本例我們實現一次真正的網路互動,將資料POST到API,然後接收伺服器的返回值進行處理,同時引入自定義型別和傳說中阿里的FastJson。
實現思路如:
1. 在API端接收客戶POST的資料還原成物件,給每個屬性加個字尾後輸出;
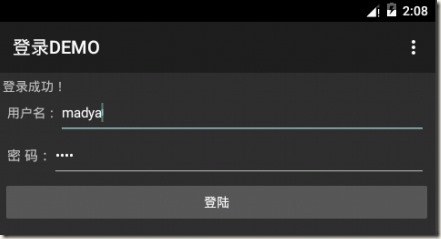
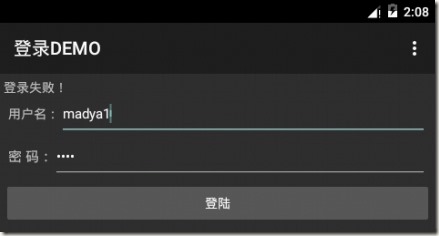
2. 在客戶端輸入使用者名稱和密碼,用來和伺服器端返回的進行對比;
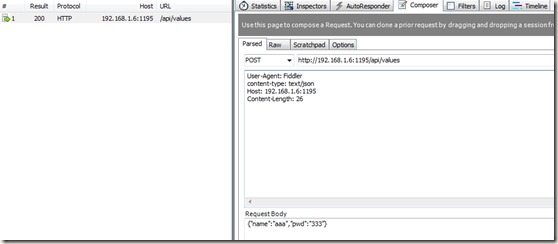
我們POST給伺服器的是name=mady&pwd=123,伺服器分別加了字尾為name=madya
&pwd=1231所以我們客戶端需要輸入madya和1231才能驗證成功。
具體操作展示如下:
一、準備API:
目前寫API使用ASP.NET WEB API2再合適不過了。在VS2013中建立一個API專案,先配置他支援JSON:
開啟專案中的WebApiConfig檔案,在Register方法中加入一個配置項:
config.Formatters.JsonFormatter.SupportedMediaTypes.Add(new MediaTypeHeaderValue("text/html"));
建立實體類如:
public class UserInfo { public string name { get; set; } public string pwd { get; set; } }
開啟ValuesController修改程式碼如下:
// POST api/values public UserInfo Post([FromBody]UserInfo value) { return new UserInfo { name = value.name + "a", pwd = value.pwd+"1" }; }
就可以開啟Fidder除錯了,直到成功為止:
二、引入阿里的FastJson包
直接右鍵貼上進去即可:
這個包真心好使:
String json=JSON.toJSONString(user); //序列化 UserInfo userInfo=JSON.parseObject(json,UserInfo.class); //反序列化
就這2句話全部搞定。
我們繼續,先新建一個Java的實體類:
import java.io.Serializable; public class UserInfo implements Serializable{ private String name; private String pwd; public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
然後修改網路訪問類,上節那個太簡陋了(見附)。
然後修改非同步部分程式碼:
protected String doInBackground(String... params) { // String citiesString ="{\"name\":\"mady\",\"pwd\":123}"; UserInfo user=new UserInfo(); user.setName("mady"); user.setPwd("123"); String str_json=JSON.toJSONString(user); return HttpUtils.sendPostMessage(params[0],str_json); }
和完成程式碼:
protected void onPostExecute(String result) { TextView lblInfo=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.form_title); EditText txt_login_name=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.txt_login_name); EditText txt_login_pass=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.txt_login_pwd); String loginName=txt_login_name.getText().toString().trim(); String loginPass=txt_login_pass.getText().toString().trim(); UserInfo userInfo=JSON.parseObject(result,UserInfo.class); if(loginPass.equals(userInfo.getPwd())&&loginName.equals(userInfo.getName())) { lblInfo.setText("登入成功!"); } else { lblInfo.setText("登入失敗!"); } }
到此完工,沒有修改的就是沒有變化的。
附上新網路訪問類:
public class HttpUtils { /** * @param path 請求的伺服器URL地址 * @param encode 編碼格式 * @return 將伺服器端返回的資料轉換成String */ public static String sendPostMessage(String path,String jsonStr) { String result = ""; HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); try { HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(path); httpPost.addHeader("content-type","text/json"); httpPost.setEntity(new StringEntity(jsonStr)); HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost); if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) { // Log.e("Json+++++2:", jsonStr); log info for debug HttpEntity httpEntity = httpResponse.getEntity(); if(httpEntity != null) { result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity, "UTF-8"); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { httpClient.getConnectionManager().shutdown(); } return result; } }