【龍印】龍芯1c上雙路16位AD晶片TM7705的linux驅動
本文為在用龍芯1c做3D印表機過程中的筆記。龍芯1c做的3d印表機簡稱“龍印”,git地址“https://gitee.com/caogos/marlin_ls1c”
TM7705和熱敏電阻一起實現3d印表機的溫度測量。本文重點放在tm7705的linux驅動上,關於溫度測量後面另外寫一篇詳細介紹。
硬體電路
測試用的硬體為“安富萊”推出的TM7705模組。這裡著重強調一下TM7705是深圳天微電子的AD晶片,很多淘寶商家把名字都寫錯了。
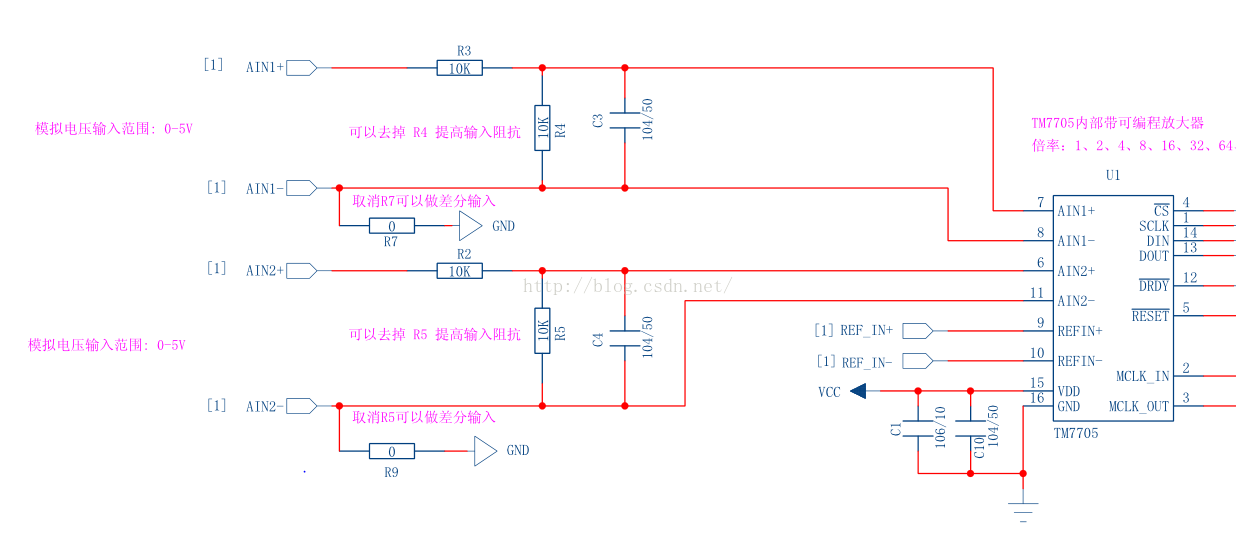
為了使原理圖更加清晰,把整個原理圖分成了幾塊分別截圖了。下面談點個人對本模組的理解,僅供參考。
1,本模組的模擬輸入端AIN1+,AIN1-和AIN2+,AIN2-分別通過兩個10k電阻並聯分壓。這樣的目的是為了把輸入電壓範圍從0-2.5v擴大到0-5v,即滿量程電壓為5v。
因為使用的是2.5v的基準電源,所以實際上AIN引腳的輸入範圍為0-2.5v,通過兩個10k電阻分壓,而AIN1+和AIN2+則接到兩個10k電阻中間,這樣就實現了把測量範圍從0-2.5v擴大到0-5v。凡事有兩面性,正是由於引入了兩個10k電阻,同時也引入了誤差。
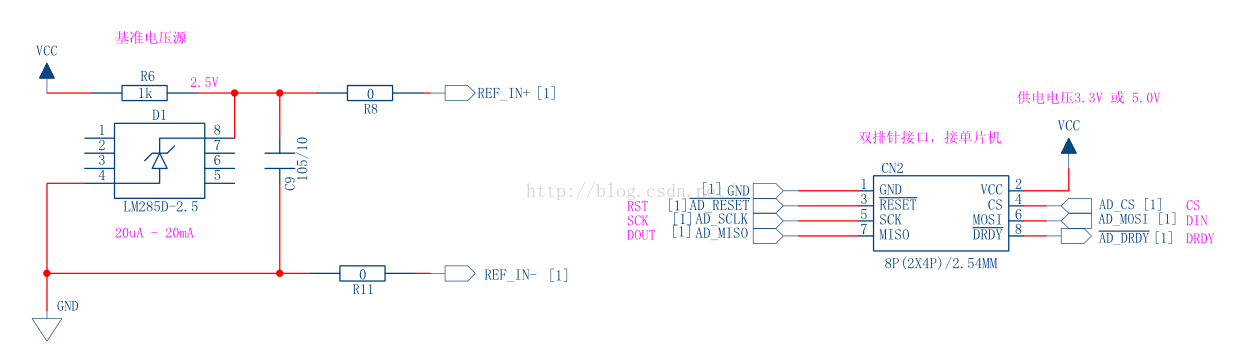
2,這個模組使用的參考電源是2.5v的,tm7705允許參考電源電壓為0到vdd之間的任意值。
對於使用在3d印表機上來說,最後改為3.3v或者5v的參考電源(如果有的話)。marlin中有個指令碼createTemperatureLookup.py可以生成一個AD值與溫度對應的表格,用於程式中快速計算溫度值。
假如待測試的電壓很小,比如是毫伏級的,那麼可以選擇電源低一些的基準電源,這樣有利於提高精度,同時如果需要,可以把增益設定大一點,tm7705最大可以支援128的增益。
3,tm7705是支援3.3v和5v供電的,具體選擇哪個根據spi sclk的電平決定。如果SPI的SCLK線上的高電平為3.3v,那麼推薦使用3.3v的電源給tm7705供電。比如龍芯1c的spi的SCLK是3.3v的,如果tm7705的vdd接5v,那麼出現介面迷失的概率大大增加。
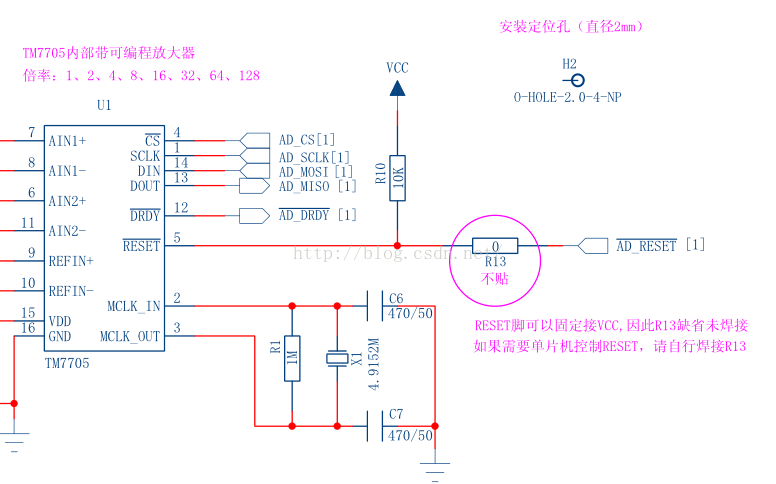
4,復位(reset)引腳。我在這裡犯了低階錯誤,拿到電路圖後,發現圖上說已經上拉到vcc了,並且R13沒貼。後面在接線時沒接復位腳,懸空的;移植tm7705驅動時,沒有操作復位腳。後來發現tm7705採集始終不是很穩定,每次上電後可以成功採集幾次,過後就超時,或者一直採集到的值為0xfff,並且把龍芯1c熱復位還不一定能解決。用示波器檢查了,沒發現問題,程式碼也檢查了,沒發現問題。經過兩週的煎熬後,突然想起來把R13焊上,用軟體復位tm7705試試。結果發現一切OK,並且後續如果出錯,通過復位tm7705也都能解決,今天我從上午不斷電連續測到現在都沒問題。即使超時了,程式碼中也通過復位tm7705很快就解決了。
所以這裡強烈建議:把tm7705復位腳接龍芯1c的一個gpio,每次上電後初始化時必須手動復位tm7705,如果出現超時或其它錯誤時,也可以通過復位tm7705來解決。
tm7705模組使用龍芯1c的SPI0_CS1
RESET -------- I2S_LRCK/GPIO89
VDD -------- 3.3V
原始碼
在檔案arch\mips\loongson\ls1x\ls1c\platform.c中,
找到“static struct spi_board_info ls1x_spi0_devices[]”,在裡面新增
#ifdef CONFIG_SPI_TM7705
{
.modalias = "TM7705",
.bus_num = 0,
.chip_select = SPI0_CS1,
// 當前cpu頻率=252.00Mhz BUS=126.00Mhz
// SPI最大的分頻係數為4096
// 所以spi最小頻率=126Mhz/4096=30.7khz
// 這裡只是設定最大頻率,實際頻率為最接近並且小於最大頻率的BUS分頻後的值
// 經過測試,最大頻率設為為1mhz也能正常採集
.max_speed_hz = 500*1000,
// .platform_data =
.mode = SPI_MODE_3,
},
#endif
tm7705.c
/*
*
* 雙路16位spi介面AD晶片--TM7705的驅動
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/signal.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/time.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/clk.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/kfifo.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/hwmon.h>
#include <linux/hwmon-sysfs.h>
// 通訊暫存器bit定義
enum
{
// 暫存器選擇 RS2 RS1 RS0
TM7705_REG_COMM = (0 << 4), // 通訊暫存器
TM7705_REG_SETUP = (1 << 4), // 設定暫存器
TM7705_REG_CLOCK = (2 << 4), // 時鐘暫存器
TM7705_REG_DATA = (3 << 4), // 資料暫存器
TM7705_REG_TEST = (4 << 4), // 測試暫存器
TM7705_REG_OFFSET = (6 << 4), // 偏移暫存器
TM7705_REG_GAIN = (7 << 4), // 增益暫存器
// 讀寫操作
TM7705_WRITE = (0 << 3), // 寫操作
TM7705_READ = (1 << 3), // 讀操作
// 通道
TM7705_CH_1 = 0, // AIN1+ AIN1-
TM7705_CH_2 = 1, // AIN2+ AIN2-
TM7705_CH_3 = 2, // AIN1- AIN1-
TM7705_CH_4 = 3 // AIN1- AIN2-
};
/* 設定暫存器bit定義 */
enum
{
TM7705_MD_NORMAL = (0 << 6), /* 正常模式 */
TM7705_MD_CAL_SELF = (1 << 6), /* 自校準模式 */
TM7705_MD_CAL_ZERO = (2 << 6), /* 校準0刻度模式 */
TM7705_MD_CAL_FULL = (3 << 6), /* 校準滿刻度模式 */
TM7705_GAIN_1 = (0 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_2 = (1 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_4 = (2 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_8 = (3 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_16 = (4 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_32 = (5 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_64 = (6 << 3), /* 增益 */
TM7705_GAIN_128 = (7 << 3), /* 增益 */
/* 無論雙極性還是單極性都不改變任何輸入訊號的狀態,它只改變輸出資料的程式碼和轉換函式上的校準點 */
TM7705_BIPOLAR = (0 << 2), /* 雙極性輸入 */
TM7705_UNIPOLAR = (1 << 2), /* 單極性輸入 */
TM7705_BUF_NO = (0 << 1), /* 輸入無緩衝(內部緩衝器不啟用) */
TM7705_BUF_EN = (1 << 1), /* 輸入有緩衝 (啟用內部緩衝器) */
TM7705_FSYNC_0 = 0, // 模擬調製器和濾波器正常處理資料
TM7705_FSYNC_1 = 1 // 模擬調製器和濾波器不啟用
};
/* 時鐘暫存器bit定義 */
enum
{
TM7705_CLKDIS_0 = (0 << 4), /* 時鐘輸出使能 (當外接晶振時,必須使能才能振盪) */
TM7705_CLKDIS_1 = (1 << 4), /* 時鐘禁止 (當外部提供時鐘時,設定該位可以禁止MCK_OUT引腳輸出時鐘以省電 */
TM7705_CLKDIV_0 = (0 << 3), // 不分頻
TM7705_CLKDIV_1 = (1 << 3), // 2分頻,外部晶振為4.9152Mhz時,應2分頻
TM7705_CLK_0 = (0 << 2), // 主時鐘=1Mhz並且CLKDIV=0,主時鐘=2Mhz並且CLKDIV=1
TM7705_CLK_1 = (1 << 2), // 主時鐘=2.4576Mhz並且CLKDIV=0, 主時鐘=4.9152Mhz並且CLKDIV=1
// 注意輸出更新率與clk位有關
// 當TM7705_CLK_0時,輸出更新率只能為20,25,100,200
TM7705_UPDATE_20 = (0),
TM7705_UPDATE_25 = (1),
TM7705_UPDATE_100 = (2),
TM7705_UPDATE_200 = (3),
// 當TM7705_CLK_1時,輸出更新率只能為50,60,250,500
TM7705_UPDATE_50 = (0),
TM7705_UPDATE_60 = (1),
TM7705_UPDATE_250 = (2),
TM7705_UPDATE_500 = (3)
};
#define TM7705_CHANNEL_NUM (2) // tm7705通道個數
#define TM7705_DRDY_PIN (87) // GPIO87/I2S_DI tm7705的引腳DRDY
#define TM7705_RESET_PIN (89) // GPIO89/I2S_LRCK tm7705的引腳RESET
struct tm7705 {
struct device *hwmon_dev;
struct mutex lock;
};
// 通過reset腳復位tm7705
static void tm7705_reset(void)
{
gpio_direction_output(TM7705_RESET_PIN, 1);
msleep(1);
gpio_direction_output(TM7705_RESET_PIN, 0);
msleep(2);
gpio_direction_output(TM7705_RESET_PIN, 1);
msleep(1);
return ;
}
// 同步spi介面時序
static void tm7705_sync_spi(struct spi_device *spi)
{
u8 tx_buf[4] = {0xFF};
// 至少32個序列時鐘內向TM7705的DIN線寫入邏輯"1"
spi_write(spi, tx_buf, sizeof(tx_buf));
return ;
}
// 等待內部操作完成
static int tm7705_wait_DRDY(void)
{
int i = 0;
int time_cnt = 500*1000;
for (i=0; i<time_cnt; i++)
{
if (0 == gpio_get_value(TM7705_DRDY_PIN))
{
break;
}
udelay(1);
}
if (i >= time_cnt)
{
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
// 自校準
static void tm7705_calib_self(struct spi_device *spi, u8 channel)
{
u8 tx_buf[2] = {0};
tx_buf[0] = TM7705_REG_SETUP | TM7705_WRITE | channel;
tx_buf[1] = TM7705_MD_CAL_SELF | TM7705_GAIN_1 | TM7705_UNIPOLAR | TM7705_BUF_EN | TM7705_FSYNC_0;
spi_write(spi, tx_buf, sizeof(tx_buf));
tm7705_wait_DRDY(); /* 等待內部操作完成 --- 時間較長,約180ms */
msleep(50);
return ;
}
// 配置tm7705的指定通道
static void tm7705_config_channel(struct spi_device *spi, u8 channel)
{
u8 tx_buf[2] = {0};
tx_buf[0] = TM7705_REG_CLOCK | TM7705_WRITE | channel;
tx_buf[1] = TM7705_CLKDIS_0 | TM7705_CLKDIV_1 | TM7705_CLK_1 | TM7705_UPDATE_50;
spi_write(spi, tx_buf, sizeof(tx_buf));
// 自校準
tm7705_calib_self(spi, channel);
return ;
}
// 復位tm7705並重新配置
static void tm7705_reset_and_reconfig(struct spi_device *spi)
{
// 通過reset腳復位tm7705
tm7705_reset();
// 同步spi介面時序
msleep(5);
tm7705_sync_spi(spi);
msleep(5);
// 配置tm7705時鐘暫存器
tm7705_config_channel(spi, TM7705_CH_1);
// tm7705_config_channel(spi, TM7705_CH_2);
return ;
}
/*
* 讀取一個通道的值
* @dev 裝置描述符
* @channel 通道
* ad 讀到的ad值
*/
static int tm7705_read_channel(struct device *dev, u8 channel, u16 *ad)
{
struct spi_device *spi = to_spi_device(dev);
struct tm7705 *adc = spi_get_drvdata(spi);
int ret = 0;
u16 value = 9;
u8 tx_buf[1] = {0};
u8 rx_buf[2] = {0};
if (mutex_lock_interruptible(&adc->lock))
{
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
// 等待轉換完成
ret = tm7705_wait_DRDY();
if(ret)
{
printk(KERN_ERR "[%s] tm7705_wait_DRDY() time out.\n", __FUNCTION__);
goto fail;
}
tx_buf[0] = TM7705_REG_DATA | TM7705_READ | channel;
ret = spi_write_then_read(spi, tx_buf, sizeof(tx_buf), rx_buf, sizeof(rx_buf));
value = (rx_buf[0]<<8) + rx_buf[1];
if (0 > ret) // spi通訊失敗
{
printk(KERN_ERR "[%s] tm7705_read_byte() fail. ret=%d\n", __FUNCTION__, ret);
goto fail;
}
if (0xfff == value) // tm7705上電一段時間後,可能會出現讀到的值一直是0xfff的情況
{
printk(KERN_ERR "[%s] value=0xfff\n", __FUNCTION__);
ret = -1;
goto fail;
}
// 輸出AD值
*ad = value;
fail:
mutex_unlock(&adc->lock);
return ret;
}
/* sysfs hook function */
static ssize_t tm7705_get_sensor_value(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *devattr,
char *buf)
{
struct spi_device *spi = to_spi_device(dev);
struct sensor_device_attribute *attr = to_sensor_dev_attr(devattr);
int ret = 0;
u16 ad = 0;
int i = 0;
/*
* 為了避免通道切換造成讀數失效,讀2次
* 實際上每次讀到的是上一次採集的結果(可以兩個通道交替採集就能看到效果)
*/
for (i=0; i<2; i++)
{
ret = tm7705_read_channel(dev, attr->index, &ad);
if (ret)
{
// 失敗,則重啟tm7705並重新配置
tm7705_reset_and_reconfig(spi);
printk(KERN_ERR "[%s] tm7705 reset and reconfig.\n", __FUNCTION__);
return ret;
}
printk(KERN_DEBUG "[%s] tm7705 ad=0x%x\n", __FUNCTION__, ad);
// ls1c的速度相當TM7705太快,延時一下避免在一次讀完後DRDY還未及時改變狀態ls1c又開始了下一次讀寫
msleep(1);
}
// 將ad值傳遞給使用者程式
ret = sprintf(buf, "%u\n", ad);
return ret;
}
static struct sensor_device_attribute ad_input[] = {
SENSOR_ATTR(ch1, S_IRUGO, tm7705_get_sensor_value, NULL, TM7705_CH_1),
SENSOR_ATTR(ch2, S_IRUGO, tm7705_get_sensor_value, NULL, TM7705_CH_2),
};
static int __devinit tm7705_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
{
struct tm7705 *adc;
int i;
int status;
adc = kzalloc(sizeof *adc, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!adc)
{
return -ENOMEM;
}
mutex_init(&adc->lock);
mutex_lock(&adc->lock);
spi_set_drvdata(spi, adc);
for (i=0; i<TM7705_CHANNEL_NUM; i++)
{
status = device_create_file(&spi->dev, &ad_input[i].dev_attr);
if (status)
{
dev_err(&spi->dev, "device_create_file() failed.\n");
goto fail_crete_file;
}
}
adc->hwmon_dev = hwmon_device_register(&spi->dev);
if (IS_ERR(adc->hwmon_dev))
{
dev_err(&spi->dev, "hwmon_device_register() fail.\n");
status = PTR_ERR(adc->hwmon_dev);
goto fail_crete_file;
}
// gpio初始化
status = gpio_request(TM7705_DRDY_PIN, "TM7705"); // tm7705 DRDY pin
if (status)
{
dev_err(&spi->dev, "gpio_request(TM7705_DRDY_PIN) fail.\n");
goto fail_device_register;
}
gpio_direction_input(TM7705_DRDY_PIN);
status = gpio_request(TM7705_RESET_PIN, "TM7705"); // tm7705 reset pin
if (status)
{
dev_err(&spi->dev, "gpio_request(TM7705_RESET_PIN) fail.\n");
goto fail_request_drdy_pin;
}
gpio_direction_output(TM7705_RESET_PIN, 1);
// 復位tm7705並重新配置
tm7705_reset_and_reconfig(spi);
mutex_unlock(&adc->lock);
return 0;
fail_request_drdy_pin:
gpio_free(TM7705_DRDY_PIN);
fail_device_register:
hwmon_device_unregister(adc->hwmon_dev);
fail_crete_file:
for (i--; i>=0; i--)
{
device_remove_file(&spi->dev, &ad_input[i].dev_attr);
}
spi_set_drvdata(spi, NULL);
mutex_unlock(&adc->lock);
kfree(adc);
return status;
}
static int __devexit tm7705_remove(struct spi_device *spi)
{
struct tm7705 *adc = spi_get_drvdata(spi);
int i;
mutex_lock(&adc->lock);
gpio_free(TM7705_DRDY_PIN);
gpio_free(TM7705_DRDY_PIN);
hwmon_device_unregister(adc->hwmon_dev);
for (i=0; i<TM7705_CHANNEL_NUM; i++)
{
device_remove_file(&spi->dev, &ad_input[i].dev_attr);
}
spi_set_drvdata(spi, NULL);
mutex_unlock(&adc->lock);
kfree(adc);
return 0;
}
static struct spi_driver tm7705_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "TM7705",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = tm7705_probe,
.remove = __devexit_p(tm7705_remove),
};
static int __init init_tm7705(void)
{
return spi_register_driver(&tm7705_driver);
}
static void __exit exit_tm7705(void)
{
spi_unregister_driver(&tm7705_driver);
}
module_init(init_tm7705);
module_exit(exit_tm7705);
MODULE_AUTHOR("勤為本 1207280597@qq.com");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("TM7705 linux driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
在“drivers\hwmon\Kconfig”中,增加
config SPI_TM7705
tristate "Titan Micro Electronics TM7705"
depends on SPI_MASTER && EXPERIMENTAL
help
say yes here to build support for Titan Micro Electronics TM7705
analog to digital converter.
在“drivers\hwmon\Makefile”中,增加
obj-$(CONFIG_SPI_TM7705) += tm7705.o
make menuconfig
Device Drivers --->
[*] SPI support --->
<*> Loongson1 SPI
ls1x spi cs mode (softcs mode) --->
(X) softcs mode
ls1x spi control mode (poll mode) --->
(X) poll mode
<*> Hardware Monitoring support --->
<*> Titan Micro Electronics TM7705
去掉音效卡的配置,tm7705使用了GPIO89/I2S_LRCK和GPIO87/I2S_DI
Device Drivers --->
< > Sound card support --->
手動測試可以使用命令
cat /sys/bus/spi/drivers/TM7705/spi0.1/ch1
也可以用下面的程式來不間斷自動測試測試
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void read_channel(char *dev_file_path)
{
int fd = 0;
int ret = 0;
unsigned char buff[128] = {0};
fd = open(dev_file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == fd)
{
printf("[%s] open device file fail.\n", __FUNCTION__);
return ;
}
memset(buff, 0, 128);
ret = read(fd, buff, 128);
if (0 > ret)
{
printf("[%s] not read data. ret=%d\n", __FUNCTION__, ret);
}
printf("[%s] buff=%s\n", __FUNCTION__, buff);
close(fd);
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
char ch1_path[] = {"/sys/bus/spi/drivers/TM7705/spi0.1/ch1"};
char ch2_path[] = {"/sys/bus/spi/drivers/TM7705/spi0.1/ch2"};
while (1)
{
read_channel(ch1_path);
usleep(100*1000);
/*
read_channel(ch2_path);
usleep(300*1000);
*/
}
}
相關文章
- 龍芯2號處理器,龍芯2K1000晶片引數晶片
- 龍芯 & Golang!Golang
- 龍芯的go之路(一)-在龍芯中安裝goGo
- ARM 和 龍芯上 Arch Linux 安裝手記Linux
- 龍芯1B晶片處理器介紹晶片
- 龍芯1D晶片處理器介紹晶片
- 龍芯2號系列功能及技術特點(龍芯2F,龍芯2H,龍芯2K1000)
- 龍芯 & Golang!Golang
- 龍芯(Loongarch64),在Linux虛擬一個龍芯OS體驗下Linux
- 龍芯3A3000和龍芯3B3000晶片處理器引數比較晶片
- 益思芯科技加入龍蜥社群,推動網路和儲存DPU晶片創新落地晶片
- 龍芯開源社群上線.NET主頁
- 龍芯應用技術合作研討會-龍芯和國產Linux謀求共同發展(轉)Linux
- 龍芯2H晶片處理器引數效能介紹晶片
- 龍芯筆記本: 將投產龍芯筆記本採用Linux系統受質疑(轉)筆記Linux
- 龍芯PC生死由Linux說了算?(轉)Linux
- 龍芯原始碼編譯MySQL原始碼編譯MySql
- 龍芯LS232使用者手冊晶片資料介紹晶片
- 圖吧垃圾佬理解的早期國產晶片歷史(龍芯中科和同行的恩怨解析)晶片
- 龍芯釋出新一代伺服器處理器:龍芯3C5000L伺服器
- 龍芯1D處理器datasheet
- 入門龍芯舊世界彙編指令
- Linux平臺的1500元龍芯筆記本將面世(轉)Linux筆記
- 《記金華的雙龍洞》教案
- 雙龍賀歲,龍蜥 LoongArch GA 版正式釋出
- LED驅動晶片(IC)-VK1616 SOP/DIP16,LED數顯/數碼管顯示驅動晶片晶片
- 龍芯 3A4000 安裝 Debian stable
- 龍芯go之路(二)-安裝opencv-goGoOpenCV
- 龍芯fedora28日常生存指南
- Linux中國對話龍蜥社群4位理事:龍蜥作業系統捐贈的背後,是誰在推動?Linux作業系統
- 龍芯1A處理器引數介紹
- 龍芯+UOS系統下java環境安裝Java
- 國產處理器龍芯地址空間詳解
- 龍芯吧小吧主彭東鋒(知乎直答)
- 驍龍845要涼了?高通驍龍855旗艦晶片已在除錯中晶片除錯
- AI晶片行業發展的來龍去脈AI晶片行業
- 驍龍750G和驍龍765G哪個好?驍龍750G與驍龍765G晶片對比評測晶片
- 龍芯釋出.NET 6.0.100開發者試用版