簡述:
MPTCP在傳送資料方面和TCP的區別是可以從多條路徑中選擇一條
路徑來傳送資料。MPTCP在接收資料方面與TCP的區別是子路徑對無序包
進行重排後,MPTCP的mpcb需要多所有子路徑的包進行排序。檢視圖1可知。
+-------------------------------+
| Application |
+---------------+ +-------------------------------+
| Application | | MPTCP |
+---------------+ + - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - +
| TCP | | Subflow (TCP) | Subflow (TCP) |
+---------------+ +-------------------------------+
| IP | | IP | IP |
+---------------+ +-------------------------------+
Figure 1: Comparison of Standard TCP and MPTCP Protocol Stacks
資料序號對映(Data Sequence Mapping)
由於所有的資料會通過不同的子路徑傳送,在接收端MPTCP需要對資料進行重新排序。
因此我們需要資料序號對映。資料序號對映定義從子路徑序列空間到資料序列空間的對映。
子路徑的序列空間是子路徑自身的序列號,而資料序列空間維護著所有需傳送的資料。如下圖
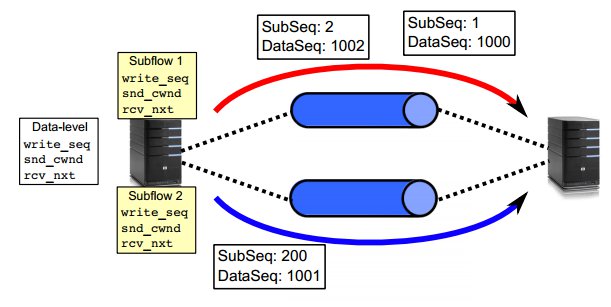
紅色子路徑上的子路徑序號分別是1、2,其資料序號是1000、1002。而下面的藍色的子路徑上的子路徑序號和
資料序號分別是200,1001。這說明從下面的藍色子路徑已經傳送了199個報文,而上面的紅色子路徑才開始傳送。
在MPTCP協議定義如下:
1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Data Sequence Number (8 octets) |
| |
+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| Subflow Sequence Number (4 octets) |
+-------------------------------+------------------------------+
| Data-Level Length (2 octets) | Zeros (2 octets) |
+-------------------------------+------------------------------+
核心中的實現:
函式mptcp_write_dss_mapping對 Data Sequeue Number 和 Subflow Sequence Number進行了賦值。實現如下:
"net/mptcp/mptcp_output.c" line 318 of 1667 318 static int mptcp_write_dss_mapping(struct tcp_sock *tp, struct sk_buff *skb, 319 __be32 *ptr) 320 { 321 struct tcp_skb_cb *tcb = TCP_SKB_CB(skb); 322 __be32 *start = ptr; 323 __u16 data_len; 324 325 *ptr++ = htonl(tcb->seq); /* data_seq */ 326 327 /* If it's a non-data DATA_FIN, we set subseq to 0 (draft v7) */ 328 if (mptcp_is_data_fin(skb) && skb->len == 0) 329 *ptr++ = 0; /* subseq */ 330 else 331 *ptr++ = htonl(tp->write_seq - tp->mptcp->snt_isn); /* subseq */ 332
第325行和331行分別對子路徑序號和資料序號進行了賦值。
###
data_seq and subseq
The mapping is identify by the relative subflow seq, the data seq and
the data len. Basically, it means that isn+sub_seq->isn+sub_seq+len at
the subflow-level corresponds to data_seq->data_seq+len at the
connection-level.
the data len. Basically, it means that isn+sub_seq->isn+sub_seq+len at
the subflow-level corresponds to data_seq->data_seq+len at the
connection-level.
###
資料接收中的重組
核心使用三種佇列接收資料,分別是:Backlog queue(sk->backlog)、Prequeue queue(tp->ucopy.prequeue)
和 Receive queue (sk->receeive_queue)。MPTCP的實現增加了一個新的佇列out-of-order queue對於各個子路徑
收到的資料進行重組。核心中 tcp_v4_rcv()的關鍵實現如下:

"net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c" line 1735 of 2581 1735 if (mptcp(tcp_sk(sk))) { 1736 meta_sk = mptcp_meta_sk(sk); 1737 1738 bh_lock_sock_nested(meta_sk); 1739 if (sock_owned_by_user(meta_sk)) 1740 skb->sk = sk; 1741 } else { 1742 meta_sk = sk; 1743 bh_lock_sock_nested(sk); 1744 } 1745 1746 ret = 0; 1747 if (!sock_owned_by_user(meta_sk)) { 1748 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA 1749 struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(meta_sk); 1750 if (!tp->ucopy.dma_chan && tp->ucopy.pinned_list) 1751 tp->ucopy.dma_chan = net_dma_find_channel(); 1752 if (tp->ucopy.dma_chan) 1753 ret = tcp_v4_do_rcv(sk, skb); 1754 else 1755 #endif 1756 { 1757 if (!tcp_prequeue(meta_sk, skb)) 1758 ret = tcp_v4_do_rcv(sk, skb); 1759 } 1760 } else if (unlikely(sk_add_backlog(meta_sk, skb, 1761 meta_sk->sk_rcvbuf + meta_sk->sk_sndbuf))) { 1762 bh_unlock_sock(meta_sk); 1763 NET_INC_STATS_BH(net, LINUX_MIB_TCPBACKLOGDROP); 1764 goto discard_and_relse; 1765 } 1766 bh_unlock_sock(meta_sk);
從第1757和1760可以看出skb只進入meta的backlog和prequeue,而和子路徑的sock沒有什麼關係。因此,我們得出包的入隊操作如下:
1.進入meta_sk的backlog
2.進入meta_sk的prequeue
3.進入子路徑的receive_queue
第1和2種入隊操作後續操作和正常TCP一致,如果是第3種情況,後續將通過函式mptcp_queue_skb()進入tcp_sk(meta_sk)->out_of_order_queue。
結論:
1.MPTCP利用自身的Data Sequeue Number 和 Subflow Sequence Number進行了資料在各種子路徑間的傳輸。此實現獨立於TCP。
2.為了實現子路徑的資料重組,MPTCP利用了佇列out_of_order_queue。
問題:
1. DATA_ACK作用是?
The Data ACK is analogous to the behavior of the standard TCP
cumulative ACK -- indicating how much data has been successfully received (with no holes). The Data ACK specifies the next data sequence number it expects to
receive.
