嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十)------通俗易懂式分析瞭解i2c框架
你好!這裡是風箏的部落格,
歡迎和我一起交流。
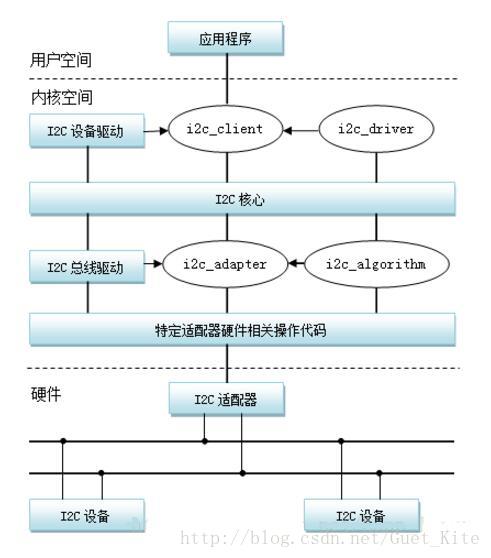
瞭解i2c框架時,在別的部落格看到一張圖,非常好,引用如下:
其中,i2c_client是具體的裝置例項,是通過i2c匯流排連線到i2c_adapter的。無論是什麼i2c裝置,都可以通過i2c_adapter來訪問i2c匯流排,i2c_adapter遮蔽了底層i2c匯流排控制時序,向上層提供一個統一的介面。
以kernel4.8.17為例:
在mach-smdk2440.c檔案,
static struct platform_device *smdk2440_devices[] __initdata = {
&s3c_device_ohci,
&s3c_device_lcd,
&s3c_device_wdt,
&s3c_device_i2c0,
&s3c_device_iis,
&smdk2440_device_eth,
};
static void __init smdk2440_map_io(void)
{
s3c24xx_init_io(smdk2440_iodesc, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_iodesc));
s3c24xx_init_uarts(smdk2440_uartcfgs, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_uartcfgs));
samsung_set_timer_source(SAMSUNG_PWM3, SAMSUNG_PWM4);
}
static void __init smdk2440_machine_init(void)
{
s3c24xx_fb_set_platdata(&smdk2440_fb_info);
s3c_i2c0_set_platdata(NULL);
platform_add_devices(smdk2440_devices, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_devices));
smdk_machine_init();
}在smdk2440_map_io函式裡,呼叫s3c24xx_init_io函式:
void __init s3c24xx_init_io(struct map_desc *mach_desc, int size)
{
arm_pm_idle = s3c24xx_default_idle;
/* initialise the io descriptors we need for initialisation */
iotable_init(mach_desc, size);
iotable_init(s3c_iodesc, ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_iodesc));
if (cpu_architecture() >= CPU_ARCH_ARMv5) {
samsung_cpu_id = s3c24xx_read_idcode_v5();
} else {
samsung_cpu_id = s3c24xx_read_idcode_v4();
}
s3c_init_cpu(samsung_cpu_id, cpu_ids, ARRAY_SIZE(cpu_ids));
samsung_pwm_set_platdata(&s3c24xx_pwm_variant);
}其中有s3c_init_cpu(samsung_cpu_id, cpu_ids, ARRAY_SIZE(cpu_ids)),
引數cpu_ids是:
static struct cpu_table cpu_ids[] __initdata = {
/*太多了,省略......*/
{
.idcode = 0x32440000,
.idmask = 0xffffffff,
.map_io = s3c2440_map_io,
.init_uarts = s3c244x_init_uarts,
.init = s3c2440_init,
.name = name_s3c2440
},
/*太多了,省略......*/繼續跟蹤s3c_init_cpu函式:
void __init s3c_init_cpu(unsigned long idcode,
struct cpu_table *cputab, unsigned int cputab_size)
{
cpu = s3c_lookup_cpu(idcode, cputab, cputab_size);
if (cpu == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "Unknown CPU type 0x%08lx\n", idcode);
panic("Unknown S3C24XX CPU");
}
printk("CPU %s (id 0x%08lx)\n", cpu->name, idcode);
if (cpu->init == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "CPU %s support not enabled\n", cpu->name);
panic("Unsupported Samsung CPU");
}
if (cpu->map_io)
cpu->map_io();
}就是最後一行,會呼叫map_io函式,即前面的s3c2440_map_io函式:
void __init s3c2440_map_io(void)
{
s3c244x_map_io();
s3c24xx_gpiocfg_default.set_pull = s3c24xx_gpio_setpull_1up;
s3c24xx_gpiocfg_default.get_pull = s3c24xx_gpio_getpull_1up;
}進入s3c244x_map_io函式:
void __init s3c244x_map_io(void)
{
/* register our io-tables */
iotable_init(s3c244x_iodesc, ARRAY_SIZE(s3c244x_iodesc));
/* rename any peripherals used differing from the s3c2410 */
s3c_device_sdi.name = "s3c2440-sdi";
s3c_device_i2c0.name = "s3c2440-i2c";
s3c_nand_setname("s3c2440-nand");
s3c_device_ts.name = "s3c2440-ts";
s3c_device_usbgadget.name = "s3c2440-usbgadget";
s3c2410_device_dclk.name = "s3c2440-dclk";
}這裡,即是把s3c_device_i2c0結構體的名字改為了”s3c2440-i2c” !!!
好了,回到文章最開頭的mach-smdk2440.c檔案,看下smdk2440_machine_init函式,
裡面會通過s3c_i2c0_set_platdata函式,設定default_i2c_data結構體的bus_num為0,以及設定i2c的IO口:npd->cfg_gpio = s3c_i2c0_cfg_gpio;
接著就會呼叫platform_add_devices(smdk2440_devices, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_devices));在platform平臺下進行裝置註冊,裝置名字為”s3c2440-i2c”
有了platform-device,自然有driver!
在i2c-s3c2410.c檔案:
static const struct platform_device_id s3c24xx_driver_ids[] = {
{
.name = "s3c2410-i2c",
.driver_data = 0,
}, {
.name = "s3c2440-i2c",
.driver_data = QUIRK_S3C2440,
}, {
.name = "s3c2440-hdmiphy-i2c",
.driver_data = QUIRK_S3C2440 | QUIRK_HDMIPHY | QUIRK_NO_GPIO,
}, { },
};
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = {
.probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe,
.remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove,
.id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids,
.driver = {
.name = "s3c-i2c",
.pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(s3c24xx_i2c_match),
},
};
static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);
}可以看到,s3c24xx_driver_ids裡是有”s3c2440-i2c”的,所以能和之前的device匹配成功,呼叫probe函式:
static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
/*太長了,部分省略......*/
strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name));
i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;
i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;
i2c->adap.retries = 2;
i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_DEPRECATED;
i2c->tx_setup = 50;
/* setup info block for the i2c core */
i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c;
i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
i2c->pctrl = devm_pinctrl_get_select_default(i2c->dev);
i2c->adap.nr = i2c->pdata->bus_num;
i2c->adap.dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);
}這裡主要注意兩個地方:
一是:i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;
這裡的s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm是:
/* i2c bus registration info */
static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,
};還記得文章開始的那張圖嗎?
i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm 都是操作i2c bus的結構體,前者定義一個i2c模組,後者定義操作模組的方法。(或者理解為:i2c_adapter對應於物理上的一個介面卡,而i2c_algorithm對應一套通訊方法。)
這裡就是i2c_algorithm!!
i2c的底層實現函式,進行封裝好,
.master_xfer 用於i2c匯流排傳輸,傳遞給它的i2c_msg陣列中每個I2C訊息。
.functionality 用於返回algorithm所支援的通訊協議,如I2C_FUNC_I2C、I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR、I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE、I2C_FUNC_SUMBUS_WRITE_BYTE等。
二是:ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);
這就是i2c_adapter了,進去看下函式實現:
int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
if (adap->nr == -1) /* -1 means dynamically assign bus id */
return i2c_add_adapter(adap);
return __i2c_add_numbered_adapter(adap);
}static int __i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
int id;
mutex_lock(&core_lock);
id = idr_alloc(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap, adap->nr, adap->nr + 1, GFP_KERNEL);
mutex_unlock(&core_lock);
if (WARN(id < 0, "couldn't get idr"))
return id == -ENOSPC ? -EBUSY : id;
return i2c_register_adapter(adap);
}即最後呼叫i2c_register_adapter(adap)函式,在i2c_bus匯流排上註冊,名字為:
dev_set_name(&adap->dev, “i2c-%d”, adap->nr);
這裡說下i2c_adapter與i2c_client的關係:i2c_client依附於i2c_adapter,由於一個介面卡上可以連線多個I2C裝置,所以一個i2c_adapter也可以被多個i2c_client依附,i2c_adapter中包含依附於它的i2c_client的連結串列。
.
好咯,i2c框架差不多就是這樣咯,我們以一個kernel裡的例子來看下:
at24.c函式:
static struct i2c_driver at24_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "at24",
.acpi_match_table = ACPI_PTR(at24_acpi_ids),
},
.probe = at24_probe,
.remove = at24_remove,
.id_table = at24_ids,
};
static int __init at24_init(void)
{
if (!io_limit) {
pr_err("at24: io_limit must not be 0!\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
io_limit = rounddown_pow_of_two(io_limit);
return i2c_add_driver(&at24_driver);
}這裡呼叫i2c_add_driver函式在i2c_bus匯流排下注冊,然後看下他的讀寫函式,以讀函式為例:
static ssize_t at24_eeprom_read_i2c(struct at24_data *at24, char *buf,
unsigned int offset, size_t count)
{
unsigned long timeout, read_time;
struct i2c_client *client;
struct i2c_msg msg[2];
int status, i;
u8 msgbuf[2];
memset(msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
client = at24_translate_offset(at24, &offset);
if (count > io_limit)
count = io_limit;
i = 0;
if (at24->chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16)
msgbuf[i++] = offset >> 8;
msgbuf[i++] = offset;
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msg[0].buf = msgbuf;
msg[0].len = i;
msg[1].addr = client->addr;
msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
msg[1].buf = buf;
msg[1].len = count;
loop_until_timeout(timeout, read_time) {
status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 2);
if (status == 2)
status = count;
dev_dbg(&client->dev, "read %zu@%d --> %d (%ld)\n",
count, offset, status, jiffies);
if (status == count)
return count;
}
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}裡面就是會呼叫到i2c_transfer函式了,函式裡面以i2c_msg(即I2C訊息)為單位通訊,i2c_transfer函式裡又會呼叫到__i2c_transfer函式:
int __i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
unsigned long orig_jiffies;
int ret, try;
if (adap->quirks && i2c_check_for_quirks(adap, msgs, num))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
if (static_key_false(&i2c_trace_msg)) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
if (msgs[i].flags & I2C_M_RD)
trace_i2c_read(adap, &msgs[i], i);
else
trace_i2c_write(adap, &msgs[i], i);
}
/* Retry automatically on arbitration loss */
orig_jiffies = jiffies;
for (ret = 0, try = 0; try <= adap->retries; try++) {
ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap, msgs, num);
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
break;
if (time_after(jiffies, orig_jiffies + adap->timeout))
break;
}
if (static_key_false(&i2c_trace_msg)) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ret; i++)
if (msgs[i].flags & I2C_M_RD)
trace_i2c_reply(adap, &msgs[i], i);
trace_i2c_result(adap, i, ret);
}
return ret;
}就是這裡,裡面實現:ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap, msgs, num);
這就是之前說的i2c_algorithm 裡實現的.master_xfer函式裡,實現i2c匯流排傳輸函式。
相關文章
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十二)------通俗易懂式分析瞭解spi框架Linux筆記框架
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十一)------i2c裝置之mpu6050驅動Linux筆記
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十七)------詳解V4L2框架(UVC驅動)Linux筆記框架
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十四)------詳解clock時鐘(CCF)框架及clk_get函式Linux筆記框架函式
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十六)------裝置驅動模型(kobject、kset、ktype)Linux筆記模型Object
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十八)------淺析V4L2框架之ioctlLinux筆記框架
- 嵌入式Linux驅動學習筆記(十六)------裝置驅動模型(kobject、kset、ktype)Linux筆記模型Object
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十三)------spi裝置之RFID-rc522驅動Linux筆記
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(九)------dts裝置樹在2440使用Linux筆記
- 嵌入式Linux驅動筆記(十五)------編譯使用tslib支援LCD觸控式螢幕Linux筆記編譯
- 嵌入式Linux驅動學習筆記(十五)------編譯使用tslib支援LCD觸控式螢幕Linux筆記編譯
- 嵌入式Linux中的LED驅動控制(續)Linux
- 嵌入式Linux中platform平臺裝置模型的框架(實現LED驅動)LinuxPlatform模型框架
- 【原創】Linux PCI驅動框架分析(一)Linux框架
- 【原創】Linux PCI驅動框架分析(二)Linux框架
- Linux驅動之I2C匯流排裝置以及驅動Linux
- 嵌入式Linux中的LED驅動控制(基於misc)Linux
- 嵌入式筆記5.1 定時器詳解筆記定時器
- ArmSoM系列板卡 嵌入式Linux驅動開發實戰指南 之 字元裝置驅動Linux字元
- 向嵌入式Linux移植實時裝置驅動程式(轉)Linux
- 嵌入式Linux中的LED驅動控制(裝置樹方式)Linux
- 框架-裝置與驅動的拆分及實現-I2C框架
- Linux的作業系統I2C驅動架構解說(轉)Linux作業系統架構
- 嵌入式系統基礎知識:瞭解嵌入式系統
- 嵌入式Linux下3G無線上網路卡的驅動Linux
- 嵌入式Linux中的LED驅動控制(裝置樹方式)(續)Linux
- 筆記:瞭解Elasticsearch筆記Elasticsearch
- 痞子衡嵌入式:瑞薩RA系列FSP韌體庫分析之外設驅動
- 一個嵌入式Linux系統的鍵盤驅動實現(轉)Linux
- 嵌入式之Makefile學習筆記筆記
- 嵌入式之uboot原始碼分析-啟動第二階段學習筆記(上篇)boot原始碼筆記
- 手把手教你寫Linux I2C裝置驅動薦Linux
- 嵌入式Linux中的LED驅動控制(使用多個次裝置號)Linux
- Linux驅動開發筆記(一):helloworld驅動原始碼編寫、makefile編寫以及驅動編譯Linux筆記原始碼編譯
- 嵌入式筆記4.1 GPIO 功能複用筆記
- 【原創】Linux虛擬化KVM-Qemu分析(十)之virtio驅動Linux
- 嵌入式系統開發:基於Linux學習筆記整理Linux筆記
- 自己動手設計並實現一個linux嵌入式UI框架LinuxUI框架