資料結構與演算法面試題80道
題目來源“資料結構與演算法面試題80道”。這是第一部分,包含其中的第1題到第5題。
在此給出我的解法,如你有更好的解法,歡迎留言。
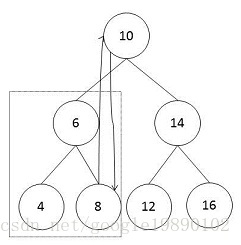
問題分析:二叉查詢樹是一種二叉樹的結構,其中,根節點的值大於左子樹的值,小於右子樹的值。而二叉查詢樹的中序遍歷即為排序的結果。對於根節點,前驅指標指向左子樹中最大的節點,同理,後驅指標指向右子樹中最小的節點,如下圖所示:
樹是一種遞迴的結果,因此,對於左右子樹,也需要執行相同的操作。
方法:
BSTreeNode* convert(BSTreeNode *root){
if (NULL == root ||
(NULL == root->m_pLeft && NULL == root->m_pRight)){
return root;
}
convert(root->m_pLeft);
BSTreeNode* p_left = root->m_pLeft;
while(p_left->m_pRight != NULL){
p_left = p_left->m_pRight;
}
root->m_pLeft = p_left;
p_left->m_pRight = root;
convert(root->m_pRight);
BSTreeNode* p_right = root->m_pRight;
while(p_right->m_pLeft != NULL){
p_right = p_right->m_pLeft;
}
root->m_pRight = p_right;
p_right->m_pLeft = root;
BSTreeNode *p = root;
while (NULL != p->m_pLeft){
p = p->m_pLeft;
}
return p;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
問題分析:棧的特點是先進後出。要能夠取出當前的最小值,需要用另一個棧儲存當前的最小值,所以可採用“雙棧”的結構,一個棧儲存所有的值,另一個棧儲存當前的最小值。
方法:
template <class Type> class min_stack{
private:
stack<Type> s1;
stack<Type> s2;
public:
min_stack(){}
~min_stack(){}
Type min(){
if (!s2.empty()){
return s2.top();
}
}
void push(Type a){
s1.push(a);
if (s2.empty() || a <= s2.top()){
s2.push(a);
}
}
Type pop(){
if (!s1.empty() && !s2.empty()){// 非空
if (s1.top() == s2.top()){
s2.pop();
}
return s1.pop();
}
}
};- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
問題分析:在陣列的每一個位置處儲存當前的最大值,當前的最大值組成為:
解決方案:
int get_max_subarray(int *a, int length, bool &is_array_ok){
if (NULL == a || length <= 0){
is_array_ok = false;
return 0;
}
int *p_h_a = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * length);
// 遍歷陣列
int max_num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && p_h_a[i-1] <= 0)){
p_h_a[i] = a[i];
}else{
p_h_a[i] = p_h_a[i-1] + a[i];
}
if (max_num < p_h_a[i]) max_num = p_h_a[i];
}
free(p_h_a);
is_array_ok = true;
return max_num;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
問題分析:核心是樹的遍歷,注意題目中“路徑”的定義,是從根節點到葉子節點。先序遍歷正好是從根節點開始,因此可以利用先序遍歷的過程來實現這個過程。
方法:
void print_vector(vector<BinaryTreeNode *> &v){
vector<BinaryTreeNode *>::iterator it;
for (it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it ++){
printf("%d\t", (*it)->m_nValue);
}
printf("\n");
}
void pre_order_route(BinaryTreeNode *p, int num, vector<BinaryTreeNode *> &q, int ¤t){
if (NULL == p) return;
current += p->m_nValue;
q.push_back(p);
bool is_leaf = (NULL == p->m_pLeft) && (NULL == p->m_pRight);
if (current == num && is_leaf){
print_vector(q);
}
if (NULL != p->m_pLeft){
pre_order_route(p->m_pLeft, num, q, current);
}
if (NULL != p->m_pRight){
pre_order_route(p->m_pRight, num, q, current);
}
current -= (*(q.end() - 1))->m_nValue;
q.pop_back();
}
void print_route(BinaryTreeNode *root, int num){
vector<BinaryTreeNode *> q;// 用佇列儲存已經訪問過的節點
int current = 0;
pre_order_route(root, num, q, current);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
問題分析:這是一道比較經典的題目,查詢最小的k個元素,最簡單的方法就是對這n個整數排序,排序完成後,直接輸出前k個最小的元素。那麼最快的排序方法是快速排序,其演算法的時間複雜度為O(nlogn)。是否還存在比這個更快的方法呢?
方法一:利用快速排序的思想,時間複雜度為O(n)
按照某個點將陣列劃分成左右兩部分,左邊的數都小於該劃分節點,右邊的數都大於該劃分節點。如果最終該劃分節點的位置小於k-1,則在右邊節點中繼續劃分;如果最終該劃分節點的位置大於k-1,則在左邊節點中繼續劃分。這個過程直到最終的劃分節點的位置正好為k-1。
int swap(int *a, int start, int end, int point_index){
int par_point = a[point_index];
while (start < end){
if (a[start] >= par_point && a[end] <= par_point){
int tmp = a[start];
a[start] = a[end];
a[end] = tmp;
start ++;
end --;
}else if(a[start] < par_point){
start ++;
}else{
end --;
}
}
return start;
}
void get_min_k(int *a, int length, int k){
if (k > length || NULL == a || length <= 0) return;
int new_index = swap(a, 0, length-1, k);
while (true){
if (new_index == k-1) break;
else if (new_index > k-1){
new_index = swap(a, 0, new_index-1, k);
}else{
new_index = swap(a, new_index+1, length-1, k);
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
方法二:利用堆排序,時間複雜度為O(nlogk)
上述方法的缺點是其對陣列進行了修改,在堆排序中,可採用小頂堆,其中堆的大小為k,若此時堆的大小小於k時,則將數插入堆中;若此時堆中的大小大於等於k,則比較堆中最大的整數與待插入整數的大小,插入較小的整數。
void get_min_k(int *a, int length, int k, set<int> &s){
if (k > length || NULL == a || length <= 0) return;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if (s.size() < k){
s.insert(a[i]);
}else{
set<int>::iterator it = --s.end();
if (a[i] < *it){
s.erase(*it);
s.insert(a[i]);
}
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
相關文章
- 基礎面試題 — 資料結構與演算法面試題資料結構演算法
- 10 道資料結構演算法題,不看答案你會幾道題資料結構演算法
- 演算法、資料結構 常見面試題演算法資料結構面試題
- 資料結構與演算法常見問題(面試題)不定時更新資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—棧資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—字串資料結構演算法面試題字串
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—連結串列資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構與演算法之一道題感受演算法(演算法入門)資料結構演算法
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—數字題總結資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構與演算法入門題資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法-資料結構(棧)資料結構演算法
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—揹包問題總結資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—遞迴演算法總結資料結構演算法面試題遞迴
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—隨機演算法總結資料結構演算法面試題隨機
- [面試專題]資料結構和演算法-JS之魂面試資料結構演算法JS
- 資料結構面試100題資料結構面試
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—二叉樹面試題彙總資料結構演算法面試題二叉樹
- 資料結構演算法題資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法資料結構演算法
- 資料結構:初識(資料結構、演算法與演算法分析)資料結構演算法
- Java資料結構與演算法面試題-兩數之和 作者:哇塞大嘴好帥Java資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—二叉堆資料結構演算法面試題
- 資料結構與演算法:圖形結構資料結構演算法
- 演算法與資料結構1800題演算法資料結構
- 【資料結構與演算法】揹包問題總結梳理資料結構演算法
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—排序演算法之快速排序資料結構演算法面試題排序
- 資料結構和演算法面試題系列—C指標、陣列和結構體資料結構演算法面試題指標陣列結構體
- 每日一道演算法題之陣列實現資料結構演算法陣列資料結構
- leetcode演算法資料結構題解---資料結構LeetCode演算法資料結構
- 刷了80道演算法題以後演算法
- 【JavaScript 演算法與資料結構】JavaScript演算法資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法03資料結構演算法
- 演算法與資料結構——序演算法資料結構
- 資料結構與演算法——概述資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法-堆資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法02資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法(1)資料結構演算法
- 資料結構與演算法——排序資料結構演算法排序