Valgrind是一個GPL的軟體,用於Linux(For x86, amd64 and ppc32)程式的記憶體除錯和程式碼剖析。你可以在它的環境中執行你的程式來監視記憶體的使用情況,比如C 語言中的malloc和free或者 C++中的new和 delete。使用Valgrind的工具包,你可以自動的檢測許多記憶體管理和執行緒的bug,避免花費太多的時間在bug尋找上,使得你的程式更加穩固。
Valgrind的主要功能
Valgrind工具包包含多個工具,如Memcheck,Cachegrind,Helgrind, Callgrind,Massif。下面分別介紹個工具的作用:
Memcheck 工具主要檢查下面的程式錯誤:
1.使用未初始化的記憶體 (Use of uninitialised memory)
2.使用已經釋放了的記憶體 (Reading/writing memory after it has been free’d)
3.使用超過 malloc分配的記憶體空間(Reading/writing off the end of malloc’d blocks)
4.對堆疊的非法訪問 (Reading/writing inappropriate areas on the stack)
5.申請的空間是否有釋放 (Memory leaks – where pointers to malloc’d blocks are lost forever)
6.malloc/free/new/delete申請和釋放記憶體的匹配(Mismatched use of malloc/new/new [] vs free/delete/delete [])
7.src和dst的重疊(Overlapping src and dst pointers in memcpy() and related functions)
Callgrind
Callgrind收集程式執行時的一些資料,函式呼叫關係等資訊,還可以有選擇地進行cache 模擬。在執行結束時,它會把分析資料寫入一個檔案。callgrind_annotate可以把這個檔案的內容轉化成可讀的形式。
Cachegrind
它模擬 CPU中的一級快取I1,D1和L2二級快取,能夠精確地指出程式中 cache的丟失和命中。如果需要,它還能夠為我們提供cache丟失次數,記憶體引用次數,以及每行程式碼,每個函式,每個模組,整個程式產生的指令數。這對優化程式有很大的幫助。
Helgrind
它主要用來檢查多執行緒程式中出現的競爭問題。Helgrind 尋找記憶體中被多個執行緒訪問,而又沒有一貫加鎖的區域,這些區域往往是執行緒之間失去同步的地方,而且會導致難以發掘的錯誤。Helgrind實現了名為” Eraser” 的競爭檢測演算法,並做了進一步改進,減少了報告錯誤的次數。
Massif
堆疊分析器,它能測量程式在堆疊中使用了多少記憶體,告訴我們堆塊,堆管理塊和棧的大小。Massif能幫助我們減少記憶體的使用,在帶有虛擬記憶體的現代系統中,它還能夠加速我們程式的執行,減少程式停留在交換區中的機率。
Ubuntu 安裝valgrind:
#> sudo apt-get install valgrind
valgrind 使用:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char *ptr = (char *)malloc(1024); ptr[1024] = 0; // memcpy(ptr+1, ptr, 100); char ch = ptr[1024]; free(ptr); free(ptr); char *ptr1; *ptr1 = 'a'; char *ptr2 = (char *)malloc(1024); return 0; }
#> valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=yes ./valgTest
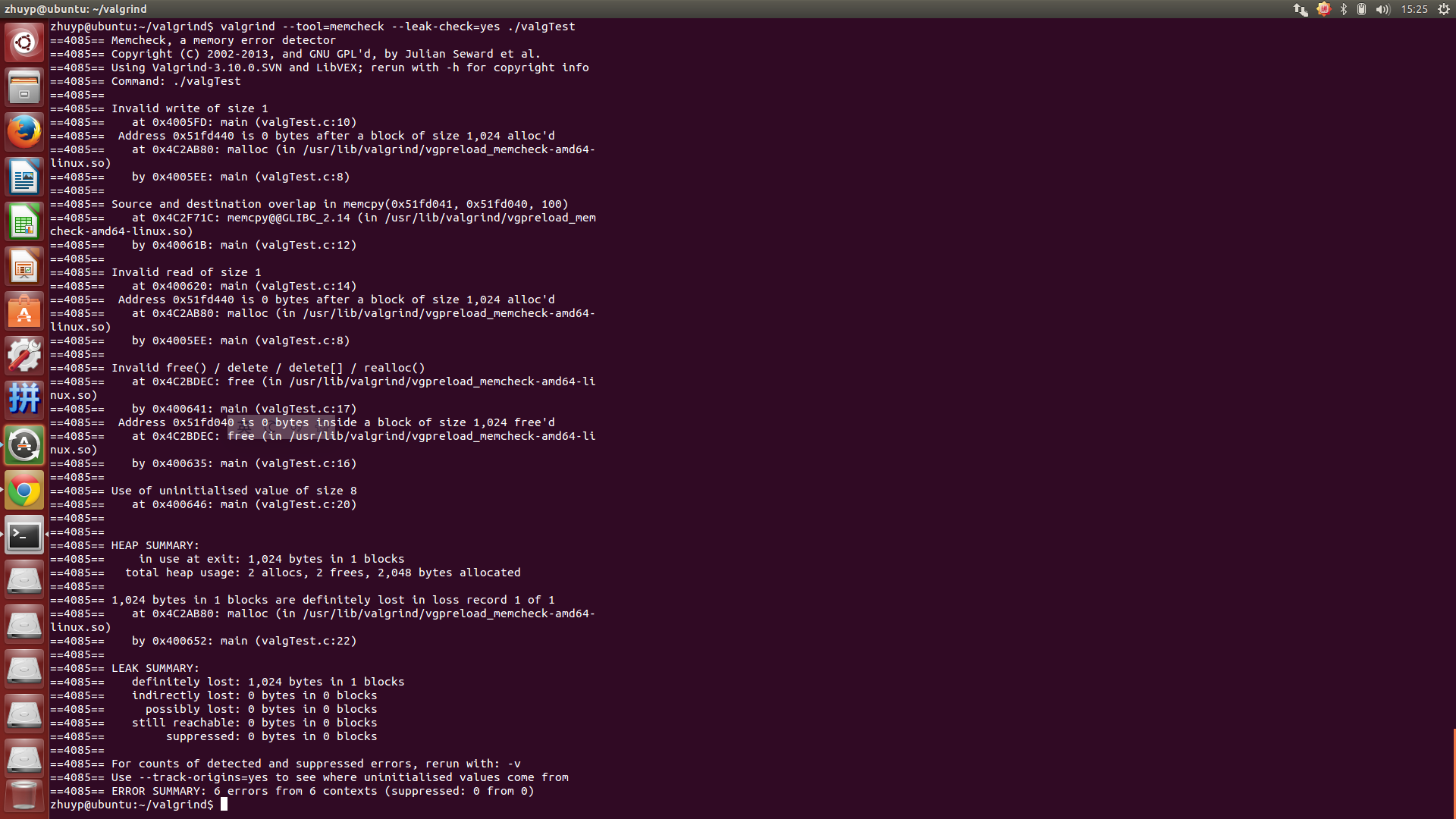
注意在編譯程式的時候加上-g選項,列印錯誤資訊的時候會給出行號。上面的執行結果給出了六個錯誤。
下面看一個多執行緒競爭的情況:
#include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> int a = 0; void* child_fn (void* arg) { a++; return NULL; } int main () { pthread_t child; pthread_create(&child,NULL, child_fn, NULL); a++; pthread_join(child,NULL); return 0; }
zhuyp@ubuntu:~/valgrind$ valgrind --tool=helgrind ./helTest
==5639== Helgrind, a thread error detector
==5639== Copyright (C) 2007-2013, and GNU GPL'd, by OpenWorks LLP et al.
==5639== Using Valgrind-3.10.0.SVN and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==5639== Command: ./helTest
==5639==
==5639== ---Thread-Announcement------------------------------------------
==5639==
==5639== Thread #1 is the program's root thread
==5639==
==5639== ---Thread-Announcement------------------------------------------
==5639==
==5639== Thread #2 was created
==5639== at 0x51562CE: clone (clone.S:74)
==5639== by 0x4E44199: do_clone.constprop.3 (createthread.c:75)
==5639== by 0x4E458BA: pthread_create@@GLIBC_2.2.5 (createthread.c:245)
==5639== by 0x4C30C90: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5639== by 0x40068D: main (helTest.c:15)
==5639==
==5639== ----------------------------------------------------------------
==5639==
==5639== Possible data race during read of size 4 at 0x60104C by thread #1
==5639== Locks held: none
==5639== at 0x40068E: main (helTest.c:16)
==5639==
==5639== This conflicts with a previous write of size 4 by thread #2
==5639== Locks held: none
==5639== at 0x40065E: child_fn (helTest.c:8)
==5639== by 0x4C30E26: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5639== by 0x4E45181: start_thread (pthread_create.c:312)
==5639== by 0x515630C: clone (clone.S:111)
==5639==
==5639== ----------------------------------------------------------------
==5639==
==5639== Possible data race during write of size 4 at 0x60104C by thread #1
==5639== Locks held: none
==5639== at 0x400697: main (helTest.c:16)
==5639==
==5639== This conflicts with a previous write of size 4 by thread #2
==5639== Locks held: none
==5639== at 0x40065E: child_fn (helTest.c:8)
==5639== by 0x4C30E26: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5639== by 0x4E45181: start_thread (pthread_create.c:312)
==5639== by 0x515630C: clone (clone.S:111)
==5639==
==5639==
==5639== For counts of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -v
==5639== Use --history-level=approx or =none to gain increased speed, at
==5639== the cost of reduced accuracy of conflicting-access information
==5639== ERROR SUMMARY: 2 errors from 2 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
前面寫過一個使用coredump除錯死鎖的方法,這裡使用valgrind 的 helgrind 工具也可以檢查出死鎖問題。
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <chrono> using namespace std; mutex m1,m2; void func_2() { m2.lock(); cout<< "about to dead_lock"<<endl; m1.lock(); } void func_1() { m1.lock(); chrono::milliseconds dura( 1000 );// delay to trigger dead_lock this_thread::sleep_for( dura ); m2.lock(); } int main() { thread t1(func_1); thread t2(func_2); t1.join(); t2.join(); return 0; }
zhuyp@ubuntu:~/valgrind$ g++ -Wall dead_lock_demo.cpp -o dead_lock_demo -g -std=c++11 -lpthread
zhuyp@ubuntu:~/valgrind$ valgrind --tool=helgrind ./dead_lock_demo
==5646== Helgrind, a thread error detector
==5646== Copyright (C) 2007-2013, and GNU GPL'd, by OpenWorks LLP et al.
==5646== Using Valgrind-3.10.0.SVN and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==5646== Command: ./dead_lock_demo
==5646==
about to dead_lock // 執行到這裡,Ctrl + C 結束程式,則列印出如下資訊
^C==5646== ---Thread-Announcement------------------------------------------
==5646==
==5646== Thread #2 was created
==5646== at 0x56702CE: clone (clone.S:74)
==5646== by 0x4E44199: do_clone.constprop.3 (createthread.c:75)
==5646== by 0x4E458BA: pthread_create@@GLIBC_2.2.5 (createthread.c:245)
==5646== by 0x4C30C90: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646== by 0x510CE3E: std::thread::_M_start_thread(std::shared_ptr<std::thread::_Impl_base>) (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6.0.19)
==5646== by 0x401789: std::thread::thread<void (&)()>(void (&)()) (thread:135)
==5646== by 0x40112D: main (dead_lock_demo.cpp:33)
==5646==
==5646== ----------------------------------------------------------------
==5646==
==5646== Thread #2: Exiting thread still holds 1 lock
==5646== at 0x4E4BF2C: __lll_lock_wait (lowlevellock.S:135)
==5646== by 0x4E47656: _L_lock_909 (pthread_mutex_lock.c:151)
==5646== by 0x4E4747E: pthread_mutex_lock (pthread_mutex_lock.c:79)
==5646== by 0x4C32072: pthread_mutex_lock (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646== by 0x40101B: __gthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t*) (gthr-default.h:748)
==5646== by 0x401421: std::mutex::lock() (mutex:134)
==5646== by 0x401111: func_1() (dead_lock_demo.cpp:25)
==5646== by 0x40278C: void std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()>::_M_invoke<>(std::_Index_tuple<>) (functional:1732)
==5646== by 0x4026E6: std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()>::operator()() (functional:1720)
==5646== by 0x40267F: std::thread::_Impl<std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()> >::_M_run() (thread:115)
==5646== by 0x510CBEF: ??? (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6.0.19)
==5646== by 0x4C30E26: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646==
==5646== ---Thread-Announcement------------------------------------------
==5646==
==5646== Thread #3 was created
==5646== at 0x56702CE: clone (clone.S:74)
==5646== by 0x4E44199: do_clone.constprop.3 (createthread.c:75)
==5646== by 0x4E458BA: pthread_create@@GLIBC_2.2.5 (createthread.c:245)
==5646== by 0x4C30C90: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646== by 0x510CE3E: std::thread::_M_start_thread(std::shared_ptr<std::thread::_Impl_base>) (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6.0.19)
==5646== by 0x401789: std::thread::thread<void (&)()>(void (&)()) (thread:135)
==5646== by 0x40113E: main (dead_lock_demo.cpp:35)
==5646==
==5646== ----------------------------------------------------------------
==5646==
==5646== Thread #3: Exiting thread still holds 1 lock
==5646== at 0x4E4BF2C: __lll_lock_wait (lowlevellock.S:135)
==5646== by 0x4E47656: _L_lock_909 (pthread_mutex_lock.c:151)
==5646== by 0x4E4747E: pthread_mutex_lock (pthread_mutex_lock.c:79)
==5646== by 0x4C32072: pthread_mutex_lock (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646== by 0x40101B: __gthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t*) (gthr-default.h:748)
==5646== by 0x401421: std::mutex::lock() (mutex:134)
==5646== by 0x4010DF: func_2() (dead_lock_demo.cpp:14)
==5646== by 0x40278C: void std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()>::_M_invoke<>(std::_Index_tuple<>) (functional:1732)
==5646== by 0x4026E6: std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()>::operator()() (functional:1720)
==5646== by 0x40267F: std::thread::_Impl<std::_Bind_simple<void (*())()> >::_M_run() (thread:115)
==5646== by 0x510CBEF: ??? (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6.0.19)
==5646== by 0x4C30E26: ??? (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_helgrind-amd64-linux.so)
==5646==
==5646==
==5646== For counts of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -v
==5646== Use --history-level=approx or =none to gain increased speed, at
==5646== the cost of reduced accuracy of conflicting-access information
==5646== ERROR SUMMARY: 2 errors from 2 contexts (suppressed: 1 from 1)
吐槽一下,剛剛在Linux操作並編輯該博文,各種不適應啊,還是換到Windows下來編輯要方便些。。。