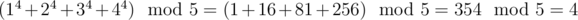A:水題,結構體排序後,看兩個陣列的是否序列相同。
B:分別寫出來1,2,3,4,的n次方對5取餘。你會發現和對5取餘有一個迴圈節。如果%4 = 0,輸出4,否則輸出0.
寫一個大數取餘就過了。
Fedya studies in a gymnasium. Fedya's maths hometask is to calculate the following expression:
(1n + 2n + 3n + 4n) mod 5
for given value of n. Fedya managed to complete the task. Can you? Note that given number n can
be extremely large (e.g. it can exceed any integer type of your programming language).
Output
Print the value of the expression without leading zeros.
Note
Operation x mod y means taking remainder after division x by y.
Note to the first sample:
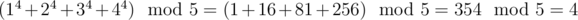
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define eps 1e-9
///#define M 1000100
///#define LL __int64
#define LL long long
///#define INF 0x7ffffff
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PI 3.1415926535898
#define zero(x) ((fabs(x)<eps)?0:x)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000010;
int main()
{
string s;
while(cin >>s)
{
int n= s.size();
int cnt = s[0]-'0';
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cnt %= 4;
cnt = (cnt*10+(s[i]-'0'))%4;
}
if(cnt%4 == 0)
cout<<4<<endl;
else cout<<0<<endl;
}
}
C:給你一些數,你取了一個數那麼比這個數大1,和小1的數字就會被刪掉。問你最大能取到的數的和。
先根據數字進行雜湊,然後線性的dp一遍,dp[i][1] = ma(dp[i-2][0], dp[i-2][1]) + vis[i]*i,dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1]).1代表取這個數,0代表不取。注意資料型別要用long long。
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define eps 1e-9
///#define M 1000100
///#define LL __int64
#define LL long long
///#define INF 0x7ffffff
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PI 3.1415926535898
#define zero(x) ((fabs(x)<eps)?0:x)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000010;
LL vis[maxn];
LL dp[maxn][2];
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >>n)
{
int x;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
vis[x] ++;
}
dp[1][1] = vis[1];
dp[2][1] = vis[2]*2;
dp[2][0] = dp[1][1];
for(int i = 3; i <= maxn-10; i++)
{
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-2][0], dp[i-2][1])+vis[i]*i;
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1]);
}
cout<<max(dp[maxn-10][0], dp[maxn-10][1])<<endl;
}
return 0;
}