FloatingActionButton原始碼解析
FloatingActionButton原始碼解析
背景
FloatingActionButton(下文以fab代替)是android support design元件庫中提供的一個檢視控制元件,是material design設計中fab的官方實現。
此控制元件的官方介紹如下:
Floating action buttons are used for a promoted action. They are distinguished by a circled icon floating above the UI and have motion behaviors that include morphing, launching, and a transferring anchor point.
關於該控制元件的設計規範及使用場景請參考文件:
http://www.google.com/design/spec/components/buttons-floating-action-button.html#
如果你還不瞭解design元件庫,請參考官方部落格:
http://android-developers.blogspot.hk/2015/05/android-design-support-library.html
開始
原始碼版本:23.3.0
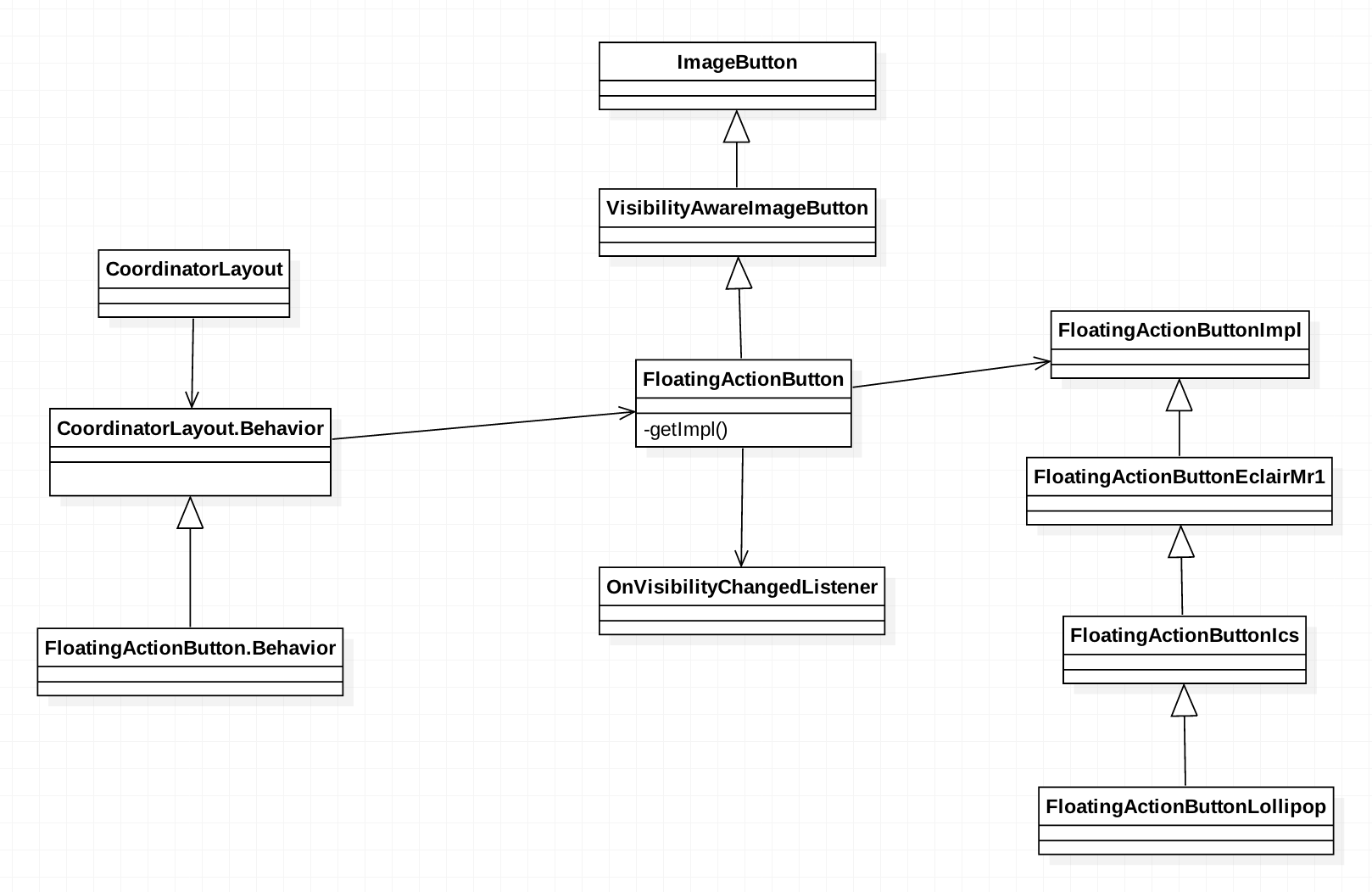
fab間接繼承自ImageView,因而擁有ImageView的大部分特性。但是其內部還是做了很多定製,我們一一來看。
1. fab的自定義屬性、背景著色相關
從構造器開始:
public FloatingActionButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//檢查是否使用Theme.Appcompat主題
ThemeUtils.checkAppCompatTheme(context);
//拿到自定義屬性並賦值
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.FloatingActionButton, defStyleAttr,
R.style.Widget_Design_FloatingActionButton);
...
a.recycle();
final int maxImageSize = (int) getResources().getDimension(R.dimen.design_fab_image_size);
mImagePadding = (getSizeDimension() - maxImageSize) / 2;
//背景著色
getImpl().setBackgroundDrawable(mBackgroundTint, mBackgroundTintMode,
mRippleColor, mBorderWidth);
//繪製陰影
getImpl().setElevation(elevation);
...
}構造器中主要是拿到使用者設定的自定義屬性,比如著色、波紋顏色、大小等等,一共有以下幾個屬性可以定義。
<declare-styleable name="FloatingActionButton">
<attr name="backgroundTint"/>
<attr name="backgroundTintMode"/>
<attr format="color" name="rippleColor"/>
<attr name="fabSize">
<enum name="normal" value="0"/>
<enum name="mini" value="1"/>
</attr>
<attr name="elevation"/>
<attr format="dimension" name="pressedTranslationZ"/>
<attr format="dimension" name="borderWidth"/>
<attr format="boolean" name="useCompatPadding"/>
</declare-styleable>
屬性的預設值定義如下:
<style name="Widget.Design.FloatingActionButton" parent="android:Widget">
<item name="android:background">@drawable/design_fab_background</item>
<item name="backgroundTint">?attr/colorAccent</item>
<item name="fabSize">normal</item>
<item name="elevation">@dimen/design_fab_elevation</item>
<item name="pressedTranslationZ">@dimen/design_fab_translation_z_pressed</item>
<item name="rippleColor">?attr/colorControlHighlight</item>
<item name="borderWidth">@dimen/design_fab_border_width</item>
</style>需要注意的是android:background屬性,這裡指定了background為design_fab_background,並且不允許改變:
@Override
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background) {
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Setting a custom background is not supported.");
}那麼我們來看下這個background長啥樣:
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="oval">
<solid android:color="@android:color/white" />
</shape>很顯然,fab的形狀固定為圓形都是因為這個background。那麼這裡指定了背景色為白色,那是不是fab只能是白色背景呢?當然不是,還有我們牛逼的backgroundTint(即背景著色),tint是android 5.x引進的一個新特性,可以動態地給drawable資源著色,其原理就是通過給控制元件設定colorFilter:
drawable.java
public void setColorFilter(@ColorInt int color, @NonNull PorterDuff.Mode mode) {
setColorFilter(new PorterDuffColorFilter(color, mode));
}預設的著色模式為SRC_IN:
static final PorterDuff.Mode DEFAULT_TINT_MODE = PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN;
在fab構造的時候,會指定著色為?attr/colorAccent,即當前主題的colorAccent屬性值。
然後執行如下程式碼,進行著色。
getImpl().setBackgroundDrawable(mBackgroundTint, mBackgroundTintMode,
mRippleColor, mBorderWidth);因為不同版本間的實現略有不同,所以這裡會根據不同版本建立不同的FloatingActionButtonImpl實現類:
private FloatingActionButtonImpl createImpl() {
final int sdk = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
if (sdk >= 21) {
return new FloatingActionButtonLollipop(this, new ShadowDelegateImpl());
} else if (sdk >= 14) {
return new FloatingActionButtonIcs(this, new ShadowDelegateImpl());
} else {
return new FloatingActionButtonEclairMr1(this, new ShadowDelegateImpl());
}
}以5.x為例,其setBackgroundDrawable實現程式碼如下:
先建立著色的背景drawable。
GradientDrawable createShapeDrawable() {
GradientDrawable d = new GradientDrawable();
d.setShape(GradientDrawable.OVAL);
d.setColor(Color.WHITE);
return d;
}再對此drawable設定tint:
@Override
void setBackgroundDrawable(ColorStateList backgroundTint,
PorterDuff.Mode backgroundTintMode, int rippleColor, int borderWidth) {
// Now we need to tint the shape background with the tint
mShapeDrawable = DrawableCompat.wrap(createShapeDrawable());
//著色,這裡會其實就是設定了下colorFilter
DrawableCompat.setTintList(mShapeDrawable, backgroundTint);
if (backgroundTintMode != null) {
DrawableCompat.setTintMode(mShapeDrawable, backgroundTintMode);
}
final Drawable rippleContent;
if (borderWidth > 0) {
mBorderDrawable = createBorderDrawable(borderWidth, backgroundTint);
rippleContent = new LayerDrawable(new Drawable[]{mBorderDrawable, mShapeDrawable});
} else {
mBorderDrawable = null;
rippleContent = mShapeDrawable;
}
mRippleDrawable = new RippleDrawable(ColorStateList.valueOf(rippleColor),
rippleContent, null);
mContentBackground = mRippleDrawable;
mShadowViewDelegate.setBackgroundDrawable(mRippleDrawable);
}經過著色,fab就呈現出我們想要的顏色啦。
2. fab的大小
再來看fab的大小,fab有兩種大小,一種是NORMAL,一種是MINI,實際大小分別是56dp和40dp,其定義可以在design庫的values.xml中看到。
fab如何控制控制元件大小隻有這兩種規格呢(這樣說不準確,事實上你可以通過設定fab的layout_width/layout_height指定為任意大小,但是我們最好按照MD規範來)?必然是通過複寫onMeasure啦:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//我們希望的大小
final int preferredSize = getSizeDimension();
//最終測量的大小
final int w = resolveAdjustedSize(preferredSize, widthMeasureSpec);
final int h = resolveAdjustedSize(preferredSize, heightMeasureSpec);
//取小值,保證最後繪製的是圓形
final int d = Math.min(w, h);
// We add the shadow's padding to the measured dimension
setMeasuredDimension(
d + mShadowPadding.left + mShadowPadding.right,
d + mShadowPadding.top + mShadowPadding.bottom);
}其中getSizeDimension方法計算出來的是我們期望的大小:
final int getSizeDimension() {
switch (mSize) {
case SIZE_MINI:
return getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.design_fab_size_mini);//40dp
case SIZE_NORMAL:
default:
return getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.design_fab_size_normal);//56dp
}
}但是最終的值還是得看我們設定的LayoutParams。關於控制元件測量相關內容不在此文介紹範圍內,大家可以自行google。
3.fab的動畫
fab還支援fab以動畫的方式顯現/隱藏,通常和AppBarLayout一起使用,可以通過hide()/show()兩個方法控制。
那麼動畫是如何實現的呢:
private void show(OnVisibilityChangedListener listener, boolean fromUser) {
getImpl().show(wrapOnVisibilityChangedListener(listener), fromUser);
}
private void hide(@Nullable OnVisibilityChangedListener listener, boolean fromUser) {
getImpl().hide(wrapOnVisibilityChangedListener(listener), fromUser);
}這裡因為要相容不同版本,所以具體實現也交給了不同的fab實現類。3.x之後很好辦,直接使用屬性動畫,如果是3.x之前的話,那麼只能使用傳統的Animation了
以hide()為例,使用屬性動畫較為簡單,直接使用View#animate()即可鏈式呼叫。
@Override
void hide(@Nullable final InternalVisibilityChangedListener listener, final boolean fromUser) {
if (mIsHiding || mView.getVisibility() != View.VISIBLE) {
// A hide animation is in progress, or we're already hidden. Skip the call
if (listener != null) {
listener.onHidden();
}
return;
}
if (!ViewCompat.isLaidOut(mView) || mView.isInEditMode()) {
// If the view isn't laid out, or we're in the editor, don't run the animation
mView.internalSetVisibility(View.GONE, fromUser);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onHidden();
}
} else {
mView.animate().cancel();
mView.animate()
.scaleX(0f)
.scaleY(0f)
.alpha(0f)
.setDuration(SHOW_HIDE_ANIM_DURATION)
.setInterpolator(AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_LINEAR_IN_INTERPOLATOR)
.setListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
private boolean mCancelled;
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
mIsHiding = true;
mCancelled = false;
mView.internalSetVisibility(View.VISIBLE, fromUser);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
mIsHiding = false;
mCancelled = true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
mIsHiding = false;
if (!mCancelled) {
mView.internalSetVisibility(View.GONE, fromUser);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onHidden();
}
}
}
});
}
}如果使用傳統動畫的話,則先在xml中定義好動畫,然後構造Animation例項,啟動動畫。
@Override
void hide(@Nullable final InternalVisibilityChangedListener listener, final boolean fromUser) {
if (mIsHiding || mView.getVisibility() != View.VISIBLE) {
// A hide animation is in progress, or we're already hidden. Skip the call
if (listener != null) {
listener.onHidden();
}
return;
}
Animation anim = android.view.animation.AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(
mView.getContext(), R.anim.design_fab_out);
anim.setInterpolator(AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_LINEAR_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
anim.setDuration(SHOW_HIDE_ANIM_DURATION);
anim.setAnimationListener(new AnimationUtils.AnimationListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
mIsHiding = true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
mIsHiding = false;
mView.internalSetVisibility(View.GONE, fromUser);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onHidden();
}
}
});
mView.startAnimation(anim);
}4. fab與CoordinatorLayout的互動
fab並不直接與CoordinatorLayout聯絡,而是通過CoordinatorLayout#Behavior作為橋樑。CoordinatorLayout類通過CoordinatorLayout#Behavior可以間接控制其直系子View的行為,能控制什麼行為?View測量、佈局、touch事件攔截、監聽、NestedScroll等等。是不是很屌。
關於這塊內容也不在本文範圍內,大家可以自行參考相關資料。
fab內部實現了CoordinatorLayout#Behavior抽象類,並有選擇性地實現了三個方法:
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent,
FloatingActionButton child, View dependency);
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
View dependency);
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
int layoutDirection);
fab為啥要實現Behavior?主要是為了配合其他控制元件完成一些複雜的互動,比較經典的像這個:
fab需要在snackBar彈出的時候自動向上平移,這就得知道SnackBar的狀態了,實現Behavior讓fab有機會監聽到其他CoordinatorLayout子View的狀態,並根據狀態更新自己。
複寫layoutDependsOn方法可以告訴CoordinatorLayout我對哪個View感興趣,
這裡當然是SnackBar了。(注意哦,SnackBar最終展現的是SnackbarLayout,SnackBar本身並不是View)
private static final boolean SNACKBAR_BEHAVIOR_ENABLED = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 11;
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent,
FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
// We're dependent on all SnackbarLayouts (if enabled)
return SNACKBAR_BEHAVIOR_ENABLED && dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout;
}為什麼API LEVEL要大於11呢?因為google偷懶想直接使用屬性動畫。
前面告訴了CoordinatorLayoutfab對SnackBar比較感興趣,那麼當SnackBar狀態改變的時候,CoordinatorLayout就會通過onDependentViewChanged回撥通知fab:
fab就可以更新自己的UI拉(這裡當然是平移嘍):
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
View dependency) {
if (dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout) {
updateFabTranslationForSnackbar(parent, child, dependency);
} else if (dependency instanceof AppBarLayout) {
// If we're depending on an AppBarLayout we will show/hide it automatically
// if the FAB is anchored to the AppBarLayout
updateFabVisibility(parent, (AppBarLayout) dependency, child);
}
return false;
}如果是SnackBar狀態變化了,那麼fab就會根據情況進行平移:
private void updateFabTranslationForSnackbar(CoordinatorLayout parent,
final FloatingActionButton fab, View snackbar) {
final float targetTransY = getFabTranslationYForSnackbar(parent, fab);
if (mFabTranslationY == targetTransY) {
// We're already at (or currently animating to) the target value, return...
return;
}
final float currentTransY = ViewCompat.getTranslationY(fab);
// Make sure that any current animation is cancelled
if (mFabTranslationYAnimator != null && mFabTranslationYAnimator.isRunning()) {
mFabTranslationYAnimator.cancel();
}
if (fab.isShown()
&& Math.abs(currentTransY - targetTransY) > (fab.getHeight() * 0.667f)) {
// If the FAB will be travelling by more than 2/3 of it's height, let's animate
// it instead
if (mFabTranslationYAnimator == null) {
mFabTranslationYAnimator = ViewUtils.createAnimator();
mFabTranslationYAnimator.setInterpolator(
AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
mFabTranslationYAnimator.setUpdateListener(
new ValueAnimatorCompat.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimatorCompat animator) {
ViewCompat.setTranslationY(fab,
animator.getAnimatedFloatValue());
}
});
}
mFabTranslationYAnimator.setFloatValues(currentTransY, targetTransY);
mFabTranslationYAnimator.start();
} else {
// Now update the translation Y
ViewCompat.setTranslationY(fab, targetTransY);
}
mFabTranslationY = targetTransY;
}程式碼裡的註釋很多,我就不解釋了。
前面說到AppBarLayout和fab一起使用可以完成另一個效果,即AppBarLayout伸縮時,fab也可以以動畫的形式顯現、隱藏,其實現如下:
private boolean updateFabVisibility(CoordinatorLayout parent,
AppBarLayout appBarLayout, FloatingActionButton child) {
final CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams lp =
(CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//注意到我們必須為fab指定layout_anchor為appBarLayout
if (lp.getAnchorId() != appBarLayout.getId()) {
// The anchor ID doesn't match the dependency, so we won't automatically
// show/hide the FAB
return false;
}
if (child.getUserSetVisibility() != VISIBLE) {
// The view isn't set to be visible so skip changing it's visibility
return false;
}
if (mTmpRect == null) {
mTmpRect = new Rect();
}
// First, let's get the visible rect of the dependency
final Rect rect = mTmpRect;
ViewGroupUtils.getDescendantRect(parent, appBarLayout, rect);
if (rect.bottom <= appBarLayout.getMinimumHeightForVisibleOverlappingContent()) {
// If the anchor's bottom is below the seam, we'll animate our FAB out
child.hide(null, false);
} else {
// Else, we'll animate our FAB back in
child.show(null, false);
}
return true;
}除此之外,fab#Behavior還實現了onLayoutChild,主要是為了根據AppBarLayout的當前狀態來判斷自己是否需要隱藏。
@Override
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
int layoutDirection) {
// First, lets make sure that the visibility of the FAB is consistent
final List<View> dependencies = parent.getDependencies(child);
for (int i = 0, count = dependencies.size(); i < count; i++) {
final View dependency = dependencies.get(i);
if (dependency instanceof AppBarLayout
&& updateFabVisibility(parent, (AppBarLayout) dependency, child)) {
break;
}
}
// Now let the CoordinatorLayout lay out the FAB
parent.onLayoutChild(child, layoutDirection);
// Now offset it if needed
offsetIfNeeded(parent, child);
return true;
}此方法會在CoordinatorLayout對孩子佈局的時候進行呼叫,CoordinatorLayout會檢查所有的直系孩子,是否設定了Behavior,如果設定了,那麼就執行其onLayoutChild方法:
CoordinatorLayout#onLayout
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
final int layoutDirection = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(this);
final int childCount = mDependencySortedChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = mDependencySortedChildren.get(i);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final Behavior behavior = lp.getBehavior();
if (behavior == null || !behavior.onLayoutChild(this, child, layoutDirection)) {
onLayoutChild(child, layoutDirection);
}
}
}如果該Behavior實現了OnLayoutChild,並且返回了true,那麼將不會執行CoordinatorLayout #onLayoutChild,否則執行預設的佈局方案。
最後一點,這裡的Behavior如何生效的呢?通過註解:
@CoordinatorLayout.DefaultBehavior(FloatingActionButton.Behavior.class)
public class FloatingActionButton extends VisibilityAwareImageButton {CoordinatorLayout在解析孩子的LayoutParams時,會check有無註解:
LayoutParams getResolvedLayoutParams(View child) {
final LayoutParams result = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (!result.mBehaviorResolved) {
Class<?> childClass = child.getClass();
DefaultBehavior defaultBehavior = null;
while (childClass != null &&
(defaultBehavior = childClass.getAnnotation(DefaultBehavior.class)) == null) {
childClass = childClass.getSuperclass();
}
if (defaultBehavior != null) {
try {
result.setBehavior(defaultBehavior.value().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Default behavior class " + defaultBehavior.value().getName() +
" could not be instantiated. Did you forget a default constructor?", e);
}
}
result.mBehaviorResolved = true;
}
return result;
}至此fab解析完畢,謝謝觀看!
如有疑惑,可以issue。
微博:楚奕RX
License
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2015 Rowandjj
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
相關文章
- 【原始碼解析】- ArrayList原始碼解析,絕對詳細原始碼
- Spark原始碼-SparkContext原始碼解析Spark原始碼Context
- CountDownLatch原始碼解析CountDownLatch原始碼
- LeakCanary原始碼解析原始碼
- vuex原始碼解析Vue原始碼
- ArrayBlockQueue原始碼解析BloC原始碼
- AsyncTask原始碼解析原始碼
- CopyOnWriteArrayList原始碼解析原始碼
- Express原始碼解析Express原始碼
- Observer原始碼解析Server原始碼
- SparseArray 原始碼解析原始碼
- RecyclerView原始碼解析View原始碼
- Promise 原始碼解析Promise原始碼
- Koa原始碼解析原始碼
- RateLimiter原始碼解析MIT原始碼
- redux原始碼解析Redux原始碼
- SDWebImage原始碼解析Web原始碼
- CyclicBarrier原始碼解析原始碼
- Semaphore原始碼解析原始碼
- Exchanger原始碼解析原始碼
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer原始碼解析原始碼
- OKio原始碼解析原始碼
- Koa 原始碼解析原始碼
- RxPermission原始碼解析原始碼
- MyBatis原始碼解析MyBatis原始碼
- ArrayList原始碼解析原始碼
- Aspects 原始碼解析原始碼
- LeakCanary 原始碼解析原始碼
- Vue原始碼解析Vue原始碼
- React原始碼解析React原始碼
- ButterKnife原始碼解析原始碼
- HashSet原始碼解析原始碼
- Retrofit 原始碼解析原始碼
- Javapoet原始碼解析Java原始碼
- Vuex 原始碼解析Vue原始碼
- OKHttp原始碼解析HTTP原始碼
- Retrofit原始碼解析原始碼
- Handler原始碼解析原始碼