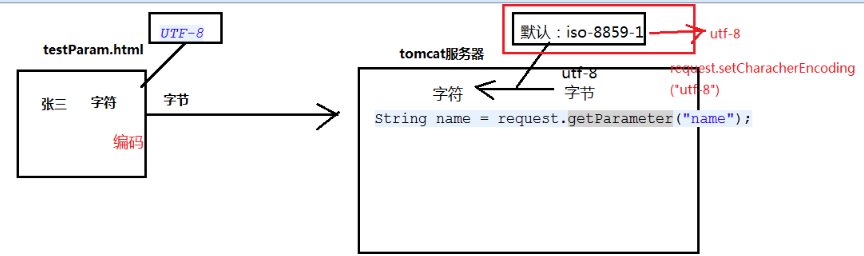
修改方式如下:
1、修改POST方式引數編碼:
request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);//放在方法程式碼前面
2、修改GET方式引數編碼:
手動解碼:String name = new String(name.getBytes(“iso-8859-1”),”utf-8”);//需要一個一個的解析
HttpServletResponse
什麼是HttpServletResponse
HttpServletResponse可以設定http響應資料,包括響應行、響應頭和響應實體內容
核心API
響應行:
response.setStatus() 設定狀態碼
//response.setStatus(404);//修改狀態碼
//response.sendError(404); // 傳送404的狀態碼+404的錯誤頁面
響應頭:
response.setHeader("name","value") 設定響應頭
實體內容:
response.getWriter().writer(); 傳送字元實體內容
response.getOutputStream().writer() 傳送位元組實體內容
響應中文編碼問題
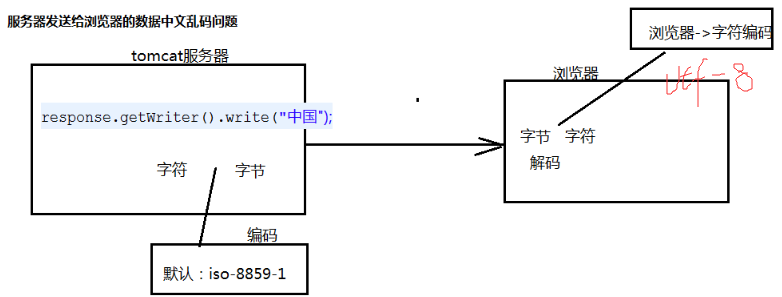
解決:
在開始寫入之前加上:
response.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);
案例
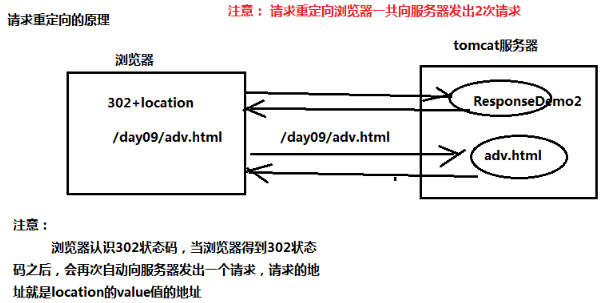
1、請求重定向
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 案例- 請求重定向
* (相當於超連結跳轉頁面)
* @author APPle
*
*/
public class ResponseDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
/**
* 需求: 跳轉到adv.html
* 使用請求重定向: 傳送一個302狀態碼+location的響應頭
*/
/*response.setStatus(302);//傳送一個302狀態碼
response.setHeader("location", "/day09/adv.html"); //location的響應頭
*/ response.getWriter().write("頁面跳轉....");
//請求重定向簡化寫法
response.sendRedirect("/day09/adv.html");
}
}第一次返回內容分析
原理:
2、定時重新整理
/**
* 案例- 定時重新整理
* @author APPle
*
*/
public class ResponseDemo3 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
/**
* 定時重新整理
* 原理:瀏覽器認識refresh頭,得到refresh頭之後重新請求當前資源
*/
//response.setHeader("refresh", "1"); //每隔1秒重新整理次頁面
/**
* 隔n秒之後跳轉另外的資源
*/
response.setHeader("refresh", "3;url=/day09/adv.html");//隔3秒之後跳轉到adv.html
}
}3、content-Type作用
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 案例- content-Type作用
* @author APPle
*
*/
public class ResponseDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
/**
* 設定響應實體內容編碼
*/
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setHeader("content-type", "text/html");//瀏覽器會使用html的格式來解讀下面的內容
//response.setContentType("text/xml");////瀏覽器會使用xml的格式來解讀下面的內容
response.getWriter().write("<html><head><title>this is my tiheadlte</title></><body>中國</body></html>");//字元
//response.getOutputStream().write("<html><head><title>this is tilte</title></head><body>中國</body></html>".getBytes("utf-8"));//位元組
}
}圖片:
response.setContentType("image/jpg");//二進位制 圖片
File file = new File("e:/mm.jpg");
//設定以下載方式開啟檔案
//response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename="+file.getName());
//傳送圖片
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//把圖片內容寫出到瀏覽器
while( (len=in.read(buf))!=-1 ){
response.getOutputStream().write(buf, 0, len);
}相關文章
- JavaWeb Servlet Http協議 HttpServletRequestJavaWebServletHTTP協議
- HTTP 協議HTTP協議
- [HTTP協議]HTTP協議
- http協議HTTP協議
- #SpringMVC:使用原生的Servlet API #HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse @FDDLCSpringMVCServletAPIHTTP
- RTSP協議、RTMP協議、HTTP協議的區別協議HTTP
- http協議分析HTTP協議
- 理解http協議HTTP協議
- HTTP協議概述HTTP協議
- HTTP 協議類HTTP協議
- HTTP協議(2)HTTP協議
- 小解http協議HTTP協議
- 02 前端HTTP協議(圖解HTTP) 之 簡單的HTTP協議前端HTTP協議圖解
- HTTP 協議圖解HTTP協議圖解
- 瞭解HTTP協議HTTP協議
- HTTP協議那些事HTTP協議
- HTTP協議簡述HTTP協議
- HTTP 協議簡介HTTP協議
- Http協議簡介HTTP協議
- HTTP2 協議HTTP協議
- 簡述HTTP協議HTTP協議
- HTTP 協議完全解析HTTP協議
- HTTP協議基礎HTTP協議
- Http協議入門HTTP協議
- HTTP通訊協議HTTP協議
- 淺談HTTP協議HTTP協議
- HTTP 協議入門HTTP協議
- 圖解 HTTP 協議圖解HTTP協議
- http協議內容HTTP協議
- HTTP 協議詳解HTTP協議
- HTTP協議概念篇HTTP協議
- HTTP協議詳解HTTP協議
- HTTP協議之:HTTP/1.1和HTTP/2HTTP協議
- HTTP協議-HTTP響應報文HTTP協議
- HTTP協議和MQTT協議對比誰更好HTTP協議MQQT
- 網路通訊協議-HTTP協議詳解!協議HTTP
- http協議學習系列(協議詳解篇)HTTP協議
- 如何優雅地讀寫HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的請求體HTTPServlet