Spring學習筆記五: AOP入門
一、AOP術語
- 切面(aspect):要實現的交叉功能,是系統模組化的一個切面或領域。如日誌記錄。
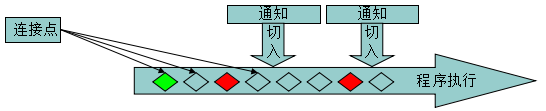
- 連線點:應用程式執行過程中插入切面的地點,可以是方法呼叫,異常丟擲,或者要修改的欄位。
- 通知:切面的實際實現,他通知系統新的行為。如在日誌通知包含了實
現日誌功能的程式碼,如向日志檔案寫日誌。通知在連線點插入到應用系統中。 - 切入點:定義了通知應該應用在哪些連線點,通知可以應用到AOP框架支援的任何連線點。
- 引入:為類新增新方法和屬性。
目標物件:被通知的物件。既可以是你編寫的類也可以是第三方類。
代理:將通知應用到目標物件後建立的物件,應用系統的其他部分不用為了支援代理物件而改變。
- 織入:將切面應用到目標物件從而建立一個新代理物件的過程。織入發生在目標物件生命週期的多個點上:
編譯期:切面在目標物件編譯時織入.這需要一個特殊的編譯器.
類裝載期:切面在目標物件被載入JVM時織入.這需要一個特殊的類載入器.
執行期:切面在應用系統執行時織入。
二、Spring AOP實現
在spring中所有的通知都是以java類的形式編寫的。切入點定義在配置檔案中編寫,所以切面程式碼和配置檔案對我們來說都很熟悉。
對於其他框架(Aspectj),需要特定的語法編寫,如果使用的話,還需學習新的語言。
spring的執行時通知物件
spring在執行期建立代理,不需要特殊的編譯器.
spring有兩種代理方式:
若目標物件實現了若干介面,spring使用JDKjava.lang.reflect.Proxy類代理。該類讓spring動態產生一個新類,它實現了所需的介面,織入了通知,並且代理對目標物件的所有請求。
若目標物件沒有實現任何介面,spring使用CGLIB庫生成目標物件的子類。使用該方式時需要注意:
2.1對介面建立代理優於對類建立代理,因為會產生更加鬆耦合的系統。
對類代理是讓遺留系統或無法實現介面的第三方類庫同樣可以得到通知,這種方式應該是備用方案。
2.2.標記為final的方法不能夠被通知。spring是為目標類產生子類。任何需要被通知的方法都被複寫,將通知織入。final方法是不允許重寫的。
spring只支援方法連線點:不提供屬性接入點,spring的觀點是屬性攔截破壞了封裝。物件導向的概念是物件自己處理工作,其他物件只能通過方法呼叫的得到的結果。
三、建立通知
| 通知型別 | 介面 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Around | MethodInterceptor | 攔截對目標方法呼叫 |
| Before | MethodBeforeAdvice | 在目標方法呼叫前呼叫 |
| After | AfterReturningAdvice | 在目標方法呼叫後呼叫 |
| Throws | ThrowsAdvice | 當目標方法丟擲異常時呼叫 |
1、前置通知
public interface MethodBeforeAdvice
{
void before(Method m,Object[] os ,Object target)
{
}
}該介面提供了獲得目標方法、引數和目標物件的機會。不能夠改變執行時引數,即不能替換引數物件和目標物件。
注意:在方法結束後不返回任何值東西。原因是該介面返回後,目標方法將會被呼叫,應該返回目標物件的返回值。該介面唯一能阻止目標方法被呼叫的途徑是丟擲異常或(System.exit())。
實現程式碼如下:
package jiankunking.aop;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice
{
/**
* method: 被呼叫方法名字
* args: 給method傳遞的引數
* target: 目標物件
*/
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target)
throws Throwable
{
System.out.println("*****************************************"+"");
System.out.println("MethodBeforeAdvice在目標方法呼叫前呼叫..." + method.getName());
}
}
ProxyFactoryBean是一個在BeanFactory中顯式建立代理物件的中心類,可以給它一個要實現的介面、一個要代理的目標物件、一個要織入的通知,並且他將建立一個嶄新的代理物件。
2、後置通知
同前置通知類似:
public interface AfterReturningAdvice{
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue,Method
m,Object[] os,Object target);
}實現程式碼如下:
public class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice
{
/**
* Callback after a given method successfully returned.
*
* @param returnValue the value returned by the method, if any
* @param method method being invoked
* @param args arguments to the method
* @param target target of the method invocation. May be {@code null}.
* @throws Throwable if this object wishes to abort the call.
* Any exception thrown will be returned to the caller if it's
* allowed by the method signature. Otherwise the exception
* will be wrapped as a runtime exception.
*/
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable
{
System.out.println("AfterReturningAdvice..." + method.getName());
}
}3、環繞通知
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor{
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation);
}該介面同前兩種通知有兩個重要區別:
- 該通知能夠控制目標方法是否真的被呼叫。通過invocation.proceed()方法來呼叫。
- 該通知可以控制返回的物件。可以返回一個與proceed()方法返回物件完全不同的物件。但要謹慎使用。
實現程式碼如下:
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor
{
/**
* Implement this method to perform extra treatments before and
* after the invocation. Polite implementations would certainly
* like to invoke {@link Joinpoint#proceed()}.
*
* @param invocation the method invocation joinpoint
* @return the result of the call to {@link Joinpoint#proceed();
* might be intercepted by the interceptor
* @throws Throwable if the interceptors or the target object
* throws an exception
*/
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable
{
System.out.println("MethodInterceptor...呼叫方法前執行" + invocation.getClass());
Object obj = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("MethodInterceptor...呼叫方法後執行" + invocation.getClass());
return obj;
}
}4、異常通知
public interface ThrowsAdvice{
}該介面為標識性介面,沒有任何方法,但實現該介面的類必須要有如下形
式的方法:
public void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable)
{
}
public void afterThrowing(Method m,Object[] os,Object
target,Exception throwable)
{
}第一個方法只接受一個引數:需要丟擲的異常。
第二個方法接受異常、被呼叫的方法、引數以及目標物件。
實現程式碼如下:
public class myThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice
{
/**
* 對應在 target 執行異常時增強處理
* @param m
* @param os
* @param target
* @param throwable
*/
public void afterThrowing(Method m, Object[] os, Object target, Exception throwable)
{
System.out.println("ThrowsAdvice出大事了..." + throwable.getMessage());
}
}
5、引入通知(待續)
以前定義的通知型別是在目標物件的方法被呼叫的周圍織入。引入通知給目標物件新增新的方法和屬性。
四、定義切入點
如果不能表達在應用系統的什麼地方應用通知的話,通知將毫無用處,這就是切入點的用處。切入點決定了一個特定的類的特定方法是否滿足一定的規則。若符合,通知就應用到該方法上。
以上4種通知的配置檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"
>
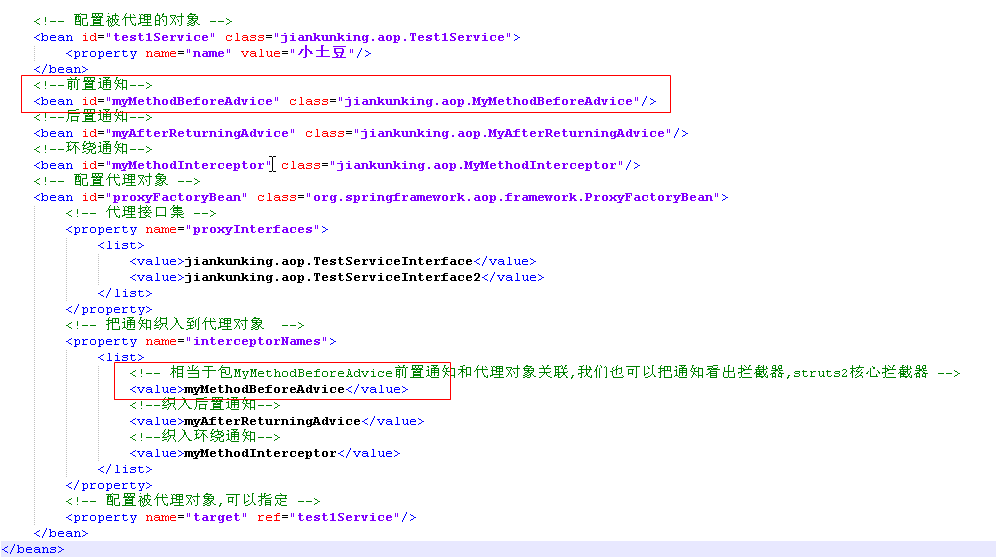
<!-- 配置被代理的物件 -->
<bean id="test1Service" class="jiankunking.aop.Test1Service">
<property name="name" value="小土豆"/>
</bean>
<!--前置通知-->
<bean id="myMethodBeforeAdvice" class="jiankunking.aop.MyMethodBeforeAdvice"/>
<!--後置通知-->
<bean id="myAfterReturningAdvice" class="jiankunking.aop.MyAfterReturningAdvice"/>
<!--環繞通知-->
<bean id="myMethodInterceptor" class="jiankunking.aop.MyMethodInterceptor"/>
<!-- 配置代理物件 -->
<bean id="proxyFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 代理介面集 -->
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>jiankunking.aop.TestServiceInterface</value>
<value>jiankunking.aop.TestServiceInterface2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 把通知織入到代理物件 -->
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<!-- 相當於包MyMethodBeforeAdvice前置通知和代理物件關聯,我們也可以把通知看出攔截器,struts2核心攔截器 -->
<value>myMethodBeforeAdvice</value>
<!--織入後置通知-->
<value>myAfterReturningAdvice</value>
<!--織入環繞通知-->
<value>myMethodInterceptor</value>
<!--織入異常通知-->
<value>myThrowsAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 配置被代理物件,可以指定 -->
<property name="target" ref="test1Service"/>
</bean>
</beans>以上四種通知的具體案例參考demo:Spring Aop 演示demo
是不是很想看一下具體攔截的效果,快點來下載demo吧
1. 正規表示式切入點(RegexpMethodPointcut):
2. NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor (根據方法名匹配織入)
配置檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"
>
<!-- 配置被代理的物件 -->
<bean id="test1Service" class="jiankunking.aop.Test1Service">
<property name="name" value="小土豆"/>
</bean>
<!--前置通知-->
<bean id="myMethodBeforeAdvice" class="jiankunking.aop.MyMethodBeforeAdvice"/>
<!--定義前置通知的切入點-->
<bean id="nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myMethodBeforeAdvice"/>
<property name="mappedName" value="sayHello" />
<!--使用下面的mappedNames不知道為什麼無法起到攔截的作用-->
<!--<property name="mappedNames">-->
<!--<list>-->
<!--<value>-->
<!--sayHello-->
<!--</value>-->
<!--</list>-->
<!--</property>-->
</bean>
<!-- 配置代理物件 -->
<bean id="proxyFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 代理介面集 -->
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>jiankunking.aop.TestServiceInterface</value>
<value>jiankunking.aop.TestServiceInterface2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 把通知織入到代理物件 -->
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<!--使用自定義切入點來控制前置通知-->
<value>nameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 配置被代理物件,可以指定 -->
<property name="target" ref="test1Service"/>
</bean>
</beans>具體程式碼參考(AOP根據方法名匹配織入演示demo)):
http://download.csdn.net/detail/xunzaosiyecao/9584181
作者:jiankunking 出處:http://blog.csdn.net/jiankunking相關文章
- Spring AOP學習筆記01:AOP概述Spring筆記
- Spring AOP學習筆記02:如何開啟AOPSpring筆記
- Spring AOP學習筆記05:AOP失效的罪因Spring筆記
- AOP學習筆記筆記
- Spring學習筆記之Spring MVC 入門教程Spring筆記MVC
- TS入門學習筆記筆記
- 【PostgreSQL】入門學習筆記SQL筆記
- git入門學習筆記Git筆記
- Docker入門學習筆記Docker筆記
- Unity學習筆記--入門Unity筆記
- ActionScript 學習筆記(入門)筆記
- Spring學習筆記2(IOC註解方式&AOP)Spring筆記
- JavaScript入門學習學習筆記(上)JavaScript筆記
- 學習筆記|AS入門(五) 高階控制元件篇(下)筆記控制元件
- 學習筆記|AS入門(五) 高階控制元件篇(中)筆記控制元件
- 學習筆記|AS入門(五) 高階控制元件篇(上)筆記控制元件
- Go 入門指南學習筆記Go筆記
- React入門指南(學習筆記)React筆記
- pandas 學習筆記 (入門篇)筆記
- HTML入門學習筆記(二)HTML筆記
- MySQL學習筆記---入門使用MySql筆記
- JavaScript入門-學習筆記(一)JavaScript筆記
- Dubbo學習筆記(一) 入門筆記
- golang入門學習筆記(一)Golang筆記
- Kotlin 入門學習筆記Kotlin筆記
- LDA入門級學習筆記LDA筆記
- springcloud學習筆記(五)Spring Cloud ActuatorSpringGCCloud筆記
- Spring 學習筆記(五)執行時注入Spring筆記
- Spring框架學習筆記(一):官方文件介紹,IoC與AOP概念學習Spring框架筆記
- Spring Boot 入門(五):整合 AOP 進行日誌管理Spring Boot
- Elasticsearch入門學習重點筆記Elasticsearch筆記
- 【MongoDB學習筆記】MongoDB 快速入門MongoDB筆記
- java學習筆記1(入門級)Java筆記
- JavaScript學習筆記1—快速入門JavaScript筆記
- 安卓學習筆記20:Fragment入門安卓筆記Fragment
- 爬蟲入門學習筆記3爬蟲筆記
- node 學習筆記 基礎入門筆記
- webpack 學習筆記:入門介紹Web筆記