作業系統(Linux)--按優先數排程演算法實現處理器排程
這道題慢悠悠地做,出現了很多錯誤,大多都是空指標產生的中斷,最後還是實現了,程式碼寫得有點亂,有時間優化下(當然有同學指點下也是不錯的,哈哈)。
實習題目:
設計一個按優先數排程演算法實現處理器排程的程式。
[提示]:
(1) 假定系統有5個程式,每個程式用一個PCB來代表。PCB的格式為:
程式名、指標、要求執行時間、優先數、狀態。
程式名——P1~P5。
指標——按優先數的大小把5個程式連成佇列,用指標指出下一個程式PCB的首地址。
要求執行時間——假設程式需要執行的單位時間數。
優先數——賦予程式的優先數,排程時總是選取優先數大的程式先執行。
狀態——假設兩種狀態,就緒,用R表示,和結束,用E表示。初始狀態都為就緒狀態。
(2) 每次執行之前,為每個程式任意確定它的“優先數”和“要求執行時間”。
(3) 處理器總是選隊首程式執行。採用動態改變優先數的辦法,程式每執行1次,優先數減1,要求執行時間減1。
(4) 程式執行一次後,若要求執行時間不等於0,則將它加入佇列,否則,將狀態改為“結束”,退出佇列。
(5) 若就緒佇列為空,結束,否則,重複(3)。
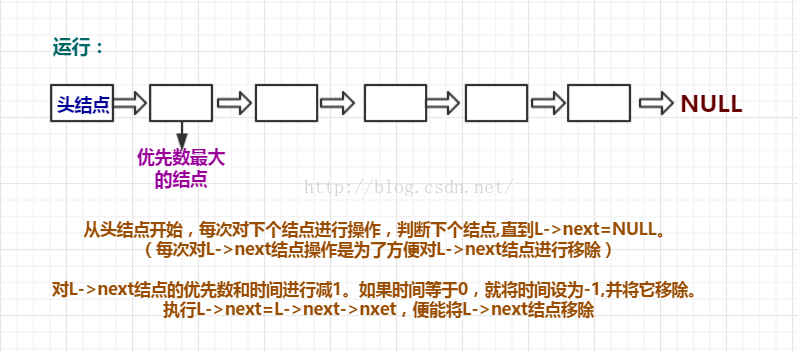
思路流程圖:
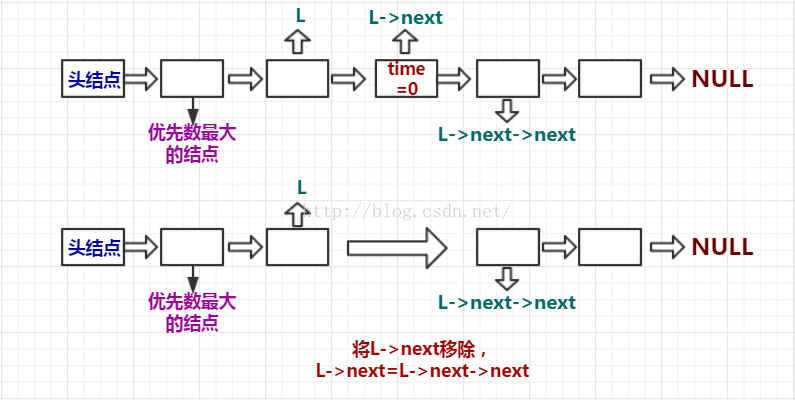
對執行時間的判斷:
對優先數的判斷:
/*
author:huangpingyi
date:2016 11 24
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
static int point = 0;//用於計算程式是否執行完成
struct PCB
{
int pid;
int priority;
int time;
PCB *next;
};
void tailCreate(PCB *L)
{
srand((unsigned int)time(0));//以時間為隨機數種子,保證每次隨機數不一樣
int priority = rand() % 5;//隨機優先數
PCB *s, *r = L;
for (int i = 0; i<5; i++)
{
//隨機時間為1到50
int number = rand() % 5;
while (number == 0)
//如果是0就一直隨機,直到出現不是0的為止
number = rand() % 5;
//tail_insert用尾插法初始化
s = new PCB;
s->pid = i + 1;
s->priority = (i + priority) % 5 + 1;
s->time = number;
if (s->priority != 5 || r->next == NULL)//如果r->next==NULL表示為佇列只有一個頭結點,就直接插入
{
r->next = s;
r = s;
}
if ((s->priority == 5) && (r->next != NULL))//如果佇列不為空,就將它放在頭結點後面
{
s->next = L->next;
L->next = s;
}
}
r->next = NULL;
}
void run(PCB *L)//執行
{
PCB *c = L;
PCB *p = L;
for (L; L; L = L->next)
{
if (L->next == NULL)
break;
//由於存在存在頭結點,所以從L->next開始
L->next->priority = L->next->priority - 1;
L->next->time = L->next->time - 1;
if (L->next->time == 0)
//如果執行時間為0,就將它移除佇列中
{
cout << "run over" <<"->PID->"<< L->next->pid << endl;
L->next->time = -1;
L->next = L->next->next;
//由於出現了L->next = L->next->next;這步,
//接著執行for迴圈的第三個表示式,便跳過了L->next->next這個結點,接著執行L->next->next->next這個結點
//所以需要判斷一下L->next->next這個結點
if (L->next != NULL&&L->next->time != 0)
{
L->next->priority = L->next->priority - 1;
L->next->time = L->next->time - 1;
}
//如果L->next->next->time的值等於0,便會將它移除佇列,接著執行L->next=L->next->next這步
//所以需要while迴圈來判斷
while (L->next != NULL&&L->next->time == 0)
{
cout << "run over" <<"->PID->"<< L->next->pid << endl;
L->next->time = -1;
L->next = L->next->next;
point = point + 1;
if (L->next != NULL)
{
L->next->priority = L->next->priority - 1;
L->next->time = L->next->time - 1;
}
}
point = point + 1;
}
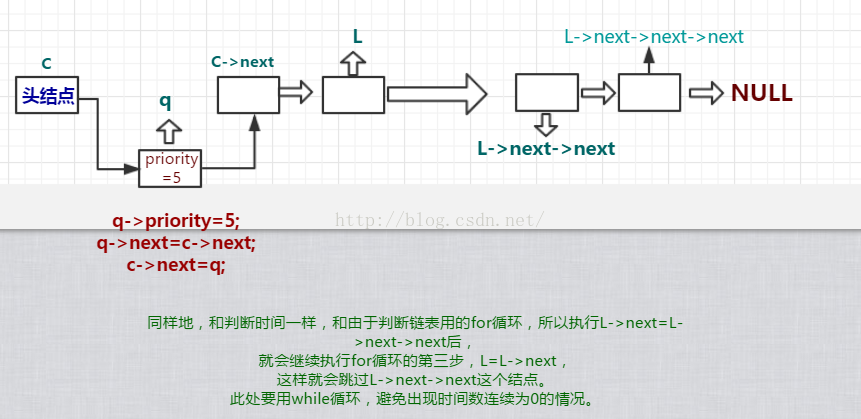
if (L->next != NULL&&L->next->priority == 0)//如果優先數為0就將它變成0放在隊首
{
//******
PCB *q = L->next;
L->next = L->next->next;
q->priority = 5;
q->next = c->next;
c->next = q;
//由於執行了L->next=L->next->next
//所以又會執行上面那步同樣地操作
if (L->next != NULL&&L->next->time != 0)
{
L->next->priority = L->next->priority - 1;
L->next->time = L->next->time - 1;
}
while (L->next != NULL&&L->next->time == 0)
{
cout << "run over" << "->PID->"<<L->next->pid << endl;
L->next->time = -1;
L->next = L->next->next;
point = point + 1;
if (L->next != NULL)
{
L->next->priority = L->next->priority - 1;
L->next->time = L->next->time - 1;
}
}
}
}
L = p;
}
int main()
{
PCB *L, *m;
L = new PCB;//初始化頭結點
L->next = NULL;
tailCreate(L);
m = L;
L = L->next;
cout << "=============" << endl;
cout << "Init" << endl;
cout << "==============" << endl;
for (L; L; L = L->next)
{
cout <<"PID :"<< L->pid << endl;
cout << "Time :"<<L->time << endl;
cout << "Priority :"<<L->priority << endl;
cout << "******* " << endl;
cout << endl;
}
cout << "=============" << endl;
cout << "Init successful!" << endl;
cout << "==============" << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "run order!" << endl;
while (point != 5)
{
run(m);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}windows下:
ubuntu:
這裡用了srand((unsigned int)time(0));函式以電腦時間為隨機數種子,保證每次隨機數不一樣
這裡設定的執行時間為1到5
相關文章
- 【作業系統】--處理器排程作業系統
- 作業系統(5)處理器排程管理作業系統
- 作業系統排程演算法作業系統演算法
- 作業系統之排程演算法作業系統演算法
- Nachos實驗實現執行緒id、限制執行緒數和更改排程演算法(按優先順序排程)執行緒演算法
- 作業系統4——處理機排程與死鎖作業系統
- 批處理作業排程問題
- Linux排程器:程序優先順序Linux
- 批處理作業排程-分支界限法
- 【作業系統】4.程序排程演算法作業系統演算法
- 0512 作業系統程式排程實驗作業系統
- 2.2.5排程演算法:時間片輪轉、優先順序排程、多級反饋排程演算法
- 作業系統常用的排程演算法總結作業系統演算法
- 如何使用Rust的gaffer實現優先順序的微批處理排程器 - njkRust
- Quartz排程系統入門和排程高可用實現方案quartz
- 猿考研之作業系統篇二(處理機排程)作業系統
- 0512作業系統之程式排程作業系統
- Flink排程之排程器、排程策略、排程模式模式
- 程式排程演算法Linux程式排程演算法演算法Linux
- linux 系統IO 排程Linux
- 作業系統精髓設計原理 程式排程作業系統
- 作業系統課程設計——處理機和程式排程演算法及記憶體分配回收機制作業系統演算法記憶體
- 實現Quartz.NET的HTTP作業排程quartzHTTP
- 排程器簡介,以及Linux的排程策略Linux
- 3.1處理機排程概述
- 07 系統排程
- Linux程式優先順序的處理--Linux程式的管理與排程(二十二)Linux
- Linux核心排程分析(程式排程)Linux
- 作業排程模擬程式
- Hadoop - Azkaban 作業排程Hadoop
- 實驗二 作業模擬排程程式
- 使用DBMS_SCHEDULER排程作業系統shell指令碼作業系統指令碼
- 課程排課系統:智慧排課+線上約課+直播上課+作業打卡!
- OS學習筆記三:處理器排程筆記
- Linux程式排程核心實現分析Linux
- 用java語言,模擬實現作業系統的程式排程演算法,先來先服務,高優先順序、高響應比、時間片輪轉和短作業Java作業系統演算法
- Hadoop作業的三種排程演算法Hadoop演算法
- 程式排程之最短作業優先