task1-1
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 4 void test1() { int a[N] = {1, 9, 8, 4}; int i; // 輸出陣列a佔用的記憶體位元組數 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n", sizeof(a)); // 輸出int型別陣列a中每個元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%p: %d\n", &a[i], a[i]); // 輸出陣列名a對應的值 printf("a = %p\n", a); } void test2() { char b[N] = {'1', '9', '8', '4'}; int i; // 輸出陣列b佔用的記憶體位元組數 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n", sizeof(b)); // 輸出char型別陣列b中每個元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%p: %c\n", &b[i], b[i]); // 輸出陣列名b對應的值 printf("b = %p\n", b); } int main() { printf("測試1: int型別一維陣列\n"); test1(); printf("\n測試2: char型別一維陣列\n"); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; }
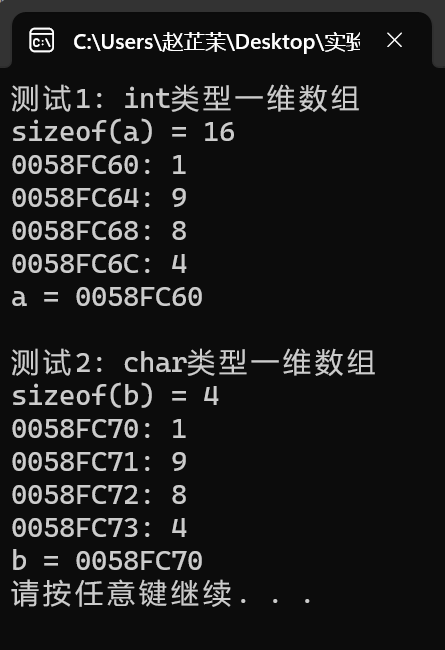
1、是連續存放。佔4個記憶體位元組單元。一樣。
2、是連續存放。佔1個記憶體位元組單元。一樣。
task1-2
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 2 #define M 4 void test1() { int a[N][M] = {{1, 9, 8, 4}, {2, 0, 4, 9}}; int i, j; // 輸出int型別二維陣列a佔用的記憶體位元組數 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n", sizeof(a)); // 輸出int型別二維陣列a中每個元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) printf("%p: %d\n", &a[i][j], a[i][j]); printf("\n"); // 輸出int型別二維陣列名a, 以及,a[0], a[1]的值 printf("a = %p\n", a); printf("a[0] = %p\n", a[0]); printf("a[1] = %p\n", a[1]); printf("\n"); } void test2() { char b[N][M] = {{'1', '9', '8', '4'}, {'2', '0', '4', '9'}}; int i, j; // 輸出char型別二維陣列b佔用的記憶體位元組數 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n", sizeof(b)); // 輸出char型別二維陣列b中每個元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) printf("%p: %c\n", &b[i][j], b[i][j]); printf("\n"); // 輸出char型別二維陣列名b, 以及,b[0], b[1]的值 printf("b = %p\n", b); printf("b[0] = %p\n", b[0]); printf("b[1] = %p\n", b[1]); } int main() { printf("測試1: int型兩維陣列"); test1(); printf("\n測試2: char型兩維陣列"); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; }
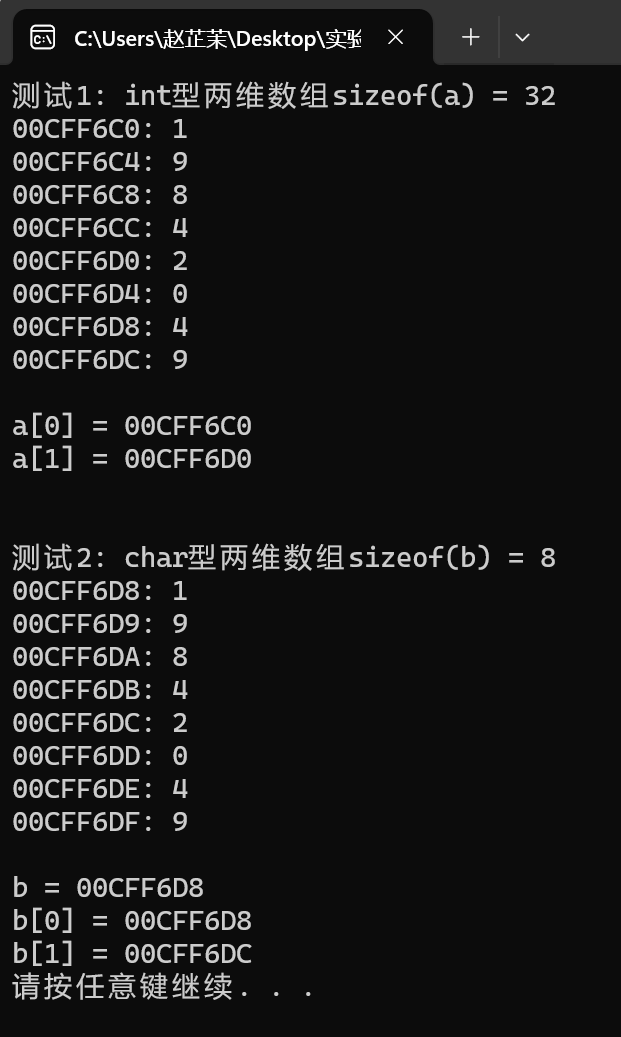
1、是按行連續存放的。佔4個記憶體位元組單元。一樣。
2、是按行連續存放的。佔1個記憶體位元組單元。一樣,
3、相差16。相差4。規律:相鄰兩行元素地址差值等於一行元素佔用的記憶體位元組單元。
task2
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 80 void swap_str(char s1[], char s2[]); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { printf("測試1: 用兩個一維char陣列,實現兩個字串交換\n"); test1(); printf("\n測試2: 用二維char陣列,實現兩個字串交換\n"); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; } void test1() { char views1[N] = "hey, C, I hate u."; char views2[N] = "hey, C, I love u."; printf("交換前: \n"); puts(views1); puts(views2); swap_str(views1, views2); printf("交換後: \n"); puts(views1); puts(views2); } void test2() { char views[2][N] = {"hey, C, I hate u.", "hey, C, I love u."}; printf("交換前: \n"); puts(views[0]); puts(views[1]); swap_str(views[0], views[1]); printf("交換後: \n"); puts(views[0]); puts(views[1]); } void swap_str(char s1[N], char s2[N]) { char tmp[N]; strcpy(tmp, s1); strcpy(s1, s2); strcpy(s2, tmp); }
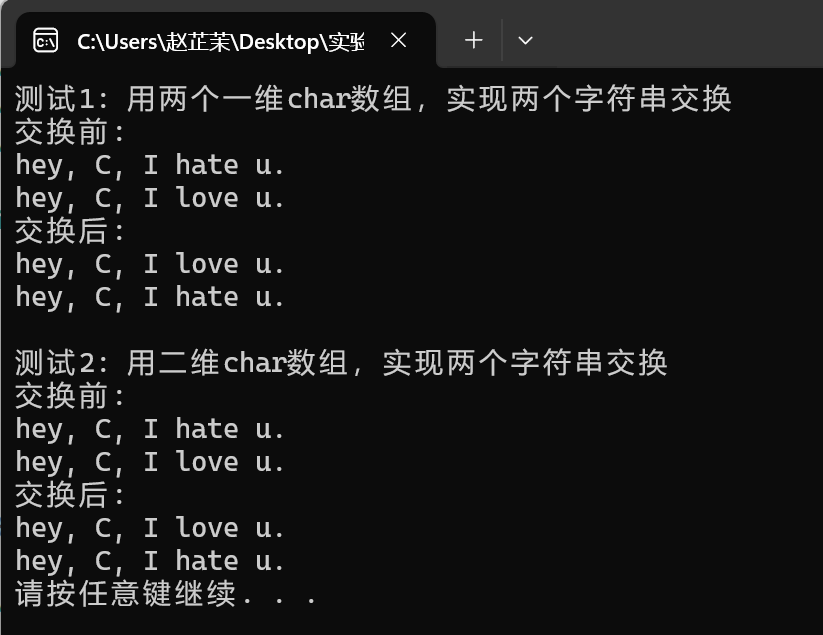
思考:一維陣列的陣列名可以直接訪問元素,無需加【】;二維陣列的陣列名對應某一行的元素。
task3-1
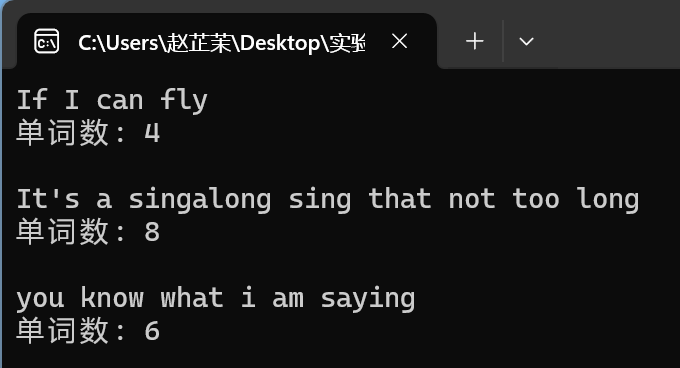
/* 從鍵盤輸入一行英文文字,統計英文單詞總數 為了簡化問題處理,只考慮單詞以空格間隔的情形 對教材例5.22程式碼做了些微改動: 1. 統計單詞個數,編寫成函式模組;增加了多組輸入 2. 去掉了不必要的中間變數 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 80 int count(char x[]); int main() { char words[N+1]; int n; while(gets(words) != NULL) { n = count(words); printf("單詞數: %d\n\n", n); } system("pause"); return 0; } int count(char x[]) { int i; int word_flag = 0; // 用作單詞標誌,一個新單詞開始,值為1;單詞結束,值為0 int cnt = 0; // 統計單詞個數 for(i = 0; x[i] != '\0'; i++) { if(x[i] == ' ') word_flag = 0; else if(word_flag == 0) { word_flag = 1; cnt++; } } return cnt; }
task3-2
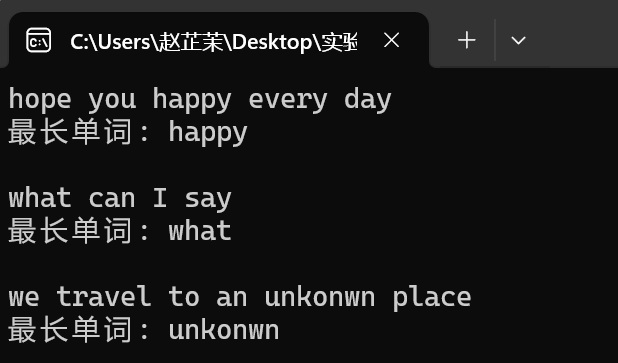
/* 輸入一行英文文字,統計最長單詞,並列印輸出。 為簡化問題,只考慮單詞之間用空格間隔的情形。 相較於教材例5.24,做了以下改動: 1. 增加了多組輸入,因此,一些變數初始化放到了第一層迴圈裡面 2. 微調了程式碼書寫邏輯和順序 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 1000 int main() { char line[N]; int word_len; // 記錄當前單詞長度 int max_len; // 記錄最長單詞長度 int end; // 記錄最長單詞結束位置 int i; while(gets(line) != NULL) { word_len = 0; max_len = 0; end = 0; i = 0; while(1) { // 跳過連續空格 while(line[i] == ' ') { word_len = 0; // 單詞長度置0,為新單詞統計做準備 i++; } // 在一個單詞中,統計當前單詞長度 while(line[i] != '\0' && line[i] != ' ') { word_len++; i++; } // 更新更長單詞長度,並,記錄最長單詞結束位置 if(max_len < word_len) { max_len = word_len; end = i; // end儲存的是單詞結束的下一個座標位置 } // 遍歷到文字結束時,終止迴圈 if(line[i] == '\0') break; } // 輸出最長單詞 printf("最長單詞: "); for(i = end - max_len; i < end; ++i) printf("%c", line[i]); printf("\n\n"); } system("pause"); return 0; }
task4
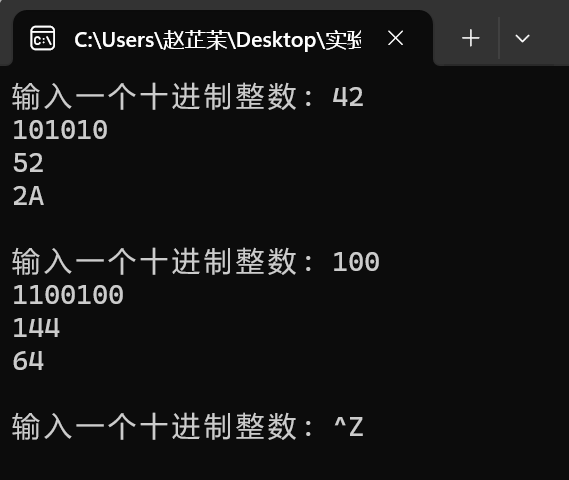
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 100 void dec_to_n(int x, int n); // 函式宣告 int main() { int x; printf("輸入一個十進位制整數: "); while(scanf("%d", &x) != EOF) { dec_to_n(x, 2); // 函式呼叫: 把x轉換成二進位制輸出 dec_to_n(x, 8); // 函式呼叫: 把x轉換成八進位制輸出 dec_to_n(x, 16); // 函式呼叫: 把x轉換成十六進位制輸出 printf("\n輸入一個十進位制整數: "); } system("pause"); return 0; } // 函式定義 // 功能: 把十進位制數x轉換成n進位制,列印輸出 // 補足函式實現 // ××× void dec_to_n(int x, int n){ char ans[N];//儲存結果 char map[17]="0123456789ABCDEF"; int d,r;//d商,r餘數 int cnt,i; cnt=0; while(1) { d=x/n; r=x%n; ans[cnt++]=map[r]; if(d==0) break; x=d; } for(i=cnt-1;i>=0;--i) printf("%c",ans[i]); printf("\n"); }
task5
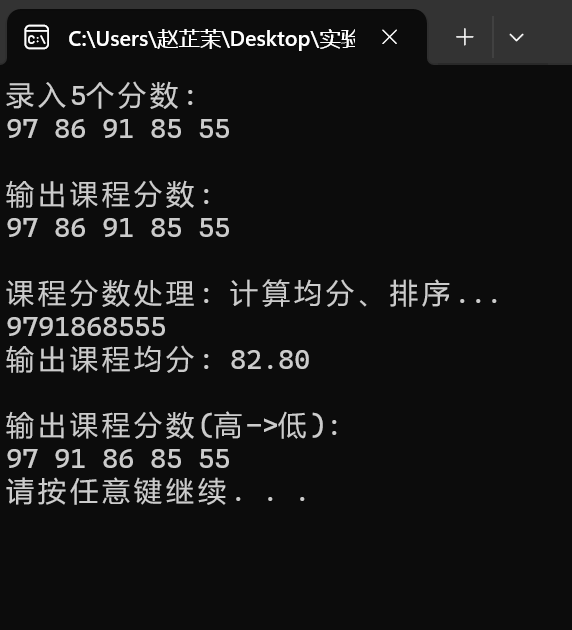
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 5 // 函式宣告 void input(int x[], int n); void output(int x[], int n); double average(int x[], int n); void bubble_sort(int x[], int n); int main() { int scores[N]; double ave; printf("錄入%d個分數:\n", N); input(scores, N); printf("\n輸出課程分數: \n"); output(scores, N); printf("\n課程分數處理: 計算均分、排序...\n"); ave = average(scores, N); bubble_sort(scores, N); printf("\n輸出課程均分: %.2f\n", ave); printf("\n輸出課程分數(高->低):\n"); output(scores, N); system("pause"); return 0; } // 函式定義 // 輸入n個整數儲存到整型陣列x中 void input(int x[], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", &x[i]); } // 輸出整型陣列x中n個元素 void output(int x[], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%d ", x[i]); printf("\n"); } double average(int x[], int n){ int i; int sum=0; double ave; for(i=0;i<n;++i){ sum=sum+x[i]; } ave = (double)1.0*sum/n; return ave; } void bubble_sort(int x[], int n){ int i,j,t; for(j=0;j<N-1;j++) for(i=0;i<N-j-1;i++) if(x[i]<x[i+1]) { t=x[i]; x[i]=x[i+1]; x[i+1]=t; } for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d",x[i]); }
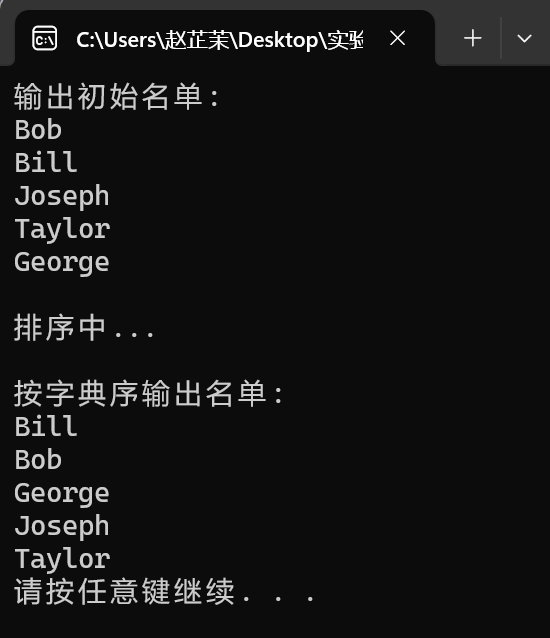
task6
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 5 #define M 20 // 函式宣告 void output(char str[][M], int n); void bubble_sort(char str[][M], int n); int main() { char name[][M] = {"Bob", "Bill", "Joseph", "Taylor", "George"}; int i; printf("輸出初始名單:\n"); output(name, N); printf("\n排序中...\n"); bubble_sort(name, N); // 函式呼叫 printf("\n按字典序輸出名單:\n"); output(name, N); system("pause"); return 0; } // 函式定義 // 功能:按行輸出二維陣列中的字串 void output(char str[][M], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%s\n", str[i]); } // 函式定義 // 功能:使用氣泡排序演算法對二維陣列str中的n個字串按字典序排序 // 補足函式bubble_sort()實現 // ××× void bubble_sort(char str[][M], int n){ int i,j; char t[M]; for(j=0;j<n-1;j++){ for(i=0;i<n-j-1;i++){ if(strcmp(str[i],str[i+1])>0){ strcpy(t,str[i]); strcpy(str[i],str[i+1]); strcpy(str[i+1],t); }}} }
task7
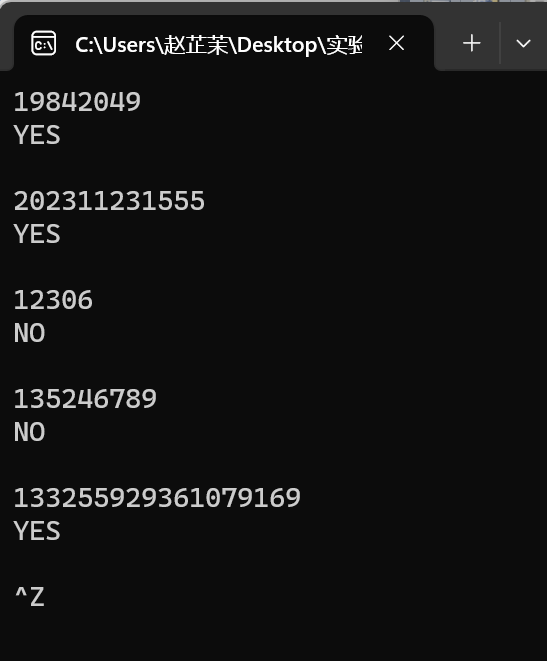
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 105 int is_repeated(char x[]); int main(){ char num[N]; while(scanf("%s",num)!=EOF){ if(is_repeated(num)) printf("YES\n"); else printf("NO\n"); } system("pause"); return 0; } int is_repeated(char x[]){ int cnt[10]={0}; int i,j; for(i=0;x[i]!='\0';++i){ j=x[i]-'0'; cnt[j]++; if(cnt[j]>1) return 1; } return 0; }
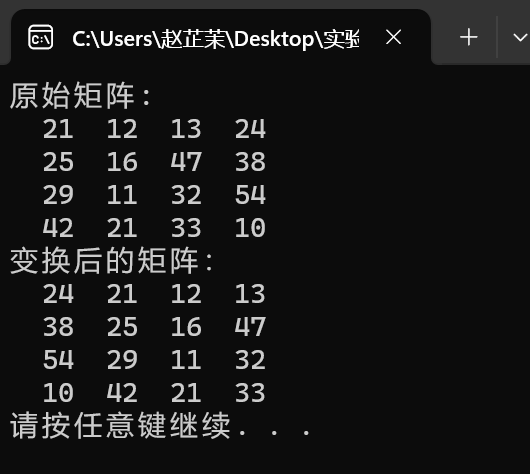
task8
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 100 #define M 4 void output(int x[][N], int n); void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n); int main() { int t[][N] = {{21, 12, 13, 24}, {25, 16, 47, 38}, {29, 11, 32, 54}, {42, 21, 33, 10}}; printf("原始矩陣:\n"); output(t, M); rotate_to_right(t, M); printf("變換後的矩陣:\n"); output(t, M); system("pause"); return 0; } void output(int x[][N], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) printf("%4d", x[i][j]); printf("\n"); } } void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n){ int i,j; int a[M][N]; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ a[i][n-1]=x[i][n-1]; for(j=0;j<n;j++){ x[i][n-1-j]=x[i][n-j-2]; } x[i][0]=a[i][n-1];} }