前言
接上篇,已經完成了一個SpringBoot專案的基本搭建。那麼現在就要考慮要做什麼,怎麼做的問題。所以本篇內容不多,帶大家一起來簡單瞭解一下要做的東西,之前有很多人不知道從哪裡下手,那麼今天我帶著大家熟悉LayIM以及它的對接思路。由於重點是SpringBoot,所以,LayIM部分也不會講的太細,官網有詳細的文章。
LayIM有什麼?
- 非常舒服的UI
- 封裝了友好的聊天介面,訊息記錄,自定義外掛,新增好友,新增群組等等功能,前端的東西完全不必費心,把重心放到實現業務上。
- 完善的文件,開發起來不必大費力氣
文件解析
上邊一堆套話,沒有什麼實質內容,下面我簡單講一下我們的開發思路。首先看初始化介面,瀏覽器右下角有一個類似QQ似的介面,包含好友列表,群組列表,當前登入人的資訊等。
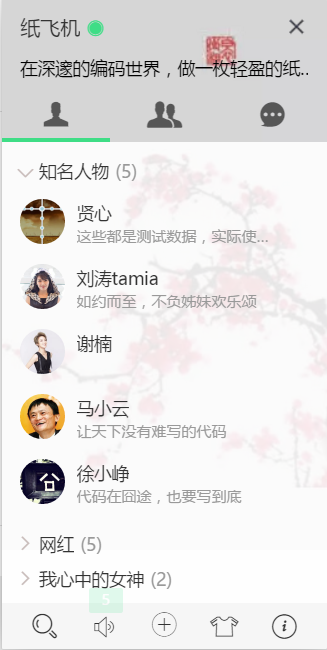
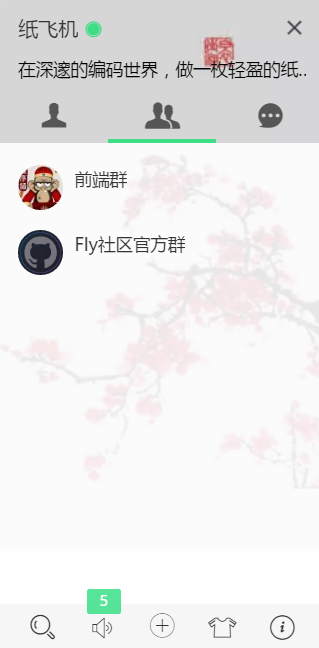
OK,檢視原始碼我們可以看到,LayIM是有多個基礎介面的。初始化介面,上傳檔案介面等等。這些資料介面是與我們將要用SpringBoot開發息息相關的。可以看到程式碼裡面有一個路徑:/layim/json/getList.json.下載程式碼包,我們看看這個檔案是什麼東東。
//基礎配置 layim.config({ //初始化介面 init: { url: '/layim/json/getList.json' ,data: {} } //檢視群員介面 ,members: { url: '/layim/json/getMembers.json' ,data: {} } ,uploadImage: { url: '' //(返回的資料格式見下文) ,type: '' //預設post } ,uploadFile: { url: '' //(返回的資料格式見下文) ,type: '' //預設post }
json的內容如下圖所示。(已經摺疊)
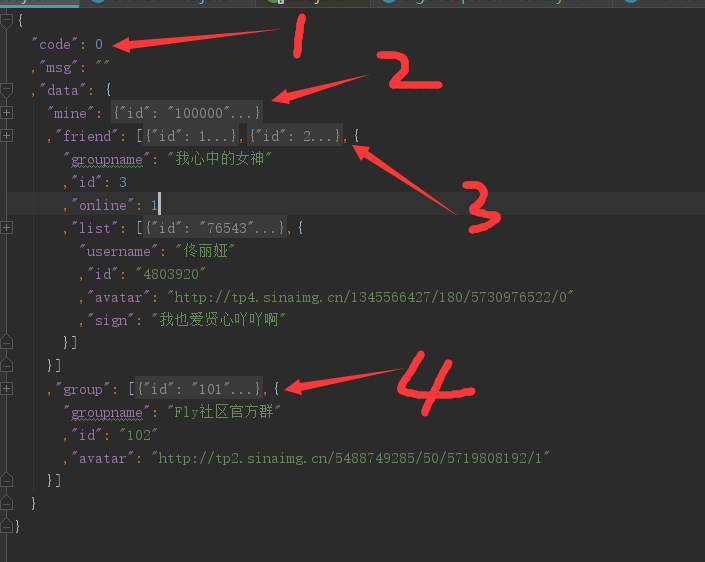
序號1:最外層的統一json格式。code:0 (success)1(failed)。msg:介面返回資訊 data :介面返回資料
序號2:mine即當前登入人的資訊,頭像,狀態,簽名等
序號3:好友分組資訊。包含多個好友分組,每個人組有若干好友
序號4:群組資訊。包含多個群組,每個群組有圖示,群名等
好,那麼到此為止,其他的先不介紹,我們直接來實現這個初始化資料的載入,不過這裡不得不說SpringBoot真的是很贊,一個RestController幫你搞定。
程式碼實戰
先根據資料格式建好相應的model。當然java裡叫pojo。由於他們對應的是最終輸出的json,所以我沒有把他們的類和對應資料庫的類(@Entity)寫在一起。程式碼在/domain/viewmodels 資料夾下。在這裡我將最終符合上圖中的json格式的程式碼貼出來
public class LayimBaseViewModel { private UserViewModel mine; private List<FriendGroupViewModel> friend; private List<BigGroupViewModel> group; //省略 getter setter }
資料結構已經出來了,相信大家迫不及待的看到頁面效果了,不要著急,先建一個Controller。加上@RestController 註解。官方說明如下:
- A convenience annotation that is itself annotated with @Controller and @ResponseBody. Types that carry this annotation are treated as controllers where @RequestMapping methods assume @ResponseBody semantics by default. (@RestController 相當於@Controller 和 @ReponseBody 的結合)
不管那麼多,總之,我覺得SpringBoot的註解還是蠻強大的。我們隨便寫一個方法試試。
@RestController @RequestMapping("/layim") public class UserController { @GetMapping("/test") public JsonResult testData(){ return ResultUtil.success("hello spring boot"); } }
執行一下:
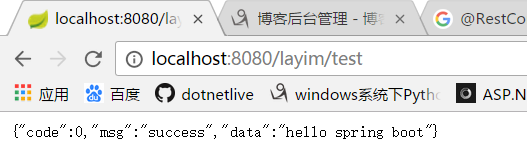
是不是很簡單,那還等什麼,還不趕緊把LayIM的資料搭建出來。新建 UserService,增加 getBaseList 方法,這裡我們先不從資料庫請求,直接模擬資料。

1 public JsonResult getBaseList(Long userId){ 2 LayimBaseViewModel baseData = new LayimBaseViewModel(); 3 4 //自己的資訊 5 UserViewModel mine = new UserViewModel(); 6 mine.setUsername("小盤子"); 7 mine.setSign("SpringBoot學習中"); 8 mine.setAvatar("https://vignette.wikia.nocookie.net/dragonball/images/d/da/Kid-Goku-psd61058.png/revision/latest?cb=20120213205410"); 9 mine.setId(userId); 10 11 baseData.setMine(mine); 12 //好友列表資訊 13 ArrayList<FriendGroupViewModel> friends = new ArrayList<FriendGroupViewModel>(); 14 15 FriendGroupViewModel frined1 = new FriendGroupViewModel(); 16 frined1.setId(1L); 17 frined1.setGroupname("我的好友"); 18 frined1.setOnline(10); 19 20 ArrayList<UserViewModel> users1 = new ArrayList<UserViewModel>(); 21 22 UserViewModel user1 = new UserViewModel(); 23 user1.setId(100001L); 24 user1.setAvatar("https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQjvcDBSg8-TYMzRSbw75MJAawM5dF9StHSisVhdhWmL6vK8K66UQ"); 25 user1.setSign("教練,我想打籃球"); 26 user1.setUsername("三井壽"); 27 28 users1.add(user1); 29 30 frined1.setList(users1); 31 friends.add(frined1); 32 33 baseData.setFriend(friends); 34 //分組資訊 35 ArrayList<BigGroupViewModel> groups = new ArrayList<BigGroupViewModel>(); 36 37 BigGroupViewModel bigGroup1 = new BigGroupViewModel(); 38 bigGroup1.setId(1000001L); 39 bigGroup1.setGroupname("SpringBoot愛好者群"); 40 bigGroup1.setAvatar("https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTp9Q8BuXHj30KbOHPY7qlnR10oI4cCpplRcBFThQFzZ4bx3mBz"); 41 groups.add(bigGroup1); 42 43 baseData.setGroup(groups); 44 return ResultUtil.success(baseData); 45 }
那麼在UserController中使用 UserService 的 getBaseList 方法即可。
@GetMapping(value = "/base/{uid}")
public JsonResult getBaseData(@PathVariable("uid") Long userId){
return userService.getBaseList(userId);
}
注意,我們這裡分別使用了 @RestController,@Autowired,@GetMapping,@PathVariable註解,由於我對註解也沒有那麼瞭解,所以想具體學習的朋友可以看相關文件。因為我們是快速使用,所以是屬於遇到什麼學什麼,用什麼的思路,也不會在某個知識點上停留太久,有問題小夥伴們可以留言一起探討。
方法寫完了,在瀏覽器中看看(/layim/base/{uid}):
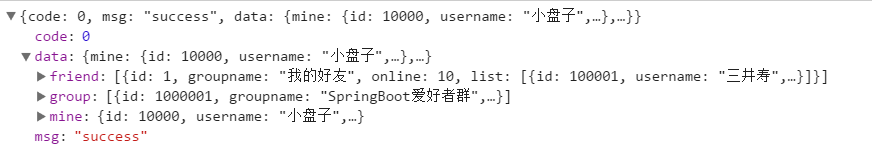
對比一下getList.json檔案,是不是沒有什麼區別。趕緊把getList.json替換了吧。開啟index.html,找到 init:url。把我們自己的url替換上去
init: {
url: '/layim/base/10000'//10000為使用者ID,後臺也可以不用路徑 使用?uid=10000的形式也可以
,data: {}//附加其他引數
}
我們在次開啟index.html,瀏覽:



沒有任何問題,大功告成?還早著呢,真正的資料是從資料庫(或其他儲存)讀出來的,正如上一篇介紹,我將會使用MySQL作為資料儲存,並且使用SpringBoot JPA 做資料操作。
總結
本片教大家如何分析一個帶有完整文件的前端框架,並開發對應後臺API。雖然只是簡單介紹了 init 介面,但是 像getMemberList 介面,或者上傳圖片啊,檔案啊,我相信大家肯定都能舉一反三來實現。當然@RestController功不可沒。現在想想以後還有很多的工作要做,彆著急。後邊要學的東西多著呢。websocket,快取,佇列等等都加上(問:用得著這麼多東西嗎? 答“我只是想通過專案來練習他們的使用)
下篇預告:從零一起學Spring Boot之LayIM專案長成記(三) 資料庫的簡單設計和JPA的簡單使用。
