程式碼入口
之前寫文章都會囉囉嗦嗦一大堆再開始,進入【Spring原始碼分析】這個板塊就直接切入正題了。
很多朋友可能想看Spring原始碼,但是不知道應當如何入手去看,這個可以理解:Java開發者通常從事的都是Java Web的工作,對於程式設計師來說,一個Web專案用到Spring,只是配置一下配置檔案而已,Spring的載入過程相對是不太透明的,不太好去找載入的程式碼入口。
下面有很簡單的一段程式碼可以作為Spring程式碼載入的入口:
1 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); 2 ac.getBean(XXX.class);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext用於載入CLASSPATH下的Spring配置檔案,可以看到,第二行就已經可以獲取到Bean的例項了,那麼必然第一行就已經完成了對所有Bean例項的載入,因此可以通過ClassPathXmlApplicationContext作為入口。為了後面便於程式碼閱讀,先給出一下ClassPathXmlApplicationContext這個類的繼承關係: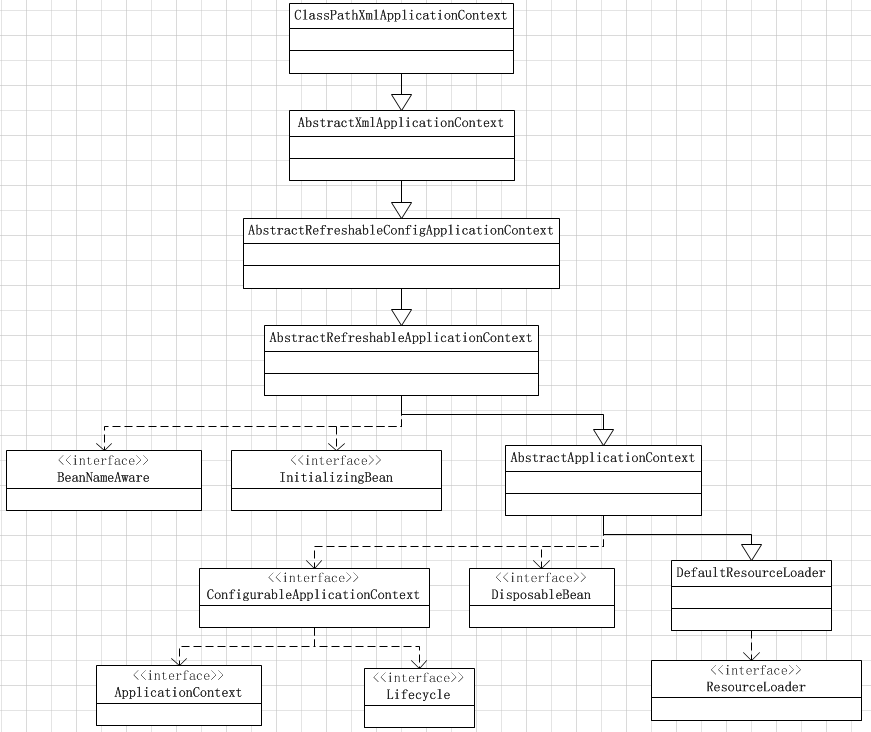
大致的繼承關係是如上圖所示的,由於版面的關係,沒有繼續畫下去了,左下角的ApplicationContext應當還有一層繼承關係,比較關鍵的一點是它是BeanFactory的子介面。
最後宣告一下,本文使用的Spring版本為3.0.7,比較老,使用這個版本純粹是因為公司使用而已。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext儲存內容
為了更理解ApplicationContext,拿一個例項ClassPathXmlApplicationContext舉例,看一下里面儲存的內容,加深對ApplicationContext的認識,以表格形式展現:
| 物件名 | 類 型 | 作 用 | 歸屬類 |
| configResources | Resource[] | 配置檔案資源物件陣列 | ClassPathXmlApplicationContext |
| configLocations | String[] | 配置檔案字串陣列,儲存配置檔案路徑 | AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext |
| beanFactory | DefaultListableBeanFactory | 上下文使用的Bean工廠 | AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext |
| beanFactoryMonitor | Object | Bean工廠使用的同步監視器 | AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext |
| id | String | 上下文使用的唯一Id,標識此ApplicationContext | AbstractApplicationContext |
| parent | ApplicationContext | 父級ApplicationContext | AbstractApplicationContext |
| beanFactoryPostProcessors | List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> | 儲存BeanFactoryPostProcessor介面,Spring提供的一個擴充套件點 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| startupShutdownMonitor | Object | refresh方法和destory方法公用的一個監視器,避免兩個方法同時執行 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| shutdownHook | Thread | Spring提供的一個鉤子,JVM停止執行時會執行Thread裡面的方法 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| resourcePatternResolver | ResourcePatternResolver | 上下文使用的資源格式解析器 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| lifecycleProcessor | LifecycleProcessor | 用於管理Bean生命週期的生命週期處理器介面 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| messageSource | MessageSource | 用於實現國際化的一個介面 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| applicationEventMulticaster | ApplicationEventMulticaster | Spring提供的事件管理機制中的事件多播器介面 | AbstractApplicationContext |
| applicationListeners | Set<ApplicationListener> | Spring提供的事件管理機制中的應用監聽器 | AbstractApplicationContext |
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext建構函式
看下ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的建構函式:
1 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { 2 this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); 3 }
1 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 super(parent); 5 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 6 if (refresh) { 7 refresh(); 8 } 9 }
從第二段程式碼看,總共就做了三件事:
1、super(parent)
沒什麼太大的作用,設定一下父級ApplicationContext,這裡是null
2、setConfigLocations(configLocations)
程式碼就不貼了,一看就知道,裡面做了兩件事情:
(1)將指定的Spring配置檔案的路徑儲存到本地
(2)解析Spring配置檔案路徑中的${PlaceHolder}佔位符,替換為系統變數中PlaceHolder對應的Value值,System本身就自帶一些系統變數比如class.path、os.name、user.dir等,也可以通過System.setProperty()方法設定自己需要的系統變數
3、refresh()
這個就是整個Spring Bean載入的核心了,它是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的父類AbstractApplicationContext的一個方法,顧名思義,用於重新整理整個Spring上下文資訊,定義了整個Spring上下文載入的流程。
refresh方法
上面已經說了,refresh()方法是整個Spring Bean載入的核心,因此看一下整個refresh()方法的定義:
1 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 3 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 4 prepareRefresh(); 5 6 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 7 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 8 9 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 10 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 11 12 try { 13 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 14 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 15 16 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 17 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 18 19 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 20 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 21 22 // Initialize message source for this context. 23 initMessageSource(); 24 25 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 26 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 27 28 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 29 onRefresh(); 30 31 // Check for listener beans and register them. 32 registerListeners(); 33 34 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 35 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 36 37 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 38 finishRefresh(); 39 } 40 41 catch (BeansException ex) { 42 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 43 destroyBeans(); 44 45 // Reset 'active' flag. 46 cancelRefresh(ex); 47 48 // Propagate exception to caller. 49 throw ex; 50 } 51 } 52 }
每個子方法的功能之後一點一點再分析,首先refresh()方法有幾點是值得我們學習的:
1、方法是加鎖的,這麼做的原因是避免多執行緒同時重新整理Spring上下文
2、儘管加鎖可以看到是針對整個方法體的,但是沒有在方法前加synchronized關鍵字,而使用了物件鎖startUpShutdownMonitor,這樣做有兩個好處:
(1)refresh()方法和close()方法都使用了startUpShutdownMonitor物件鎖加鎖,這就保證了在呼叫refresh()方法的時候無法呼叫close()方法,反之亦然,避免了衝突
(2)另外一個好處不在這個方法中體現,但是提一下,使用物件鎖可以減小了同步的範圍,只對不能併發的程式碼塊進行加鎖,提高了整體程式碼執行的效率
3、方法裡面使用了每個子方法定義了整個refresh()方法的流程,使得整個方法流程清晰易懂。這點是非常值得學習的,一個方法裡面幾十行甚至上百行程式碼寫在一起,在我看來會有三個顯著的問題:
(1)擴充套件性降低。反過來講,假使把流程定義為方法,子類可以繼承父類,可以根據需要重寫方法
(2)程式碼可讀性差。很簡單的道理,看程式碼的人是願意看一段500行的程式碼,還是願意看10段50行的程式碼?
(3)程式碼可維護性差。這點和上面的類似但又有不同,可維護性差的意思是,一段幾百行的程式碼,功能點不明確,不易後人修改,可能會導致“牽一髮而動全身”
prepareRefresh方法
下面挨個看refresh方法中的子方法,首先是prepareRefresh方法,看一下原始碼:
1 /** 2 * Prepare this context for refreshing, setting its startup date and 3 * active flag. 4 */ 5 protected void prepareRefresh() { 6 this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); 7 synchronized (this.activeMonitor) { 8 this.active = true; 9 } 10 11 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 12 logger.info("Refreshing " + this); 13 } 14 }
這個方法功能比較簡單,顧名思義,準備重新整理Spring上下文,其功能註釋上寫了:
1、設定一下重新整理Spring上下文的開始時間
2、將active標識位設定為true
另外可以注意一下12行這句日誌,這句日誌列印了真正載入Spring上下文的Java類。
obtainFreshBeanFactory方法
obtainFreshBeanFactory方法的作用是獲取重新整理Spring上下文的Bean工廠,其程式碼實現為:
1 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { 2 refreshBeanFactory(); 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 4 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); 6 } 7 return beanFactory; 8 }
其核心是第二行的refreshBeanFactory方法,這是一個抽象方法,有AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext和GenericApplicationContext這兩個子類實現了這個方法,看一下上面ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的繼承關係圖即知,呼叫的應當是AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中實現的refreshBeanFactory,其原始碼為:
1 protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { 2 if (hasBeanFactory()) { 3 destroyBeans(); 4 closeBeanFactory(); 5 } 6 try { 7 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); 8 beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); 9 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); 10 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); 11 synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { 12 this.beanFactory = beanFactory; 13 } 14 } 15 catch (IOException ex) { 16 throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); 17 } 18 }
這段程式碼的核心是第7行,這行點出了DefaultListableBeanFactory這個類,這個類是構造Bean的核心類,這個類的功能會在下一篇文章中詳細解讀,首先給出DefaultListableBeanFactory的繼承關係圖:
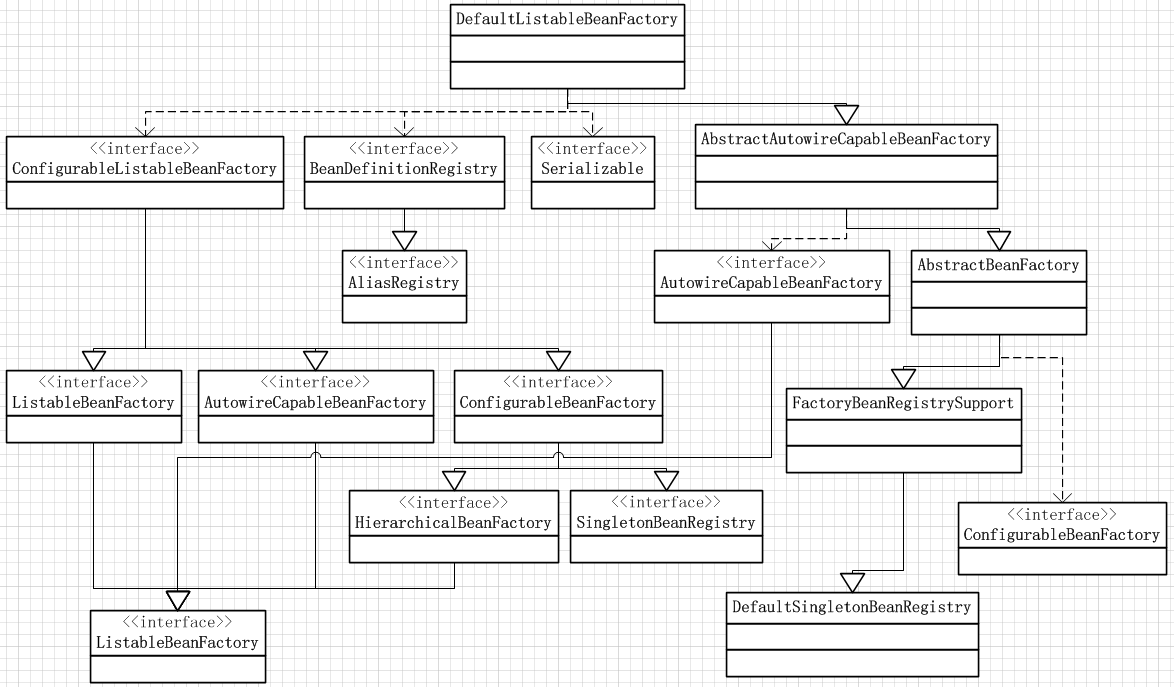
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory這個類的繼承層次比較深,版面有限,就沒有繼續畫下去了,本圖基本上清楚地展示了DefaultListableBeanFactory的層次結構。
為了更清晰地說明DefaultListableBeanFactory的作用,列舉一下DefaultListableBeanFactory中儲存的一些重要物件及物件中的內容,DefaultListableBeanFactory基本就是操作這些物件,以表格形式說明:
| 物件名 | 類 型 | 作 用 | 歸屬類 |
| aliasMap | Map<String, String> | 儲存Bean名稱->Bean別名對映關係 | SimpleAliasRegistry |
| singletonObjects | Map<String, Object> | 儲存單例Bean名稱->單例Bean實現對映關係 | DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| singletonFactories | Map<String, ObjectFactory> | 儲存Bean名稱->ObjectFactory實現對映關係 | DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| earlySingletonObjects | Map<String, Object> | 儲存Bean名稱->預載入Bean實現對映關係 | DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| registeredSingletons | Set<String> | 儲存註冊過的Bean名 | DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| singletonsCurrentlyInCreation | Set<String> | 儲存當前正在建立的Bean名 | DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| disposableBeans | Map<String, Object> |
儲存Bean名稱->Disposable介面實現Bean實現對映關係 |
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry |
| factoryBeanObjectCache | Map<String, Object> | 儲存Bean名稱->FactoryBean介面Bean實現對映關係 | FactoryBeanRegistrySupport |
| propertyEditorRegistrars | Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> | 儲存PropertyEditorRegistrar介面實現集合 | AbstractBeanFactory |
| embeddedValueResolvers | List<StringValueResolver> | 儲存StringValueResolver(字串解析器)介面實現列表 | AbstractBeanFactory |
| beanPostProcessors | List<BeanPostProcessor> | 儲存 BeanPostProcessor介面實現列表 | AbstractBeanFactory |
| mergedBeanDefinitions | Map<String, RootBeanDefinition> | 儲存Bean名稱->合併過的根Bean定義對映關係 | AbstractBeanFactory |
| alreadyCreated | Set<String> | 儲存至少被建立過一次的Bean名集合 | AbstractBeanFactory |
| ignoredDependencyInterfaces | Set<Class> | 儲存不自動裝配的介面Class物件集合 | AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory |
| resolvableDependencies | Map<Class, Object> | 儲存修正過的依賴對映關係 | DefaultListableBeanFactory |
| beanDefinitionMap | Map<String, BeanDefinition> | 儲存Bean名稱-->Bean定義對映關係 | DefaultListableBeanFactory |
| beanDefinitionNames | List<String> | 儲存Bean定義名稱列表 | DefaultListableBeanFactory |