1.什麼是RemoteView?
答:其實就是一種特殊的view結構,這種view 能夠跨程式傳輸。並且這種remoteview 還提供了一些方法 可以跨程式更新介面。具體在android裡面 一個是通知 一個是桌面小部件。
這2個就是remoteview 最直接的應用了
2.RemoteView在通知上的應用?
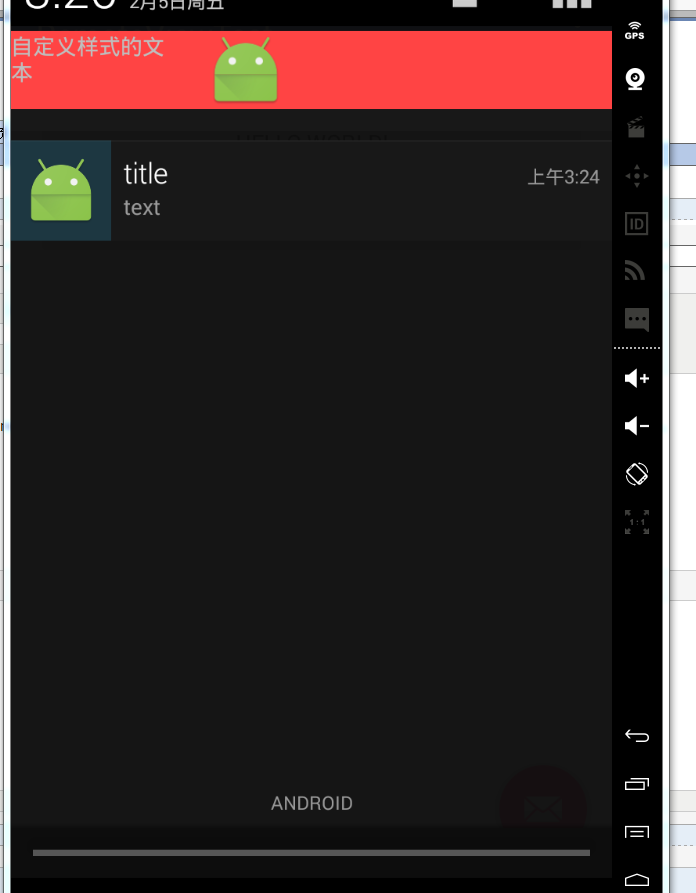
答:這裡給出一個小例子,比較粗糙 僅做演示使用。

1 //預設樣式的notification 2 private void normalStyleNotification() { 3 Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MainActivity.class); 4 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(MainActivity.this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 5 Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(MainActivity.this); 6 Notification notification = builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent).setContentTitle("title").setContentText("text").setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher).build(); 7 NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE); 8 manager.notify(1, notification); 9 } 10 11 //自定義樣式 12 private void customStyleNotification() { 13 Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MainActivity.class); 14 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(MainActivity.this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 15 Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(MainActivity.this); 16 RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), R.layout.notification_layout); 17 remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.tv, "自定義樣式的文字"); 18 remoteViews.setImageViewResource(R.id.iv, R.mipmap.ic_launcher); 19 Notification notification = builder.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher).setContentIntent(pendingIntent).setContent(remoteViews).build(); 20 NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE); 21 manager.notify(2, notification); 22 }
效果如下:
3.小部件開發 大概流程如何?
答:android的小部件開發就全都是用的remoteviews。其實就是一個廣播接收器+ui顯示 ,諸如下圖顯示:
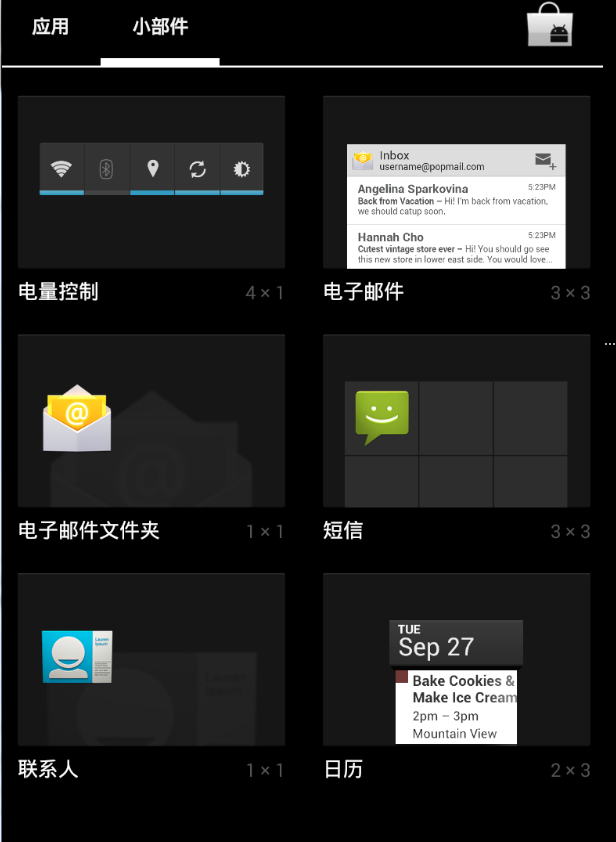
啟動某個小部件以後就可以看到:

下面給出一個簡單的例子 ,示範下小部件的基本開發流程,其實非常簡單,畢竟就只是一個廣播而已。只不過在具體app中 小部件或許會變的非常複雜。
既然是廣播,我們就首先要給他一個接收器,保證能接收到廣播:

1 <receiver android:name=".MyWidgetProvider"> 2 <meta-data 3 android:name="android.appwidget.provider" 4 android:resource="@xml/widget_info"></meta-data> 5 <intent-filter> 6 <!--這個是單擊事件的action--> 7 <action android:name="com.example.administrator.remoteviewtest.CLICK"></action> 8 <!--這個必須要有 屬於預設需要新增的--> 9 <action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"></action> 10 </intent-filter> 11 </receiver>
然後在res/xml下 建立我們的widget配置檔案:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:initialLayout="@layout/layout_widget" 4 android:minHeight="100dp" 5 android:minWidth="200dp" 6 android:updatePeriodMillis="160000" 7 ></appwidget-provider>
然後寫一個最簡單的widget 的 layout檔案:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:background="@android:color/holo_red_light" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical"> 7 8 <ImageView 9 android:id="@+id/iv2" 10 android:layout_gravity="center" 11 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 13 android:src="@mipmap/shuqi" /> 14 15 </LinearLayout>
最後 我們來編寫我們的appwidgetProvider: 只完成一件事 就是點選他以後 圖片就翻轉

1 package com.example.administrator.remoteviewtest; 2 3 import android.app.PendingIntent; 4 import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager; 5 import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider; 6 import android.content.ComponentName; 7 import android.content.Context; 8 import android.content.Intent; 9 import android.graphics.Bitmap; 10 import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; 11 import android.graphics.Matrix; 12 import android.os.SystemClock; 13 import android.util.Log; 14 import android.widget.RemoteViews; 15 import android.widget.Toast; 16 17 /** 18 * Created by Administrator on 2016/2/5. 19 */ 20 public class MyWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider { 21 22 public static final String CLICK_ACTION = "com.example.administrator.remoteviewtest.CLICK"; 23 24 25 @Override 26 public void onReceive(final Context context, Intent intent) { 27 super.onReceive(context, intent); 28 if (intent.getAction().equals(CLICK_ACTION)) { 29 Toast.makeText(context, "收到單擊事件", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 30 new Thread(new Runnable() { 31 @Override 32 public void run() { 33 34 Bitmap srcBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(), R.mipmap.shuqi); 35 AppWidgetManager appwidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context); 36 //點選以後就讓圖片不斷旋轉 37 for (int i = 0; i < 37; i++) { 38 float degree = (i * 10) % 360; 39 RemoteViews remoteviews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.layout_widget); 40 remoteviews.setImageViewBitmap(R.id.iv2, rotateBitmap(context, srcBitmap, degree)); 41 //每次更新的時候 都別忘記了給他新增點選事件 42 Intent intentClick = new Intent(); 43 intentClick.setAction(CLICK_ACTION); 44 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intentClick, 0); 45 remoteviews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.iv2, pendingIntent); 46 appwidgetManager.updateAppWidget(new ComponentName(context, MyWidgetProvider.class), remoteviews); 47 SystemClock.sleep(30); 48 } 49 } 50 }).start(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 55 @Override 56 public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { 57 super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds); 58 //這個地方couter 其實就是你widget 佈局裡面 帶有id的 view的總數,比如我們這個例子裡面就只有 59 //一個imageview 有id 所以這個地方counter的值就是1 60 final int counter = appWidgetIds.length; 61 for (int i = 0; i < counter; i++) { 62 int appWidgetId = appWidgetIds[i]; 63 //每次新增小部件或者小部件自己有更新時,我們都要重新更新小部件裡面點選事件 等view相關的資源 64 updateWidget(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId); 65 } 66 } 67 68 private void updateWidget(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int appWidgetId) { 69 RemoteViews remoteviews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.layout_widget); 70 71 //單擊小部件以後發生的事 72 Intent intentClick = new Intent(); 73 intentClick.setAction(CLICK_ACTION); 74 PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intentClick, 0); 75 remoteviews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.iv2, pendingIntent); 76 appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, remoteviews); 77 } 78 79 //將圖片翻轉一定的角度 80 private Bitmap rotateBitmap(Context context, Bitmap srcBitmap, float degree) { 81 Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); 82 matrix.reset(); 83 matrix.setRotate(degree); 84 Bitmap dstBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(srcBitmap, 0, 0, srcBitmap.getWidth(), srcBitmap.getHeight(), matrix, true); 85 return dstBitmap; 86 } 87 88 89 }
最後看一下簡單的效果:
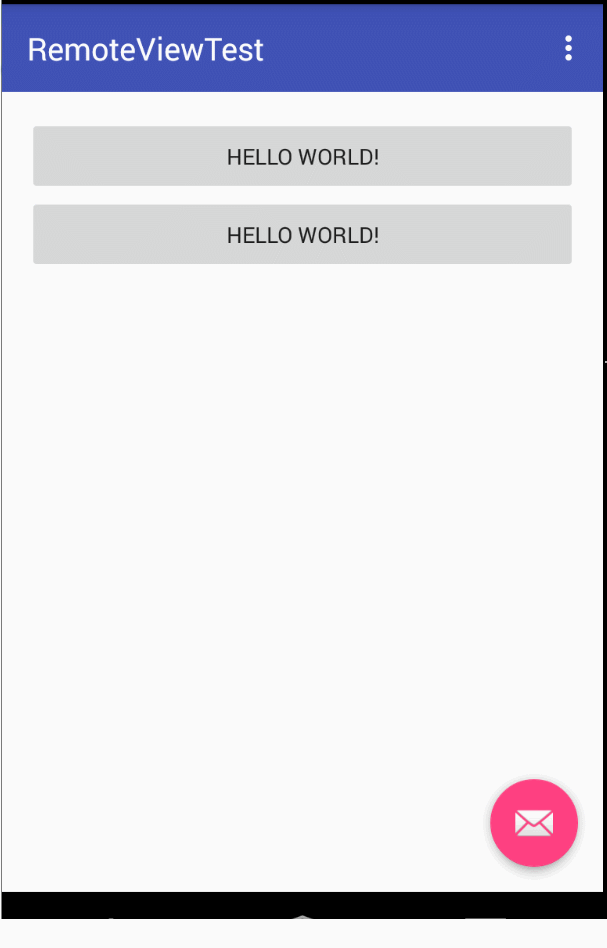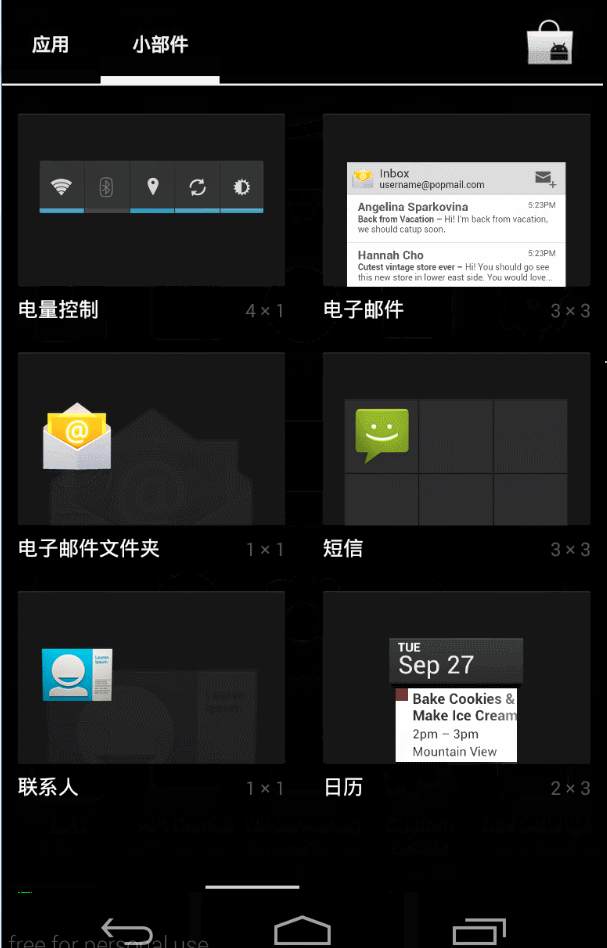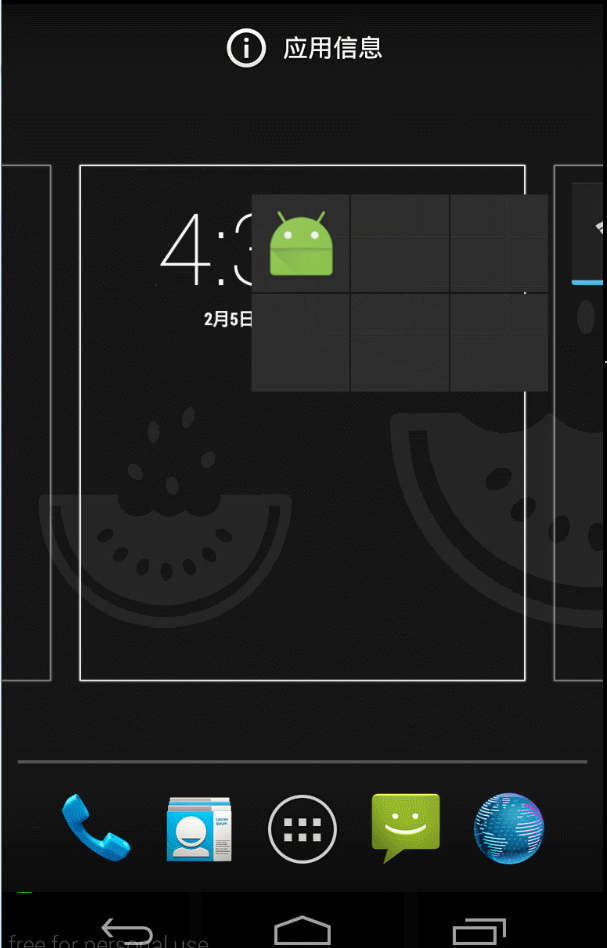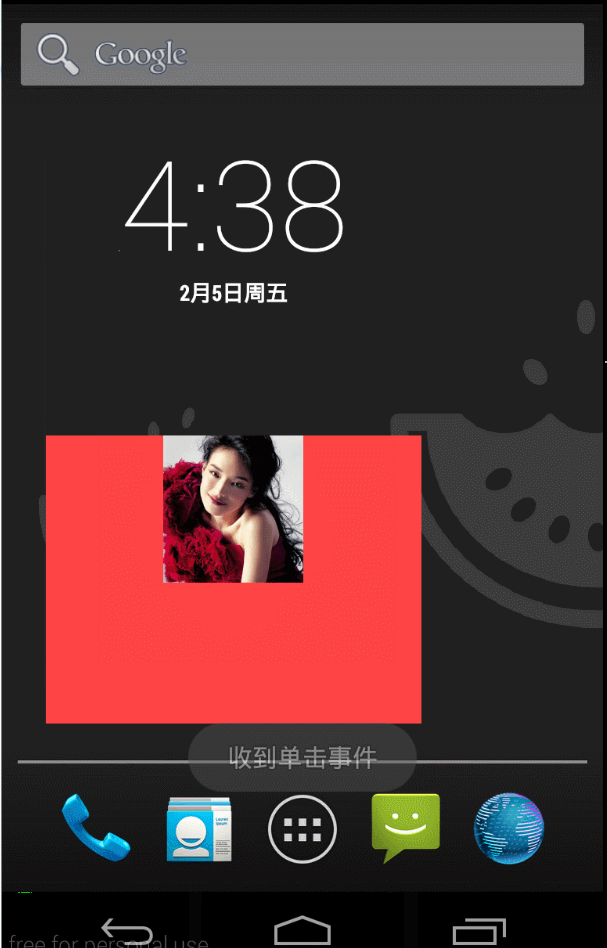
4.簡述一下 widget開發中 幾個重要的生命週期函式 都在什麼情況下被呼叫?
答:onEnable :當widget第一次被新增到桌面時呼叫,新增行為可以多次,但是這個函式只有在第一次時能得到執行。
onUpdate:widget被新增或者更新時就會執行
onDeleted:刪除的時候執行
onDisabled:最後一個該型別的widget被刪除的時候 呼叫他
onReceive:分發廣播的。我們主要的邏輯一般都寫在這裡。
5.intent和PendingIntent有什麼區別。
答:intent代表的行為 是馬上就要發生。而pendingIntent代表 這個行為是在將來的某個不確定的時間發生。 我們給RemoteView 新增點選事件的時候 都用pendingIntent。
pendingIntent通過set和cancel 方法來傳送和取消 那些intent。
6.pendingIntent 支援哪幾種?
答:三種。分別是getActivity getService 和getBroadcast。
7.pendingIntent的匹配規則是什麼?
答:內部的intent和requestCode 都相同的時候 系統就認為這2個pendingIntent是相同的。intent相同的判定原則是 intent-filter和componentName相同。
8.如何理解pendingIntent的 flags 標誌位?
答:可以從通知的角度來理解。manager.notify(1, notification); 我們平常發通知的時候 這個函式的 第一個引數 ,我們一般都是寫一個常量。注意notification裡面是有pendingintent的。
當我們這一個引數是寫死的常量的時候 那不管notification裡面的pendingIntent 是什麼,這個通知都是永遠老的被新的直接替代。
如果這notify的第一個引數 每次都不相同,情況就複雜的多,要分開來看:
notify函式的第一個引數不相同,notification裡的pendingintent不相同時:通知和通知之間互相不干擾,可以看看效果:
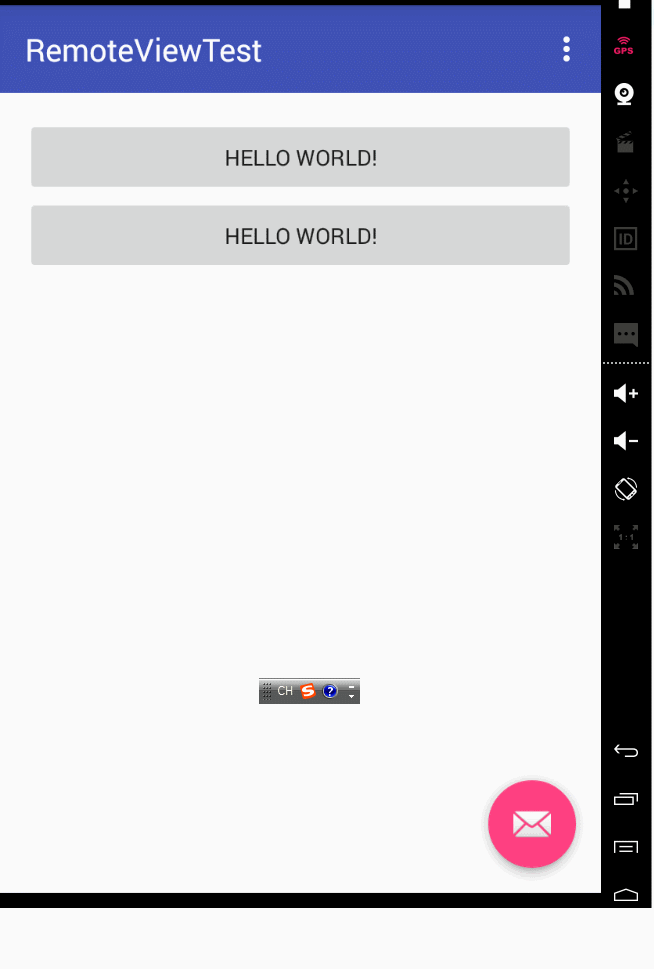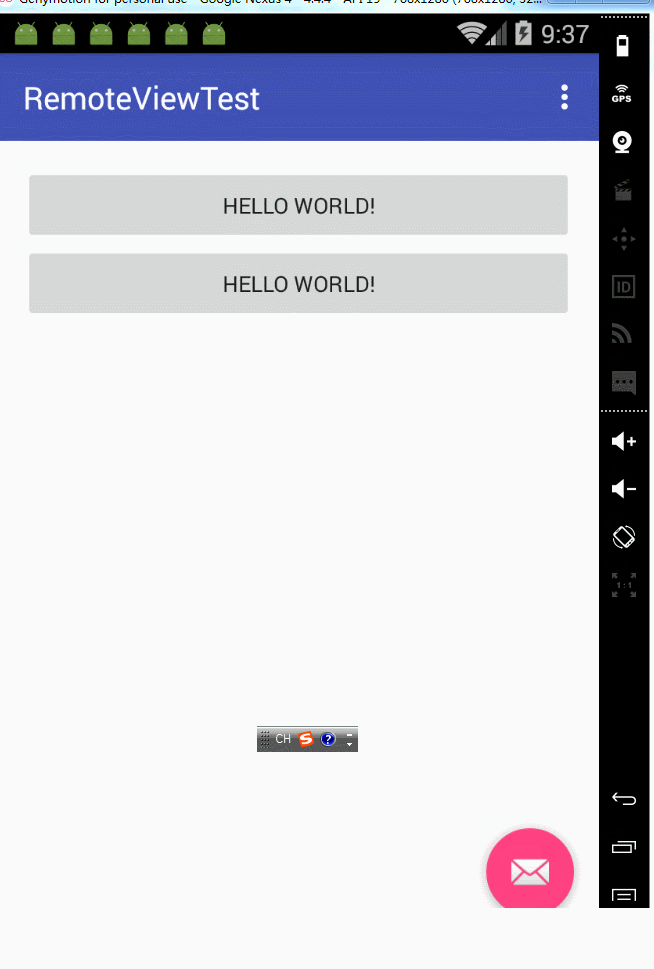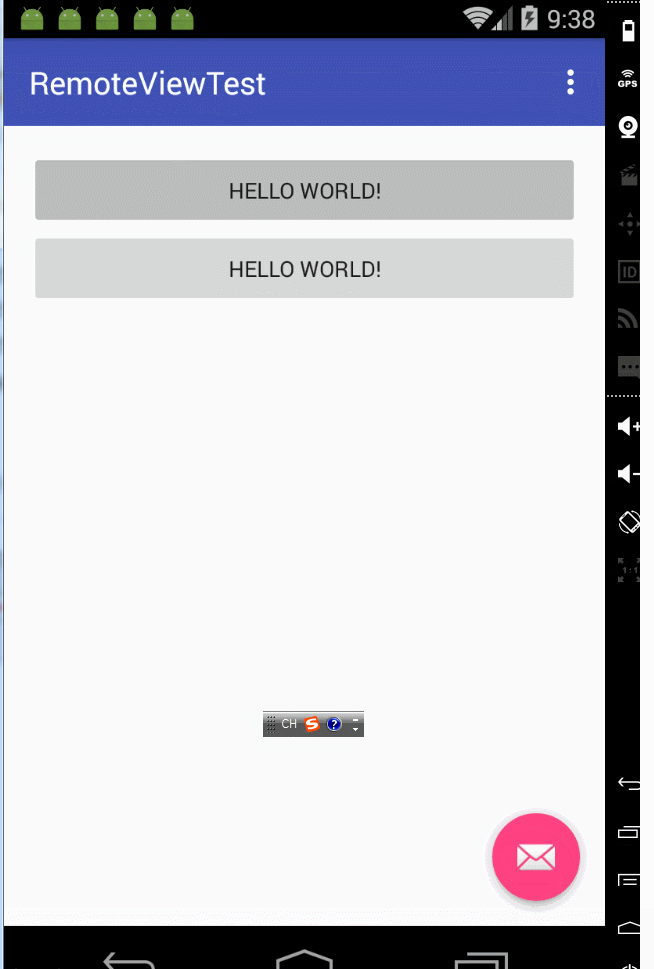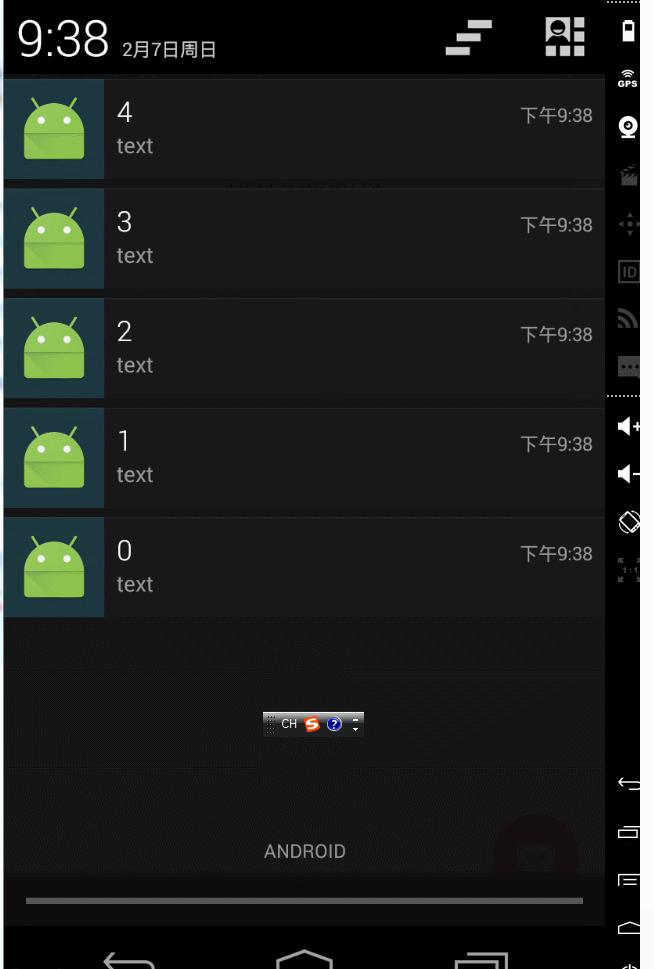
notify函式的第一個引數不相同,notification裡的pendingintent相同時,這個時候就要看flags的引數了。
如果flag=FLAG_ONE_SHOT,那後續的pendingIntent就和第一個保持一致,哪怕是intent裡面的引數extras 都是一致的。
而且如果點選任何一個通知,其他的通知都無法開啟了。
flag=FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT 只有最新的通知才能開啟,以前的通知點選都無效無法開啟。
flag=FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT 之前的通知會被更新成 和最新的那條通知是一樣的 裡面的extras都是一樣的。並且都可以開啟。
9.remoteView 支援所有的view型別嗎?
答:remoteview 僅僅支援少部分系統自帶的view。開發者的自定義view 是一律都不支援的,具體支援哪些系統的view和viewgroup,可以自行谷歌。
10.簡述remoteViews的 原理?
答:通知欄和widget 都是執行在 NotificationManagerService和AppWidgetService的,並且是在systemt server程式中。我們在apk程式碼裡
使用notificationmanager或者appwidgetmanager實際上都是通過binder 來進行與system server的程式間通訊的。

1 public class RemoteViews implements Parcelable, Filter {
可以看到remotviews是繼承了Parcelable介面。所以這個remoteviews會通過binder 傳遞到system server 這個系統程式裡。然後系統程式
會解析這個remotview 拿到他的包名和佈局檔案等資訊 然後就通過layoutInflater 來載入這個佈局了。
對於system server來說 remoteview就好像是自己這個程式裡的 資源一樣,而對於呼叫者 也就是我們自己的apk程式設計師來說,這個view
就顯然是remoteviews 遠端的了。並且值得注意的是,view的更新操作 是由action物件的apply方法來執行的!這一點千萬要記住。
我們可以從原始碼的角度來逐一分析。

1 2 3 //假設我們remoteviews是呼叫了這個方法 我們就來看看這個方法的過程 4 public void setTextViewText(int viewId, CharSequence text) { 5 setCharSequence(viewId, "setText", text); 6 } 7 8 //這裡就明白了 你看 到這還沒有實際呼叫view的方法,而是呼叫了addAciton方法 好像是新增了一個action 9 public void setCharSequence(int viewId, String methodName, CharSequence value) { 10 addAction(new ReflectionAction(viewId, methodName, ReflectionAction.CHAR_SEQUENCE, value)); 11 } 12 13 //這個方法就很簡單 就是remoteviews內部有一個mActions物件 他是一個list 每次我們呼叫remoteviews的set方法的時候 14 //實際上都是往這個列表裡面 新增了一個action 15 private void addAction(Action a) { 16 if (hasLandscapeAndPortraitLayouts()) { 17 throw new RuntimeException("RemoteViews specifying separate landscape and portrait" + 18 " layouts cannot be modified. Instead, fully configure the landscape and" + 19 " portrait layouts individually before constructing the combined layout."); 20 } 21 if (mActions == null) { 22 mActions = new ArrayList<Action>(); 23 } 24 mActions.add(a); 25 26 // update the memory usage stats 27 a.updateMemoryUsageEstimate(mMemoryUsageCounter); 28 } 29 30 31 //真正的執行view的方法 就是在apply函式裡 32 public View apply(Context context, ViewGroup parent, OnClickHandler handler) { 33 RemoteViews rvToApply = getRemoteViewsToApply(context); 34 35 View result; 36 // RemoteViews may be built by an application installed in another 37 // user. So build a context that loads resources from that user but 38 // still returns the current users userId so settings like data / time formats 39 // are loaded without requiring cross user persmissions. 40 final Context contextForResources = getContextForResources(context); 41 Context inflationContext = new ContextWrapper(context) { 42 @Override 43 public Resources getResources() { 44 return contextForResources.getResources(); 45 } 46 @Override 47 public Resources.Theme getTheme() { 48 return contextForResources.getTheme(); 49 } 50 @Override 51 public String getPackageName() { 52 return contextForResources.getPackageName(); 53 } 54 }; 55 56 LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) 57 context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); 58 59 // Clone inflater so we load resources from correct context and 60 // we don't add a filter to the static version returned by getSystemService. 61 inflater = inflater.cloneInContext(inflationContext); 62 inflater.setFilter(this); 63 result = inflater.inflate(rvToApply.getLayoutId(), parent, false); 64 //前面的就是載入資源而已 真正的呼叫 還是在perform函式裡 65 rvToApply.performApply(result, parent, handler); 66 67 return result; 68 } 69 70 //每次remoteviews的apply方法 實際上就是遍歷裡面的action 然後呼叫每個action的 applay方法 71 private void performApply(View v, ViewGroup parent, OnClickHandler handler) { 72 if (mActions != null) { 73 handler = handler == null ? DEFAULT_ON_CLICK_HANDLER : handler; 74 final int count = mActions.size(); 75 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 76 Action a = mActions.get(i); 77 a.apply(v, parent, handler); 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 82 //繼續跟 我們會發現action是一個抽象類 他的apply方法要交給他的子類自己去實現 83 private abstract static class Action implements Parcelable { 84 public abstract void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, 85 OnClickHandler handler) throws ActionException; 86 //我們就看看ReflectionAction 這個子類的實現吧 87 //很明顯的 最終的反射呼叫 都是由子類自己來實現的,action的子類很多 有興趣可以自己查 88 public void apply(View root, ViewGroup rootParent, OnClickHandler handler) { 89 final View view = root.findViewById(viewId); 90 if (view == null) return; 91 92 Class<?> param = getParameterType(); 93 if (param == null) { 94 throw new ActionException("bad type: " + this.type); 95 } 96 97 try { 98 getMethod(view, this.methodName, param).invoke(view, wrapArg(this.value)); 99 } catch (ActionException e) { 100 throw e; 101 } catch (Exception ex) { 102 throw new ActionException(ex); 103 } 104 }
基本流程就是這樣,另外注意apply和reapply的區別,後者只更新介面 而前者還要載入佈局。
11.除了 通知和widget 我們還能怎樣使用remoteviews?
答:remoteview 既然是被設計用來 跨程式 更新ui的。所有跨程式更新ui的 場景都可以使用他來做,這裡給出2個範例。
第一個範例:同一個apk下,2個程式 ,其中一個activity另外一個activity的ui。
首先我們看主activity,就是用廣播接收一個remoteviews 然後顯示出來而已

1 package com.example.administrator.remoteviewsameproject; 2 3 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 4 import android.content.Context; 5 import android.content.Intent; 6 import android.content.IntentFilter; 7 import android.os.Bundle; 8 import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton; 9 import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar; 10 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 11 import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar; 12 import android.view.View; 13 import android.view.Menu; 14 import android.view.MenuItem; 15 import android.widget.Button; 16 import android.widget.LinearLayout; 17 import android.widget.RemoteViews; 18 19 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 20 21 private Button bt; 22 23 private BroadcastReceiver mBroadcastReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { 24 25 26 @Override 27 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 28 RemoteViews remoteViews = intent.getParcelableExtra("remoteViewsFlag"); 29 if (remoteViews != null) { 30 View view = remoteViews.apply(MainActivity.this, remoteViewsLayout); 31 remoteViewsLayout.addView(view); 32 } 33 } 34 }; 35 36 private LinearLayout remoteViewsLayout; 37 38 @Override 39 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 40 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 41 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 42 registerReceiver(mBroadcastReceiver,new IntentFilter("updateRemoteview")); 43 remoteViewsLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll); 44 bt = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt); 45 bt.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 46 47 @Override 48 public void onClick(View v) { 49 Intent intent = new Intent(); 50 intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, OtherActivity.class); 51 startActivity(intent); 52 } 53 }); 54 55 56 Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar); 57 setSupportActionBar(toolbar); 58 59 FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab); 60 fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 61 @Override 62 public void onClick(View view) { 63 Snackbar.make(view, "Replace with your own action", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG) 64 .setAction("Action", null).show(); 65 } 66 }); 67 } 68 69 @Override 70 public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { 71 // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. 72 getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); 73 return true; 74 } 75 76 @Override 77 public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { 78 // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will 79 // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long 80 // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. 81 int id = item.getItemId(); 82 83 //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement 84 if (id == R.id.action_settings) { 85 return true; 86 } 87 88 return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); 89 } 90 }
然後看執行在另外一個程式裡的activity 這個activity負責傳送remoteviews,注意你們自己寫的時候 要在manifest裡 更改android:process的值

1 package com.example.administrator.remoteviewsameproject; 2 3 import android.app.PendingIntent; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.Bundle; 6 import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton; 7 import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar; 8 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 9 import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar; 10 import android.view.View; 11 import android.widget.RemoteViews; 12 import android.widget.TextView; 13 14 public class OtherActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 15 16 private TextView tv; 17 18 19 @Override 20 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 21 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 22 setContentView(R.layout.activity_other); 23 tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); 24 tv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 25 26 @Override 27 public void onClick(View v) { 28 RemoteViews remoteViews=new RemoteViews(getPackageName(),R.layout.content_other); 29 remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.tv,"雖然是otherActivity的佈局 但是我顯示在mainActivity了"); 30 PendingIntent pendingIntent=PendingIntent.getActivity(OtherActivity.this,0,new Intent(OtherActivity.this,MainActivity.class),PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT); 31 remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.tv,pendingIntent); 32 Intent intent=new Intent("updateRemoteview"); 33 intent.putExtra("remoteViewsFlag",remoteViews); 34 sendBroadcast(intent); 35 36 } 37 }); 38 39 40 41 42 Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar); 43 setSupportActionBar(toolbar); 44 45 FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab); 46 fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 47 @Override 48 public void onClick(View view) { 49 Snackbar.make(view, "Replace with your own action", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG) 50 .setAction("Action", null).show(); 51 } 52 }); 53 } 54 55 }
然後看一下執行效果:
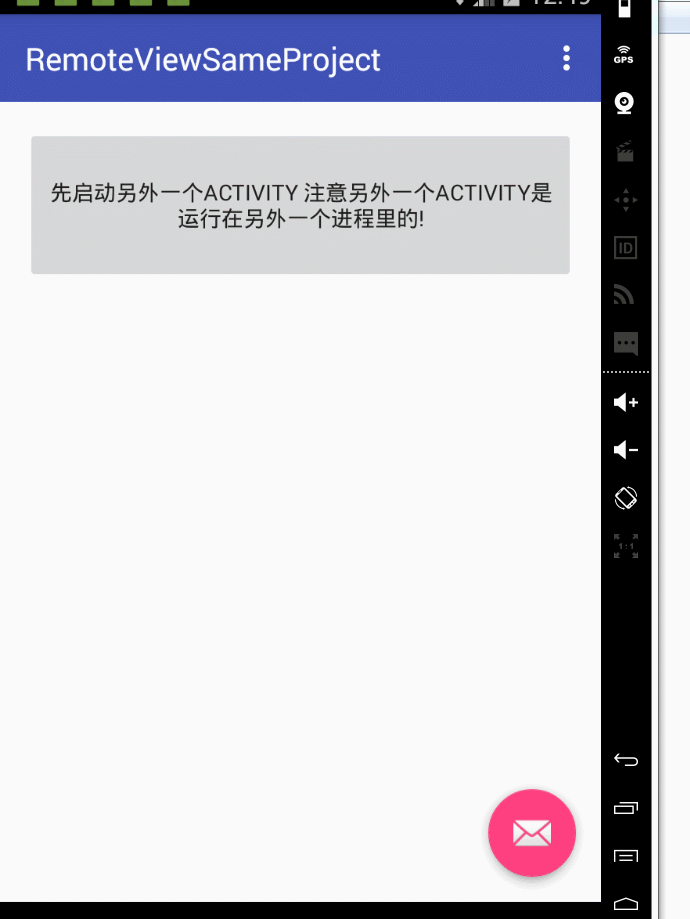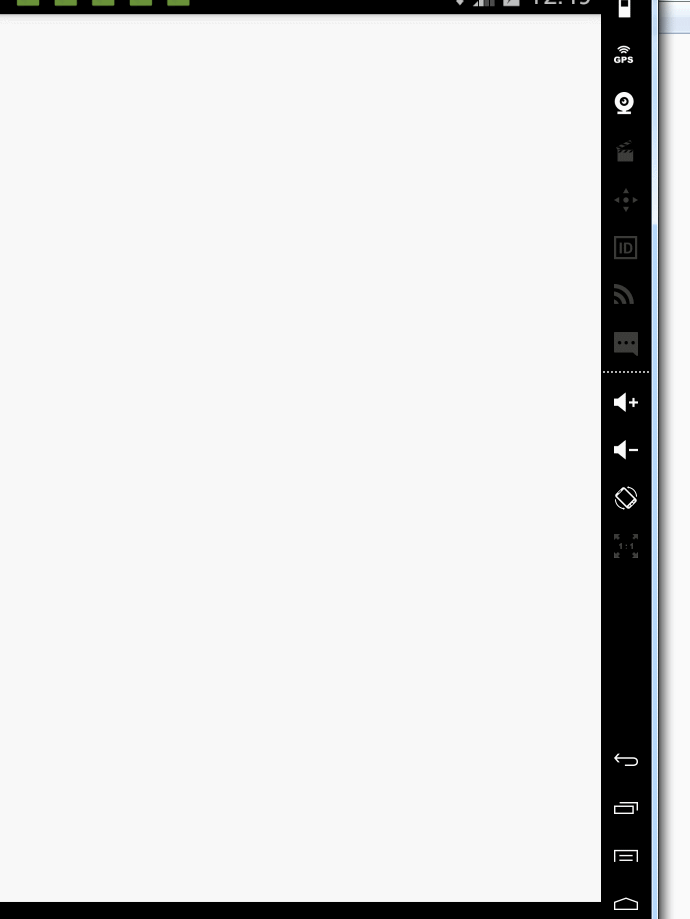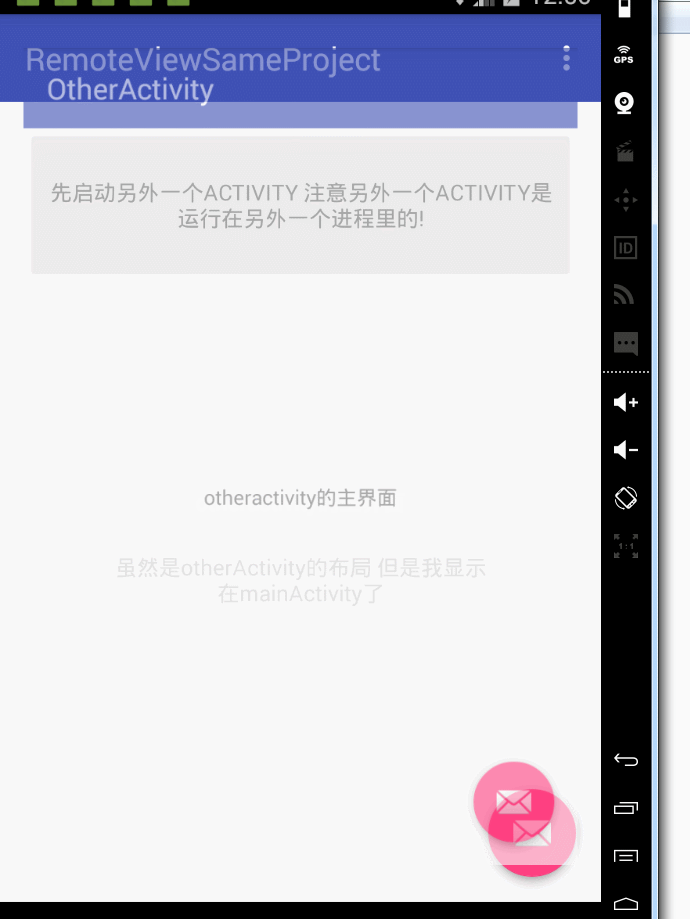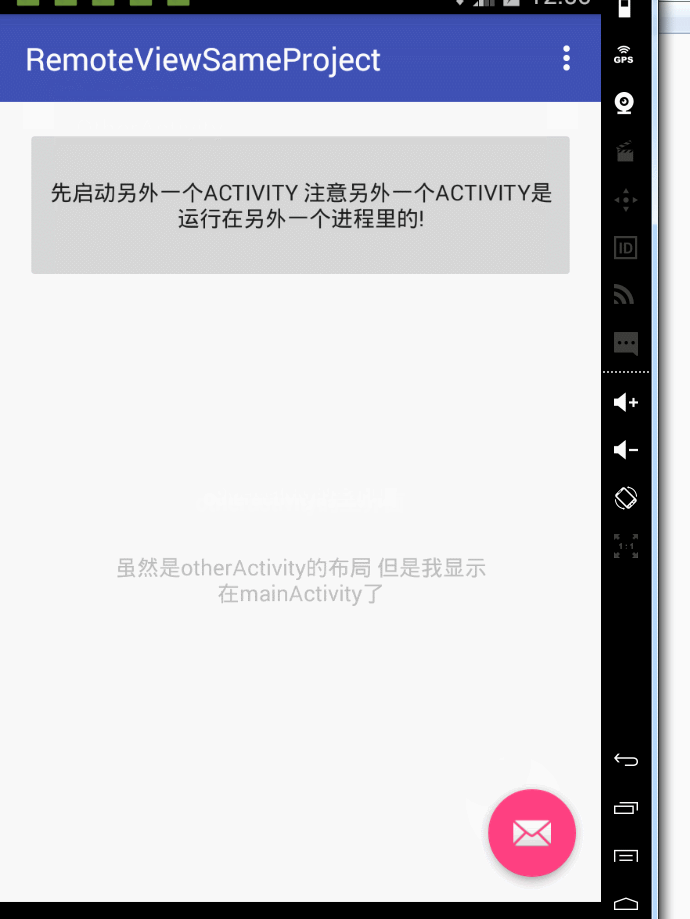
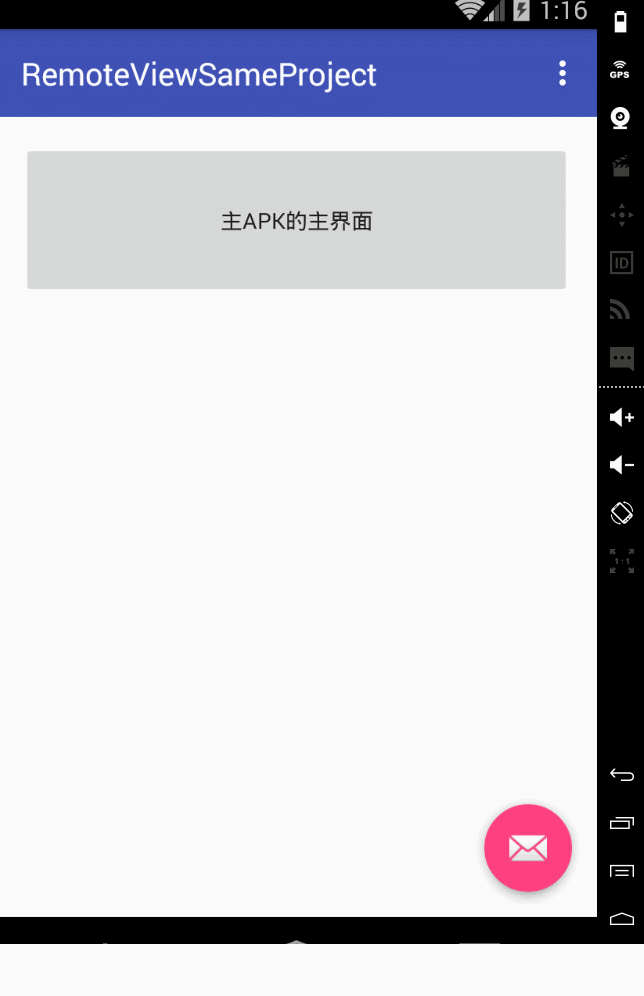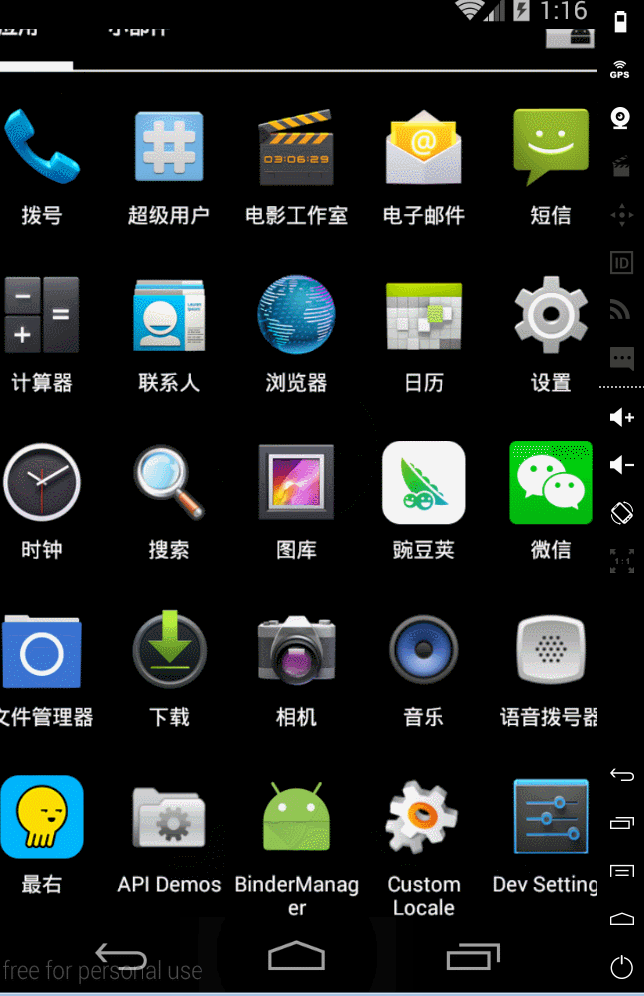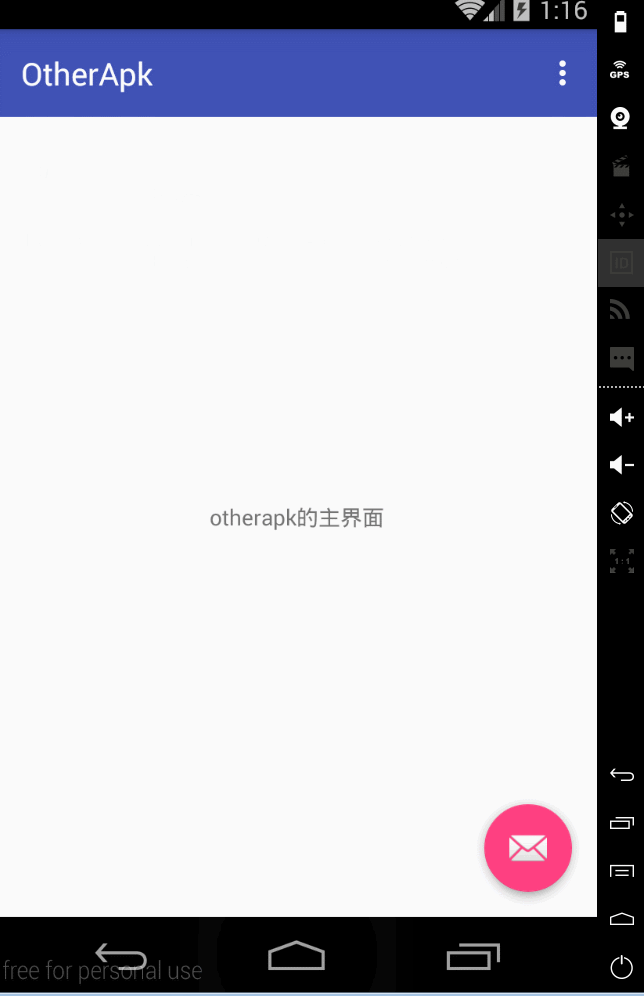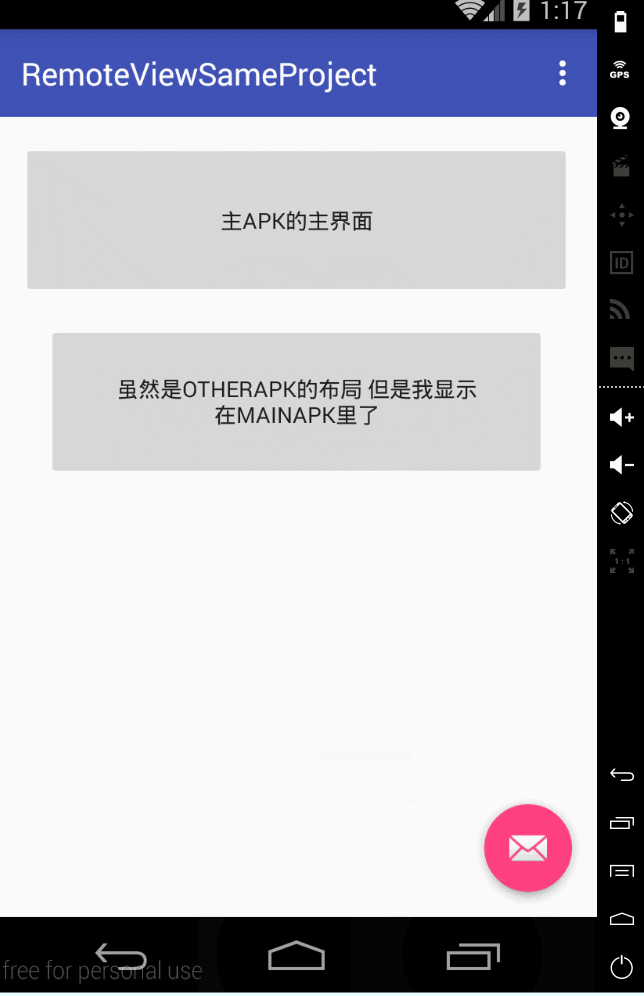
然後考慮第二種場景,就是不同apk 不同程式之間用remoteview 更新ui的例子。
因為不同apk的話,資源id是不同的,所以remoteview更新的時候 方法要改變一下。
你看我們上面的例子,取view 什麼的 都是直接通過id 因為是一個apk麼。
但是你想一下 2個apk的時候,你的id 和我的id 怎麼可能一樣?所以這種情況
我們2個apk 就要事先約定好remoteview裡面的 資源名稱。
然後我們在 根據名稱 查詢對應的佈局檔案 再進行載入。
針對這種情況 實際上我們只要修改主activity的程式碼即可

1 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 2 RemoteViews remoteViews = intent.getParcelableExtra("remoteViewsFlag"); 3 if (remoteViews != null) { 4 int layoutId = getResources().getIdentifier("content_main", "layout", getPackageName()); 5 ViewGroup view =(ViewGroup) getLayoutInflater().inflate(layoutId, remoteViewsLayout, false); 6 remoteViews.reapply(MainActivity.this, view); 7 remoteViewsLayout.addView(view); 8 9 } 10 }
然後我們就可以看到 另外一個apk的 remoteview 顯示在我們的主apk的主頁面裡了