關於string的效率,眾所周知的恐怕是“+”和StringBuilder了,這些本文就不在贅述了。關於本文,請先回答以下問題(假設都是基於多次迴圈反覆呼叫的情況下):
1.使用Insert與Format方法,哪個效率更高?
2.Contains(value)與IndexOf(value)誰效率更高?
假如您對此2問不感興趣或已非常瞭解,請忽略此文。另外本文將不對文中程式碼的實際用途做任何解釋。
<一> 首先看以下的使用場景
string str1 = "abc"; string str2 = "123"; str1 = string.Format("{0}:{1}", str1, str2); str1 = str1.Insert(0, str2);
接下來開始我們的對比之旅(不包含上述程式碼),編寫如下程式碼用來向控制檯輸出結果
static void WriteTime(string title, long time) { Console.WriteLine("{1}用時:{0} ms", time, title); }
再新增一個方法對字串進行迴圈操作
static long LoopCalc(Action<string, string> action) { string[] array = new string[260000]; for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { array[i] = i.ToString(); } Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { action(array[i], "bc"); } sw.Stop(); return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds; }
新增對string進行Insert與Format的效率對比程式碼並在Main方法中呼叫
static void StringPlusDemo() { long inserTime = LoopCalc((x, y) => x.Insert(0, y)); long formatTime = LoopCalc((x, y) => string.Format("{0}{1}", y, x)); WriteTime("Insert", inserTime); WriteTime("Format", formatTime); }
執行結果如下
明顯看到Insert效率更高,但是這種結果有侷限性,如果字串很長,那麼經過我親測他們效率相差無幾。
注:我這個只是將Format用於字串拼接的場景,更高的效率應該仍然是StringBuilder,當然Format的其他不可替代用途太多了,Insert和StringBuilder根本無法替代它,這裡就不羅嗦了。
<二> 依然是先看下Contains與IndexOf的使用場景
string str1 = "abcd"; string str2 = "bc"; if (str1.Contains(str2)) { } if (str1.IndexOf(str2) > -1) { }
在這裡仍然使用了上述的LoopCalc方法,並增加如下方法,然後在Main方法中呼叫其
static void StringContainsDemo() { long indexOfTime = LoopCalc((x, y) => { if (x.IndexOf(y) >= 0) { } }); long containersTime = LoopCalc((x, y) => { if (x.Contains(y)) { } }); WriteTime("Contains", containersTime); WriteTime("IndexOf", indexOfTime); }
結果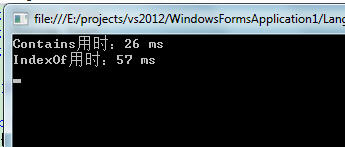
顯然Contains效率更高,為什麼呢?我之前也不懂為什麼,現在來看下String類的原始碼(關於.NET自帶類庫的原始碼可以谷歌搜到官方的下載地址,我忘了地址了),程式碼很多,我就貼出以下string類中的方法給各位看官
// Determines the position within this string of the first occurence of the specified // string, according to the specified search criteria. The search begins at // the first character of this string, it is case-sensitive and culture-sensitive, // and the default culture is used. // public int IndexOf(String value) { return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this,value); } // Determines the position within this string of the first occurence of the specified // string, according to the specified search criteria. The search begins at // startIndex, it is case-sensitive and culture-sensitve, and the default culture is used. // public int IndexOf(String value, int startIndex) { return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this,value,startIndex); }
public bool Contains( string value ) { return ( IndexOf(value, StringComparison.Ordinal) >=0 ); }
以下是有關Contains呼叫的IndexOf的過載
public int IndexOf(String value, StringComparison comparisonType) { return IndexOf(value, 0, this.Length, comparisonType); } public int IndexOf(String value, int startIndex, StringComparison comparisonType) { return IndexOf(value, startIndex, this.Length - startIndex, comparisonType); } public int IndexOf(String value, int startIndex, int count, StringComparison comparisonType) { // Validate inputs if (value == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("value"); if (startIndex < 0 || startIndex > this.Length) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("startIndex", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_Index")); if (count < 0 || startIndex > this.Length - count) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("count",Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_Count")); switch (comparisonType) { case StringComparison.CurrentCulture: return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this, value, startIndex, count, CompareOptions.None); case StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase: return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this, value, startIndex, count, CompareOptions.IgnoreCase); case StringComparison.InvariantCulture: return CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this, value, startIndex, count, CompareOptions.None); case StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase: return CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this, value, startIndex, count, CompareOptions.IgnoreCase); case StringComparison.Ordinal: return CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo.IndexOf(this, value, startIndex, count, CompareOptions.Ordinal); case StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase: return TextInfo.IndexOfStringOrdinalIgnoreCase(this, value, startIndex, count); default: throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_StringComparison"), "comparisonType"); } }
結論差不多出來了吧,不過這裡還牽扯到另一個類CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo,我也看過該類的程式碼,裡頭有unsafe程式碼,不在本文範疇,但是有個結論就是當把我的Demo裡的程式碼的IndexOf改為“x.IndexOf(y, StringComparison.Ordinal)”,那麼他們倆的相率將相差無二。
這裡沒有牽扯到正則匹配以及LastIndexOf,其實正則匹配有時可能效率比上述方式更高,但是要視場景使用,更通用的方式還是建議“IndexOf(value, StringComparison.Ordinal)”或“Contains”方法。
string其本身就是char陣列的封裝,其或多或少體現著Array的一些特點,那麼接下來再來看看在List集合中的關於Contains與IndexOf的情況。
<三> List的IndexOf方法並沒有StringComparison列舉作為引數的方法,直接上程式碼吧

/// <summary> /// 演示string,在contain中還可延伸List類(實際上string就是char的集合) /// </summary> /// <param name="action"></param> /// <returns></returns> static long LoopCalcList(Action<List<int>, int> action) { List<int>[] array = new List<int>[260000]; for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { array[i] = new List<int> { i,1,2,3,4,5,6 }; } Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) { action(array[i], 3); } sw.Stop(); return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds; } static void ListContainsDemo() { long indexOfTime = LoopCalcList((x, y) => { if (x.IndexOf(y) >= 0) { } }); long containersTime = LoopCalcList((x, y) => { if (x.Contains(y)) { } }); WriteTime("Contains", containersTime); WriteTime("IndexOf", indexOfTime); }
執行結果
很顯然在判斷是否包含時,我們應該堅定不移的使用Contains。
下面再給出List的原始碼,各位看官自行分析了,對此不做深入研究

// Contains returns true if the specified element is in the List. // It does a linear, O(n) search. Equality is determined by calling // item.Equals(). // public bool Contains(T item) { if ((Object) item == null) { for(int i=0; i<_size; i++) if ((Object) _items[i] == null) return true; return false; } else { EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default; for(int i=0; i<_size; i++) { if (c.Equals(_items[i], item)) return true; } return false; } }

// Returns the index of the first occurrence of a given value in a range of // this list. The list is searched forwards from beginning to end. // The elements of the list are compared to the given value using the // Object.Equals method. // // This method uses the Array.IndexOf method to perform the // search. // public int IndexOf(T item) { return Array.IndexOf(_items, item, 0, _size); } int System.Collections.IList.IndexOf(Object item) { if(IsCompatibleObject(item)) { return IndexOf((T)item); } return -1; } // Returns the index of the first occurrence of a given value in a range of // this list. The list is searched forwards, starting at index // index and ending at count number of elements. The // elements of the list are compared to the given value using the // Object.Equals method. // // This method uses the Array.IndexOf method to perform the // search. // public int IndexOf(T item, int index) { if (index > _size) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.index, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_Index); return Array.IndexOf(_items, item, index, _size - index); } // Returns the index of the first occurrence of a given value in a range of // this list. The list is searched forwards, starting at index // index and upto count number of elements. The // elements of the list are compared to the given value using the // Object.Equals method. // // This method uses the Array.IndexOf method to perform the // search. // public int IndexOf(T item, int index, int count) { if (index > _size) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.index, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_Index); if (count <0 || index > _size - count) ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.count, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_Count); return Array.IndexOf(_items, item, index, count); }
總結:
1.這點效率問題對於某些人來說可能無所謂,但是我覺得更重要的是編碼習慣的養成問題。
2.能用Contains的地方還是儘量使用Contains(發現我改的程式碼中有不少同事直接用了"IndexOf(value)"),當然會有特殊的例外場景,這裡不羅嗦。
3.關於Insert,我編寫了兩個擴充套件方法,如下(方法雖簡單,但是給程式碼帶來了更大的優雅性)
public static string InsertLast(this string source, string str) { return source.Insert(source.Length, str); } public static string InsertFirst(this string source, string str) { return source.Insert(0, str); }
最後本人不是什麼資深狼友,將不會提供任何福利圖片作別,抱歉!!
