Comparable使一個class具備不同例項間進行比較的行為。這些物件的集合,可作為Collections.sort或Arrays.sort的引數
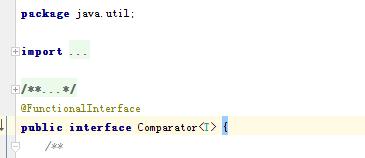
Comparator可以看成一種演算法的實現,將演算法和資料分離。實現Comparator的可以作為Collections.sort或Arrays.sort的引數
都可以多條件排序。類似於order by field1,field2
都是介面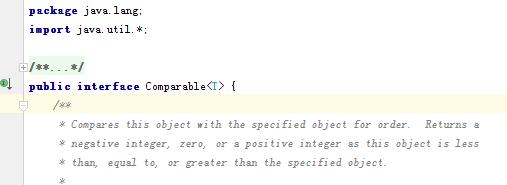

import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class UserComparator implements Comparator<User> { /** * * @param source * @param target * @return 負數:升序;0:順序不變;正數:降序 */ @Override public int compare(User source, User target) { int result = source.getAge() - target.getAge(); System.out.println(result); return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { User[] users = new User[]{new User("a", 30), new User("b", 20)}; Arrays.sort(users, new UserComparator()); for (int i = 0; i < users.length; i++) { User user = users[i]; System.out.println(user.getId() + " " + user.getAge()); } } } class User { private String id; private int age; public User(String id, int age) { this.id = id; this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } }
import java.util.Arrays; public class User implements Comparable<User> { private String id; private int age; public User(String id, int age) { this.id = id; this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } @Override public int compareTo(User target) { int result = this.age - target.getAge(); System.out.println(result); return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { User[] users = new User[]{new User("a", 30), new User("b", 20)}; Arrays.sort(users); for (int i = 0; i < users.length; i++) { User user = users[i]; System.out.println(user.getId() + " " + user.getAge()); } } }
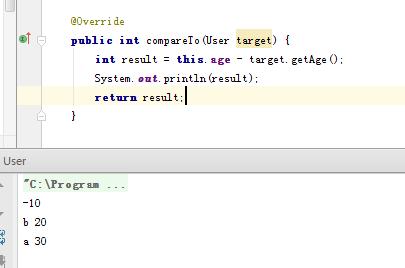
例項如下:
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ private String name; private int age; private float score; public Student(String name, int age, float score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } public String toString() { return name+"\t\t"+age+"\t\t"+score; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(this.score>o.score)//score是private的,為什麼能夠直接呼叫,這是因為在Student類內部 return -1;//由高到底排序 else if(this.score<o.score) return 1; else{ if(this.age>o.age) return 1;//由底到高排序 else if(this.age<o.age) return -1; else return 0; } } } public class ComparableDemo01 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Student stu[]={new Student("zhangsan",20,90.0f), new Student("lisi",22,90.0f), new Student("wangwu",20,99.0f), new Student("sunliu",22,100.0f)}; java.util.Arrays.sort(stu); for(Student s:stu) { System.out.println(s); } } }
程式執行結果:
sunliu 22 100.0
wangwu 20 99.0
zhangsan 20 90.0
lisi 22 90.0
但是在設計類的時候,往往沒有考慮到讓類實現Comparable介面,那麼我們就需要用到另外的一個比較器介面Comparator。
從上面的例項我們可以發現,compareTo(T o)只有一個引數,而Comparator介面中必須要實現的compare(T o1,T o2)就有兩個引數。
package edu.sjtu.ist.comutil; import java.util.Comparator; class Student { private String name; private int age; private float score; public Student(String name, int age, float score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public float getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(float score) { this.score = score; } public String toString() { return name+"\t\t"+age+"\t\t"+score; } } class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student>{ @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(o1.getScore()>o2.getScore()) return -1; else if(o1.getScore()<o2.getScore()) return 1; else{ if(o1.getAge()>o2.getAge()) return 1; else if(o1.getAge()<o2.getAge()) return -1; else return 0; } } } public class ComparableDemo02 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Student stu[]={new Student("zhangsan",20,90.0f), new Student("lisi",22,90.0f), new Student("wangwu",20,99.0f), new Student("sunliu",22,100.0f)}; java.util.Arrays.sort(stu,new StudentComparator()); for(Student s:stu) { System.out.println(s); } } }
上述程式的執行結果與程式碼例項1一樣。