計算機圖形學(二)輸出圖元_20_章節總結_程式展示_蝸形線、心形線、螺旋線
蝸形線、心形線、螺旋線
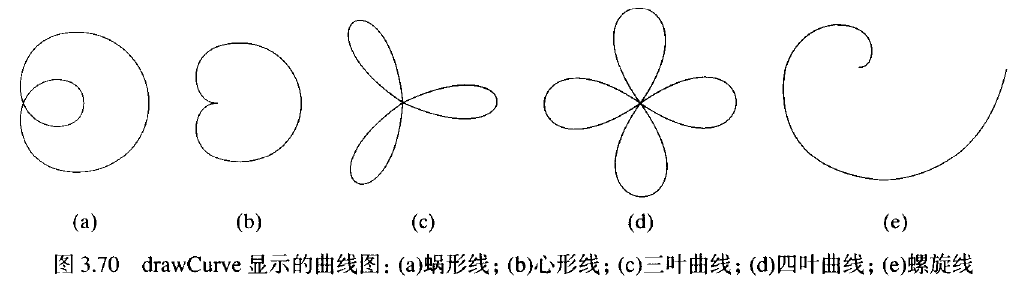
最後一個程式顯示了圓公式的某些變化,其中使用了引數極座標方程(3.28)來計算曲線路徑的點。這些點用做顯示弧的逼近折線中直線段的端點。圖3.70中的弧通過圓半徑r的變化來生成。按照r的不同變化,可生成蝸形線、心形線、螺旋線或其他類似的圖形。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "GL/glut.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
struct screenPt
{
GLint x;
GLint y;
};
typedef enum { limacon = 1, cardioid, threeLeaf, fourLeaf, spiral } curveName;
GLsizei winWidth = 600, winHeight = 500; //Initial display window size.
void init(void)
{
glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
gluOrtho2D(0.0, 200.0, 0.0, 150.0);
}
void lineSegment(screenPt pt1, screenPt pt2)
{
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2i(pt1.x, pt1.y);
glVertex2i(pt2.x, pt2.y);
glEnd();
}
void drawCurve(GLint curveName)
{
/* The limacon of Pascal is a modification of the circle equation
* with the radius varying as r = a * cos (theta) + b, where a
* and b are constants. A cardioid is a limacon with a = b.
* Three-leaf and four-leaf curves are generated when
* r = a * cos (n * theta), with n = 3 and n = 2, respectively.
* A spiral is displayed when r is a multiple of theta.
*/
const GLdouble twoPi = 6.283185;
const GLint a = 175, b = 60;
GLfloat r, theta, dtheta = 1.0 / float(a);
GLint x0 = 200, y0 = 250; // Set an initial screen position.
screenPt curvePt[2];
glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // Set curve position.
curvePt[0].x = x0; // Initialize curve position.
curvePt[0].y = y0;
switch (curveName){
case limacon: curvePt[0].x += a + b; break;
case cardioid: curvePt[0].x += a + a; break;
case threeLeaf: curvePt[0].x += a; break;
case fourLeaf: curvePt[0].x += a; break;
case spiral: break;
default: break;
}
theta = dtheta;
while (theta < twoPi){
switch (curveName){
case limacon:
r = a * cos(theta) + b; break;
case cardioid:
r = a * (1 + cos(theta)); break;
case threeLeaf:
r = a * cos(3 * theta); break;
case fourLeaf:
r = a * cos(2 * theta); break;
case spiral:
r = (a / 4.0) * theta; break;
default: break;
}
curvePt[1].x = x0 + r * cos(theta);
curvePt[1].y = y0 + r * sin(theta);
lineSegment(curvePt[0], curvePt[1]);
curvePt[0].x = curvePt[1].x;
curvePt[0].y = curvePt[1].y;
theta += dtheta;
}
}
void displayFcn(void)
{
GLint curveNum;
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear display window.
cout << "\nEnter the integer value corresponding to\n";
cout << "one of the following curve names.\n";
cout << "Press any other key to exit.\n";
cout << "\n1-limacon, 2-cardioid, 3-threeLeaf, 4-fourLeaf, 5-spiral: ";
cin >> curveNum;
if (curveNum == 1 || curveNum == 2 || curveNum == 3 || curveNum == 4 || curveNum == 5)
drawCurve(curveNum);
else
exit(0);
glFlush();
}
void winReshpeFcn(GLint newWidth, GLint newHeight)
{
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluOrtho2D(0.0, (GLdouble)newWidth, 0.0, (GLdouble)newHeight);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
}
void main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
glutInitWindowSize(winWidth, winHeight);
glutCreateWindow("Draw Curves");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(displayFcn);
glutReshapeFunc(winReshpeFcn);
glutMainLoop();
}我在這裡輸入的是3。輸出3葉曲線形


相關文章
- 計算機圖形學-線性過濾計算機
- 4次Bezier曲線--計算機圖形學 opengl計算機
- 計算機圖形學 第四章 圖形變換計算機
- 圖形學之Unity渲染管線流程Unity
- 圖形學3D渲染管線學習3D
- WPF心形線演算法演算法
- 《Real-Time Rendering 3rd》 提煉總結(二): 圖形渲染管線
- 線上編輯Word——插入圖片、圖形
- CMU出品,計算機圖形學秋季課程已上線,B站同步字幕影片計算機
- java3D與計算機圖形學期末複習 第二章Java3D計算機
- 計算機圖形學入門·光柵化計算機
- 計算機圖形學之矩陣變換計算機矩陣
- AUTOCAD——圖形的輸入與輸出
- 圖形學 畫直線 DDA掃描法與中點畫線法
- 底部K線形態圖解 金針探底圖解
- Tableau——資料前處理、折線圖、餅圖(環形圖)
- 【光能蝸牛的圖形學之旅】Unity紋理初步Unity
- Qt QPolarChart極座標圖(阿基米德線、四葉曲線、六葉花瓣、三葉花瓣、心形曲線)QT
- 小程式—九宮格心形拼圖
- canvas系列教程之多線條組成圖形Canvas
- 【java學習】GUI 圖形程式設計JavaGUI程式設計
- 環形導軌輸送線應用案例
- 圖形處理:給 Canvas 文字填充線性漸變Canvas
- 「技美之路 第01篇」圖形 1.1 渲染流水線
- FCPX外掛:直線圖形矩形線條路徑動畫預設動畫
- 好程式設計師web前端學習路線分享純css繪製各種圖形程式設計師Web前端CSS
- 計算機圖形學:虛擬和現實世界的融合計算機
- python 圖形初學Python
- 畫影圖形: SVG & Canvas 圖形對比SVGCanvas
- Xmanager4遠端連線linux圖形介面(vsftpd配置)LinuxFTP
- Quart2D 畫圖一 (簡單畫線、形狀)
- 計算機圖形學原理及實踐——C語言描述pdf計算機C語言
- 前端使用 Konva 實現視覺化設計器(22)- 繪製圖形(矩形、直線、折線)前端視覺化
- 【CG】圖形學相關
- 四邊形輔助線做法
- 折線(Polyline)、多邊形(Polygon)Go
- 計算機圖形:三維觀察之投影變換計算機
- 數學與Python有機結合及統計學、微積分、線性代數相關資源、圖形軟體Python
- 圖形程式設計問題記錄程式設計